Final Project Report Solid Waste Management Azerbaijan
advertisement

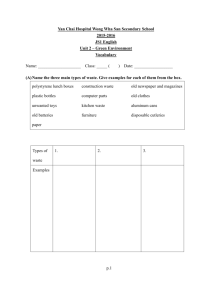
Final Project Report Solid Waste Management Improvement Project Reference Number: 3050214 Award ID: 00042114 Project ID: 00048205 Implementing Partner: Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources Award start date: 02-Dec-05 Award end date: 31 July-12 Period covered: 01 May 2009 – 31 July 2012 Report due date: 31 January 2013 Report submitted: 29 January 2013 Section I. Update on Project Outputs Outputs Progress towards outputs Output 1: Recommendations to amend the legislation on the SW management and the respective policies and regulations are prepared The comparison between respective EU legislation and Azerbaijan National legislation has been conducted. The drafts of the Cabinet of Ministers’ regulations on incineration, on the management of landfills, and on the collection, storage and transportation of the solid wastes were prepared and presented to the Government. The drafts containing amendments and changes to the Laws on “Industrial and municipal Wastes” and to the Law on “Environmental protection” of the Republic of Azerbaijan have been developed. Proposals to amend Azerbaijan Republic’s Code on Administrative Breaches in part related to solid wastes were also made. The drafts of reduction, reuse and recycling (RRR) Strategies and Cleaner Technology Programmes (CTP) were prepared and discussed at the seminar organized for the Government policy-makers. Output 2: Surveys on per capita waste generation capacities for different seasons are conducted The project conducted comprehensive and reliable surveys on per capita waste generation capacities in three locations - in Ismayilly, Sheki and in Narimanov district in Baku. This was done for the first time ever in Azerbaijan. The project used three different methods - at households, garbage collection and at the utility services levels. The survey was done during all four seasons. The results of the survey were presented to the Government, shared with the stakeholders and similar projects and with the general public. The guidelines for Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA), audit and inventory of SW have been prepared. The laboratory analysis of pollution samples taken from solid waste landfills and dumps were conducted and results of the analysis were shared with the stakeholders. The results were presented to the audience during the final workshop. Output 3: National Solid The comprehensive data forms and questionnaires were developed to collect Waste Data Bank is developed and record information on the solid waste sites, landfills and damps. Information and samples for laboratory analysis were collected from 52 regions of the country. Excel-based Data Bank was developed, and now includes information on all big illegal dump sites in the country. The main results of activities 1 and 2 were also included into the Data-Bank Output 4: SWM Feasibility Study and Planning Guidelines are prepared Guidelines for estimation of the capital investments, transportation costs, for different waste management scenarios and for environmental impact assessment of municipal wastes were prepared. The model contract on solid waste management between households, governmental organization and utility services was developed. The Strategy of Public awareness campaign for SWM has been created. Social video on sorting of municipal solid wastes and booklet for public awareness campaigns in pilot areas were made; the book containing major findings and outcomes of the project was published and disseminated among all major stakeholders. Output 5: Local Pilot Solid Waste Management Project is implemented Ismayilly rayon was selected as a location for the pilot project. Necessary estimations, matching possible technological options with the Project fund were conducted. Technological equipment for processing of “soft” and “hard” PET plastics was purchased, electricity supply improved and the workshop was set. Trainings were conducted for the staff of Ismayilly Utility Services on operating the technological equipment. Safety measures were developed and local employees passed through these trainings. The ownership of the pilot project has been passed to Ismayilly Communal Utility Services and production of plastic products has started. The pilot is located at the territory of the damp and produces multi-purpose plastic pipes. Section II. Update on Activities Activity ID: ACTIVITY 1: Project Management Planned start date Actual start date Planned end date Actual end date Purpose of Activity Description of Activity 01 January 2009 01 May 2009 31 July 2012 31 July 2012 Ensure project delivery and quality of project deliverables 1) Project management and coordination. 2) Planning, Implementation, Monitoring and Supervision 3) Liaison with the Project Steering Committee, Consultants and Stakeholders 4) Preparing Work-plans, Accounting and Progress Reporting 5) Conducting Audits and Evaluations 6) Organizing Workshops and Training 7) Reporting Progress against Activity 1) Annual Work Plans were prepared and agreed. Specific activities and targets for each year were also set. 2) The Project’s Steering Committee meetings (SCM) were held in January 2010 and in February 2011 and the Minutes of the Steering Committee meetings were shared with the donors and with the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources. Taking into account the delayed start-up of the project on the SCM in February 2011 the decision has been made to extend the project implementation period by nine month to July 31 2012. This no-cost extension was approved by the Government of Norway through an e-mail of 15 August 2011. 3) On July 14 2011 midterm Workshop was organized for the stakeholders to inform about the progress of the project and to plan future activities. 4) Donor reports were submitted to the Government of Norway in June 2010 and July 2011 and December 2011 5) 10 international and 25 local consultants were hired by the project during its life-time. 5 experts groups (Legal, Waste Survey, Data Bank, Feasibility study and Local pilot project) were formed and assisted in their work. Study tour was organized to Czech Republic for key Project experts. 6) Research trips to 52 rayons of the country were organized; all big illegal dump sites were visited. In the result of collected information, Ismayilly rayon was selected for implementation of the pilot project for plastic waste recycling. 7) Project assets were transferred from UNDP to MENR and Ismayilly Communal Utility Services in accordance to the rules. 8) The Final Workshop with the participation of the Cabinet of Ministers, Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources, all involved state agencies and local authorities and donors took place on August 2 2012 Activity ID: ACTIVITY2: Laws, Regulations, Norms and Standards & RRR Strategies, Cleaner Technology Program (CTP), etc. Planned start date Actual start date Planned end date Actual end date Purpose of Activity 01 September 2009 12 November 2009 31 July 2012 31 July 2012 To review laws and regulations, identify respective priorities and assess national priorities in developing capacities to amend the legal environment related to the solid waste management. Description of Activity 1) Review of existing sector plans, strategies, legislation, applicable norms and standards, as well as institutional arrangements, in order to identify legal barriers to proper management of non-hazardous industrial and municipal solid wastes. 2) Draft missing sector legislation, regulations, norms and standards. 3) Prepare waste reduction, reuse and recycling (RRR) strategies. 4) Recommend appropriate legal, administrative and economic instruments to support the RRR strategies. 5) Investigate the merits and steps necessary for introducing a national Cleaner Technology Program (CTP) and possibly also a second-hand raw material exchange facility. Progress against Activity 1) ToRs for international and local experts were developed, and the team of two experts, one from UK and the other from Azerbaijan, both with international-level experience was created to work on the component deliverables. 2) The team reviewed the scope of work and respective activities of other SWM projects in Azerbaijan and took them into account when defining more precisely the scope of its own work. In addition to the GoNorway/UNDP funded project, there are two more SW managementrelated projects in Azerbaijan implemented by the WB and the EU. To define more precisely the scope of work, the team conducted a comparative analysis of all three projects. It’s been revealed that the EU project is going to cover only the pilot area in Lenkaran. The WB project, in turn, sees Baku as its major focus area. Therefore, it has been confirmed that UNDP Project, as previously envisaged, should cover the entire country and concentrate on the municipal/household solid wastes. 3) The National legislative acts and policy documents (Strategies, Programmes, Decrees, Action Plans, etc.) were analyzed, their strengths and weaknesses were identified, and reports on missing sector legislation, regulations, norms and standards were prepared 4) Trips to regions were organized to collect information on the SW regulations on the local level; the status of implementation of legislative acts and existing institutional structures at the local level were analyzed; landfill regulations were observed, and relevant reports were prepared. 5) Two EU Directives, 2006/12/EC on the SW and 91/689/EC on the Toxic Wastes were analyzed and compared to the existing National Law on the SW and EU Directives. No contradictions were revealed between them, however many gaps have been identified in the national legislation. 6) Two more advanced national models on the SW, Czech Republic’s Law and Abu-Dhabi Law were reviewed and decision has been adopted to follow the Czech example, as a country with more similar historical background and recent problems with the SW. 7) The organization of work between the legal/institutional team and Databank team has been analyzed and respective questions on the institutional characteristics of the SWM in the regions were included into the open-end survey questionnaires prepared for the policy-makers. 8) Field trips organized to almost all regions of the country revealed that there are no standards, or even similar rules and procedures applied in the regions to collection and transportation of SW and to the management of the waste sites. Each rayon has created its own, in most cases arbitrary, system of the SW management without taking into account the respective regulations of the Cabinet of Ministries. 9) When deciding on the strategy of the work under the component, two paths were considered: 1) the path of cardinal legislative changes in the existing National Law, and 2) to leave the existing Law intact and to either amend already existing or create new rules/ regulations of the Cabinet of Ministries. Taking into account that: 1) the National Law on the SW does not contradict the EU Legislation; 2) Laws in Azerbaijan are framework laws and are implemented through the rules adopted by the Cabinet of Ministries, which do not require passing through the parliament, the decision has been made to work on those rules and regulations. The work on three drafts of regulations has started - on existing Cabinet Ministers’ decision #074, 21/04/2005 on collection, storage, and transportation of the SW, on incineration of SW and on the management of landfills. The decision to work on the regulations for incineration of SW was adopted taking into account that the construction of a big incinerator in Baku is underway (by the time of preparation of this report, the incinerator has been constructed), however, there are no respective rules or regulations. 10) The work has started on the draft of reduction, reuse and recycling (RRR) Strategy. 11) Drafts of the following legislative and policy documents were prepared or amended: - National Strategy for Reduction, Reuse and Recycling (RRR) of SMW; - Amendments to Decision No.074 dated: 21/04/2005 of the Cabinet of Ministers on “Rules for cleaning of inhabited localities in compliance with sanitary regulations, hygienic and environmental guidelines, temporary storage, regular transportation and neutralization of domestic waste”; - Law on “Industrial and Municipal Wastes” of the Republic of Azerbaijan, - Regulation of the Cabinet of Ministers on disposal of Waste in Landfills; - Regulation of the Cabinet of Ministers on creation of Ecological passport for Incineration of Waste; - Additions to the Law of Azerbaijan Republic on “Environmental protection” in part related to solid wastes; - Proposals to amend Azerbaijan Republic’s Code on Administrative Breaches in part related to solid wastes were developed; - Cleaner technology Program for SWM has been created; Activity ID: ACTIVITY 3: Waste Composition, Characteristics and Generation Survey Planned start date Actual start date Planned end date Actual end date Purpose of Activity 01 September 2009 12 November 2009 31 October 2011 31 December 2011 Field survey and laboratory analysis to determine generation quantities, characteristics, specific generation capacity (kg/p/day), seasonal variations, typical composition and physical characteristics of solid wastes. Description of Activity 1) Field survey to determine municipal solid waste generation quantities and rates. 2) Laboratory analyses to determine waste composition & characteristics. 3) Determine specific waste generation (kg/p/day), seasonal variations, typical composition and physical characteristics of municipal waste. 4) Survey of the present municipal waste generation, collection and disposal to determine the generation, collection and disposal situation in three locations. 5) Inventory/audit of industrial waste generation and disposal situation in three municipalities (Baku, Sheki, Ismayilly). 6) Environmental impact assessments/statements 1) Project team held a brain-storming session on the methods for data and information collection in January 2010. 2) Taking into account that it was the first time such surveys were conducted in Azerbaijan, two international experts, from Canada and the US were hired. In consultation with them, the decision was made to Progress against Activity 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) organize surveys with two types of questionnaires, one for general population and the other for decision-makers working in the field of SWM. The respective templates for data registration were developed. 10 NGOs (5 in Baku, 3 in Sheki, 2 in Ismayilli), 3 municipalities and 3 communal utility service organization (one in each location) were selected to identify per capıta daily SW generation capacity. The trainings were organized for the staff of each entity involved in surveys in survey methodology. Surveys in three localities were conducted during all four seasons. In total 1200 families, 300 individuals and 52 decision-makers were involved into the surveys. The results were summarized and presented to the stakeholders and to general public. Laboratory analysis of air, soil, and water samples taken from Balakhany waste landfill in Baku, and in waste dumps in İsmayilli and Sheki were conducted, including microbiological analysis. The template has been prepared and inventory of waste landfills and dumps in 52 rayons of the country was prepared. Guidelines for Environmental Impact Assessment of solid municipal wastes based on respective EU Directives were developed Guidelines for audit of Solid municipal wastes based on EU-Directives were developed Training was conducted for the staff of the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources and other state agencies on Environmental Impact Assessment and on the audit of SMW Activity ID: ACTIVITY 4: National Solid Waste Data Bank Planned start date Actual start date 01 March, 2010 19 July 2010 Planned end date Actual end date Purpose of Activity 31 October , 2011 31 July 2012 Assisting the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Reserves in establishing and maintaining a computerized data bank on the solid wastes. 1) Set objectives, define the scope, and establish criteria for the development of a National SW Data Bank 2) Identifying and purchasing or developing appropriate software to support the Data Bank. 3) Install and test software and train operators and managers. 4) Enter data obtained through the solid waste field surveys and other sources into the Data Bank 1) ToR was prepared and an international expert from Canada was selected to assist the Project team in identifying needs and recommending which type of data bank is more appropriate for Azerbaijan. His recommendation was: a) taking into account the level of development in Azerbaijan, and b) the needs of the country in type of data, to use simple Excel-based soft-ware for the foreseeable future. This is less sophisticated, then the systems used in the Northern America and the Western Europe, but more fitting to the countries of Eastern Europe and CIS. 2) Set of data to be included into the Data Bank has been identified with the participation of the international experts Description of Activity Progress against Activity 3) ToRs for the local consultants to work on the component were prepared, and local experts were hired to collect data, including for chemical and microbiological analysis 4) Data and information was collected. Local consultants traveled to all 52 rayons of the country, collected data from local stakeholders and regional landfills according to developed survey inventory. Samples of soil and water from landfills in 17 rayons were taken for the analysis of heavy metal content (Balakhanı, Ganja, Mingechevir, Gakh, Oguz, Sheki, Sumgait, Shirvan, Agsu, Gobustan, Kurdamir, Agdash, Barda, Goranboy, Tartar, Dashkesen, Ismayilli) and mercury content exceeding by several times acceptable level has been revealed in Sumgait area. 5) By using tendering procedure the server to support the software of data bank was acquired. 6) “AzEcoLab” laboratory was contracted to conduct analysis of chemical and microbiological compositions of waste samples taken from landfills and dumps. 7) Data bank was created containing full information on all 52 dump sites in the country, including geographic coordinates, distance to the settlements and aquifers, amount of accumulated wastes, growth speed of the dump, pictures, etc. The Data bank contains much of the results collected in components 2-5 of the project. 8) In consultation with the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources the Server with the Data Bank has been provided to the Ministry of Economic Development. Activity ID: ACTIVITY 5: SWM Feasibility Study and Planning Guidelines Planned start date Actual start date Planned end date Actual end date 01 April, 2011 01 Nov 2011 31 October 2011 31 July 2012 Purpose of Activity Creation of SWM Feasibility Study and Planning Guidelines, Public awareness strategy Description of Activity 1) Progress against Activity General feasibility study of waste collection, transportation, RRR activities, treatment and disposal systems. 2) Planning guidelines for selection of appropriate SWM systems and facilities. 3) Guidelines and model contracts for private sector participation in financing, management and operation of SW services. 4) Guidelines for public awareness campaigns. 1. The following feasibility study and planning guidelines were prepared: - Calculation methodology and guidelines of feasibility studies applicable to the management of municipal solid waste based on EU guidelines adapted to the local conditions in Azerbaijan; - Guidelines for estimation of the transportation costs (tons x per km) for the different collection scenarios; - Guidelines for estimation of the capital investments (per 1000 residents) required for establishment of the waste management technical capacity (including but not limited to vehicles, containers, construction of the landfills, collection and segregation points) in pilot municipality; - Estimation of economic cost for 3 basic waste management scenarios including: Establish procedure and cost of fines for the mismanagement of wastes in accordance with the economic costs of the environmental impact of municipal wastes. - Model contract on Solid Waste Management between households, governmental organization and operational unite has been developed - The Strategy of Public awareness campaign for SWM has been created 2. Social video clip on sorting of municipal solid wastes was prepared, and used for enhancing public awareness in pilot areas; the clip along with other project outputs was provided to the Ministry of Economic Development. 3. Booklet for public awareness on SWM was published. 4. The book containing major findings and outcomes of the project was published and disseminated among state agencies and stakeholders. Activity ID: ACTIVITY 6: Local SWM Project Planned start date Actual start date Planned end date Actual end date Purpose of Activity 01 March, 2011 01 September 2011 31 July 2012 31 July 2012 Selection and realization of a Pilot Project according to Implementation of Activities 1-5. Carry out preliminary evaluations and pre-feasibility analyses of demonstration project. Description of Activity 1. On the basis of collected information, survey and analysis and in consultation with the major stakeholders, to determine the geographic area for the pilot project. 2. Carry out preliminary evaluations and feasibility studies to determine the types of wastes being processed. 3. In consultation with the international and local experts and by taking into account locally available options, determine major characteristics of the pilot project. 4. Analyze demonstration projects identified during the workshop, and recommend the most appropriate project for further investigations and elaborations. 5. Get approval from the Steering Committee for further planning of the selected demonstration project. 6. Prepare technical plans, estimate investments and operation costs, and design the pilot project 7. Implement the pilot project 1) According to the developed RRR-strategy and information collected under components 2-5 Ismayilly rayon has been selected for the pilot project. One of the major factors for selection was a very positive attitude and genuine interest shown by this rayon’s executive authorities; 2) After serious analysis and estimations, in particular, by taking into account the absence of waste trucks with separate sections for different types of wastes, and very high cost of those cars, exceeding opportunities and scope Progress against Activity of current project, the decision has been made to concentrate attention and resources on plastic waste recycling. 3) By using recommendations of local and international experts, and on the basis of cost estimations, the decision was made to use equipment produced and refurbished in Azerbaijan. The main goal of the pilot project was to demonstrate technical feasibility and financial sustainability of such project to the local authorities and local utility services. 4) Technological equipment for pilot Project was selected according to assessments of International and local experts. Production of plastic pipes and hoses from “soft” plastic and plastic PET powder, mainly from plastic bottles was selected as the most suitable option. 5) 5 pieces of equipment were installed: one transformer, one crasher for PET with the capacity of 1 ton/per day, and 3 pieces of equipment – 1 crasher, one refined crasher and one molder to produce pipes and hoses of 3 different diameters (18 mm, 20mm and 22mm). 6) The staff of Communal Utility service enterprises in Ismayilli were trained in sorting and processing of plastic wastes and in production of new products. 7) The safety instructions for the employees of the workshop were prepared, trainings were conducted and respective control mechanisms on observing those procedures were established. 8) The ownership of the equipment of pilot project has been transformed to Communal Utility Services of Ismayilly rayon. Section III. Update on Risks Log Type of Risk Description Comment or Management Response Financial There is a risk that the budget allocated for particular components may not be sufficient to implement them in full Recommendations and suggestions of local and international experts, in consultations with the stakeholders, were used to determine the budget allocation to achieve the highest utility results for the project. As a result of close attention, this risk was low throughout the life-time of the project. Operational Lack of local capacities in modern This risk has been mitigated through the approaches to the SWM involvement of the international consultants in the project planning and implementation. International consultants worked closely with the local consultants. The inquiries and advertising methods were used to attract the best possible expertise from within the country. Special attention was paid to the implementation of local project in Ismayilly. Local experts from Baku traveled to Ismayilly and trained local specialists. This risk was medium throughout the life-time of the project, however, constant attention and necessary arrangements allowed to deal successfully with this risk. Organizational In addition to UNDP project, there are also WB and the EU projects on the SW; one more strong local institution, “Temiz Sheher” (“Clean City”) was created to improve the system of the Solid Waste management in Azerbaijan. Therefore, there is a risk of overlapping activities on the one hand, and lack of necessary coordination and communication between different projects on the other. Other Methodological: Determining per capita waste generation capacity is difficult and may produce significantly different results depending on the methodology used. Other Project results, in particular guidelines developed or results obtained under the per capita waste generation capacity survey may not be accepted by the government as contradicting to their already set policies. The consultation mechanism has been established between the project teams of different SWM related projects with the active participation of the UNDP Project team. The UNDP Project team members actively participated in the respective public events and workshops organized by other entities, and in turn other teams’ members were duly informed about results of UNDPlead project and when necessary consulted on its outputs. Selection of the pilot areas in Ismayilly and Sheki was conducted by taking into account the geographic area concentrations of other projects. Since the UNDP project was well-ahead in all components of the work, this risk was low through the life-time of UNDP project. Already the first steps in data collection revealed that risk. For example, sometimes businesses damp their wastes into private residential areas, or it was not possible to define accurately the number of people in each household surveyed. Therefore, to diminish this risk three methods of per capita waste generation capacity were developed and used by the project. Combination of results of three methods allowed to significantly reduce this risk. The risk is low. Throughout the entire project implementation period, close communication was held with both the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources and the Ministry of Economic Development. All results of the project were shared with them on time, necessary consultations were held, therefore, this risk has been minimized. Even more importantly, the results of the project, its outputs are used by the Government to set future policies of the country in the management of solid wastes. The risk has been significantly lowered, however, not completely eliminated, as still sufficient level of communication is still not attained among different government agencies. Section IV. Update on Issues Log Type of Issue Description Comment or Management Response 1) Change It's been initially planned to use complicated software for the National SW Data Bank. However, hired international consultant advised to use an Excel spreadsheet saved at the server located at the MENR 2) Change Initially the project planned to collect data on both the household wastes and on the industrial wastes. However, the project implementation has shown that there is no reliable data on the industrial wastes and it is impossible to collect any more or less meaningful data, as there is no regulatory mechanism requiring enterprises to collect and report on those data. In addition the enterprises “free ride” on the government’s promotion of entrepreneurship and easily reject any attempts to collect such data as interference. Taking into account that Excel-based nonsophisticated programs are used by countries with characteristics similar to Azerbaijan, the Project Team recommended to the Steering Committee to also use simple Excel-based spreadsheet rather than complicated and expensive software. The decision was made to use such an Excel-based spreadsheet. The decision has proved right, the Data Bank has been successfully created, contains necessary information and is user-friendly. The future usage of the Data Bank lies with the Ministry of Economic Development. Since there is no mechanism to collect data on industrial wastes, the Steering Committee has decided to limit the data collection to the domestic wastes. At the same time the Steering Committee recommended to include the industrial waste data collection and mechanism of it into the scope of the component on the waste regulation of the current project. This is being taken into account when preparing the respective regulation of the Cabinet of Ministers on waste collection, storage and transportation. 3) Change In the initial design of the project public awareness component had limited scope. However, the project implementation has shown the need to enhance this component. In particular, it was recommended by one of the international consultants, as the strengthening of this component will have a very positive impact on the implementation and impact of the entire project. 4) Change The project had a rather slow start. The surveys to determine per capita waste generation capacities had to be conducted during 4 consecutive seasons. Therefore, it was not possible to compensate for the delays of the start-up period. Therefore, the project team, following advice of the international consultants, suggested a 9-months no cost-extension. 5) Change During the project implementation, the Government of Azerbaijan took the decision (January 2012) to entrust the issues of Solid Waste Management to the Ministry of Economic Development. Taking into account recommendation provided by the international consultant and the Project Team, it’s been discussed and decided to enhance the scope of the public awareness component, which is currently the part of the “Feasibility studies” Activity of the Project. The necessary activities were taken into account, two NGOs conducted successful public awareness campaign in Ismayilly rayon, social video clip has been created and used for the meetings in schools and shown on TV to create a favorable condition for the implementation of the local pilot project in Ismayilly. The Steering Committee recommended to accept proposed 9-month no-cost extension and continue the project until July 31 2012. The project budget was adjusted accordingly. In particular, the funds freed from not-buying expensive software for the solid waste data bank were used for the broader public awareness campaign, and for the pilot project on recycling plastic wastes in Ismayilly rayon. In order to ensure the sustainability of results, the project cooperates with the Foreign Investments and Assistance Department of the Ministry of Economic Development and submitted all the project products (reports, Data Bank) to them for further use. The Project Team jointly with Sheki Communal Services Department’s staff during waste per capita generation studies Waste Disposal Site in Ismayilly rayon Youth participants of environmental awareness campaign conducted in Ismayilly and Gabala rayons Plastic Wastes Processing Workshop in Ismayilly rayon created by the Project and provided to Ismayilly Communal Services Department