Functions of Nouns
advertisement

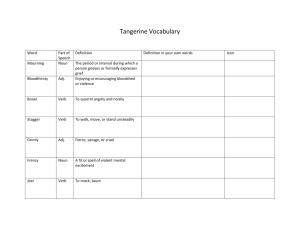
Functions of Nouns There are five major functions of nouns: 1. Subject of the sentence: Our schools need money in order to operate successfully. To find the simple subject of a sentence, ask whom or what the sentence is about. If the answer is still not clear, locate the verb first, and then ask who or what did that action. 2. Direct Object: All students received grades recently. A direct object is a noun that can only be found in a sentence that has an action verb. This noun that functions as the direct object receives the action of that verb. In the example above, “students” is the subject of the sentence, and received is the action verb. To locate the direct object, first find the action verb, then ask who or what after saying the verb. “Received who?” no answer…received what? “grades” is the answer. Grades is the noun that receives the action of the verb received, so grades is the direct object in this sentence. 3. Indirect Object; The teacher gave her students notes on the new material. A sentence cannot have an indirect object unless it first has a direct object. (Remember only sentences with action verbs can have a direct object). The indirect object is underlined in the example above. When a sentence contains both a direct object and an indirect object there will usually be two answers when you identify the action verb and ask Who? And What? If you get two answers go to the next step to ask, “To Whom and For Whom?” Or ask, “To What and For What?” The answer to these will be the noun that serves as the indirect object. The indirect object will always come before the direct object in the word order of the sentence. Functions of Nouns Here is a practice sentence: Mother bought me a new sweater. First locate the simple subject- Mother. Next identify the action verb- bought. Step three say to yourself, “Bought who? Bought what?” You get two answers. Bought who is answered by “me” and bought what is answered by “sweater.” Remember when you get an answer to both questions you need to take it a step further to check for an indirect object. For step four you will ask, “Bought sweater for whom or for what?” The answer is “ for me”, making “me” the indirect object. Remember, the indirect object will always come before the direct object in the sentence that contains both. Also, only a sentence with an action verb and a direct object is capable of also having an indirect object. Do not lose sight of the fact that we are looking at functions of nouns only . DIRECT AND INDIRECT OBJECTS HAVE TO BE NOUNS. 4. Predicate Nouns: In order for a noun to function as a predicate noun, the sentence must contain a linking verb. ( You will find a list of linking verbs in the verb section). A noun or noun functioning as a predicate noun will come after the linking verb in the sentence, ( somewhere in the predicate), and will re-name the subject of the sentence. Dr. Beenken is my English teacher. The simple subject is Dr. Beenken. The linking verb is “is.” The noun that renames Dr. Beenken is teacher. The words my and English are both adjectives telling whose teacher and what kind of teacher. To locate a predicate noun you must first identify the fact that the sentence has a linking verb. Then, you search the predicate for a word that could take the place of the subject. The sentence containing a predicate noun can be turned around without losing meaning. My English teacher is Dr. Beenken. Functions of Nouns 5. Objects of the preposition: A prepositional phrase always begins with a preposition and ends with the first noun or pronoun that follows that preposition. There is a list of prepositions in the preposition section of these grammar notes. The noun or pronoun at the end of a prepositional phrase is known as the object of the preposition. The prepositional phrases in the example sentence below are in bold and italics. The beautiful rainbow stretched ( across the sky). The object is underlined. Nouns are parts of speech that opened the world to Helen Keller. You need to master this part of speech. You should memorize the categories of nouns and understand each one. You must memorize the five functions of nouns and be able to recognize nouns working in each of these ways.