Hmwk
advertisement

Chapter 16: Acid/Base Equilibrium BookProblems (page 710)
#17 (a) Give the conjugate base for the following Bronsted-Lowry acids: (i) HIO3, (ii) NH4+. (b) Give the
conjugate acids of the following Bronsted-Lowry bases: (i) O2-, (ii) H2PO4-.
#19 Designate the Bronsted-Lowry acid and base on the left side of each equation and the conjugate acid and
base on the right side:
a) NH4+ (aq) + CN- (aq) HCN (aq) + NH3 (aq)
b) (CH3)3N (aq) + H2O (l) (CH3)3NH+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
c) HCOOH (aq) + PO43- (aq) HCOO- (aq) + HPO42- (aq)
#27 Predict the products of the following acid-base reactions and predict whether the equilibrium lies to the
left or the right:
a) O2- (aq) + H2O (l)
b) CH3COOH (aq) + HS- (aq)
c) NO2- (aq) + H2O (l)
#35 By what factor does [H+] change for a pH change of (a) 2.00 units, (b) 0.50 units?
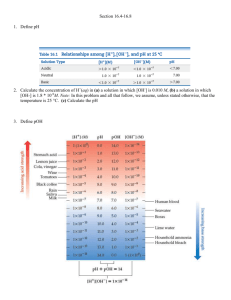
#37 (a) If NaOH is added to water, how
does the [H+] change? How does the pH
change? (b) Use the pH values in the figure
to estimate the pH of a solution with [H+] =
0.0006 M. Is the solution acidic or basic?
(c) If the pH of the solution is 5.2, first
estimate and then calculate the molar
concentrations of H+ (aq) and OH- (aq) in
the solution.
#39 Complete the following table:
[H+]
7.5 x 10-3 M
[OH-]
pH
pOH
Acidic or Basic?
3.6 x 10-10 M
8.25
5.70
#43 (a) What is a strong acid? (b)A solution is labeled 0.500 M HCl. What is the [H+] for the solution? (c) Which
of the following are strong acids: HF, HCl, HBr, HI?
#49 Calculate the concentration of an aqueous solution of NaOH that has a pH of 11.50.
#51 Write the chemical eqution and the Ka expression for the ionization of the following acids in aqueous
solution. Show with both H+ and hydronium ion: (a) HBrO2, (b) C2H5COOH
#53 Lactic acid {CH3CH(OH)COOH} has one acidic hydrogen. A 0.10 M solution of lactic acid has a pH of 2.44.
Calculate Ka.
#59 The acid dissociation constant for benzoic acid (C6H5COOH) is 6.3 x 10-5. Calculate the equilibrium
concentrations of H3O+, C6H5COO-, and C6H5COOH in the solution if the initial concentration of C6H5COOH is
0.050 M.
#63 Saccharin, a sugar substitute, is a weak acid with pKa = 2.32 at 250C. It ionizes in aqueous solution as
follows:
HNC7H4SO3 (aq) H+ (aq) + NC7H4SO3- (aq)
What is the pH of a 0.10 M solution of saccharin?
#65 Calculate the percent ionization of hydrazoic acid (HN3) in solutions of each of the following
concentrations (Ka = 1.9 x 10-5): (a) 0.250 M, (b) 0.0800 M, (c) 0.0200 M.
#67 Show that for a weak acid, the percent ionization should vary as the inverse square root of the acid
concentration.
#69 Citric acid, which is present in citrus fruits, is a triprotic acid. Calculate the pH and the citrate ion
concentration for a 0.050 M solution of citric acid. Explain any approximations or assumptions that you make
during the calculation. (Ka1 = 7.4 x 10-4, Ka2 = 1.7 x 10-5, Ka3 = 4.0 x 10-7)
#73 Write the chemical equation and the Kb expression for the ionization of each of the following bases in
aqueous solution: (a) dimethylamine (CH3)2NH, (b) carbonate, CO32- (c) formate, CHO2-.
#75 Calculate the molar concentration of OH- ions in a 0.075 M solution of ethylamine (C2H5NH2;
Kb = 6.4 x 10-4). Calculate the pH of this solution.
#79 Although the acid-dissociation constant for phenol (C6H5OH) is listed, Ka = 1.3 x 10-10, the base-dissociation
constant is not. (a)Explain why it is not necessary to list both the Ka for phenol and the Kb for the phenolate
ion. (b) Calculate the Kb for the phenolate ion. (c) Is the phenolate ion a weaker or stronger base than
ammonia (Kb = 1.8 x 10-5)?
#81 (a) Given that the Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5 and that for hypochlorous acid is 3.0 x 10-8, which is the
stronger acid? (b) Which is the stronger base, acetate or hypochlorite ion? (c) Calculate Kb values for acetate
and hypochlorite.
#87 An unknown salt is either NaF, NaCl, NaOCl. When 0.050 mol of the salt dissolved in water to form 0.500 L
of solution, the pH of the solution is 8.08. What is the identity of the salt?
#89 Sorbic acid(C5H7COOH) is a weak monoprotic acid with Ka = 1.7 x 10-5. Its salt (potassium sorbate) is added
to cheese to inhibit the formation of mold. What is the pH of a solution containing 11.25 g of potassium
sorbate in 1.75 L of solution?
#95 Based on their compositions and structures and on conjugate acid-base relationships, select the stronger
base in each of the following pairs: (a) BrO- and ClO-, (b) BrO- and BrO2-, (c) HPO42- or H2PO4-.
#101 Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base among the reactants in each of the following reactions:
a) Fe(ClO4)3 (s) + 6H2O (l) Fe(H2O)63+ (aq) + 3 ClO4- (aq)
b) CN- (aq) + H2O (l) HCN (aq) + OH- (aq)
c) (CH3)3N (g) + BF3 (g) (CH3)3NBF3 (s)
d) HIO (lq) + NH2- (lq) NH3 (lq) + IO- (lq) **(lq) denotes liquid ammonia as solvent