NAME Type Description Author Year Availability Reference FBPLOT
advertisement
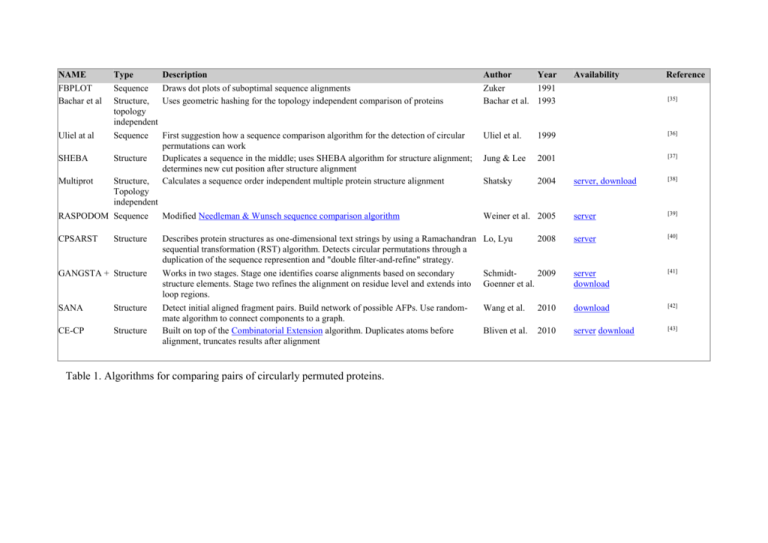
NAME FBPLOT Bachar et al Type Description Sequence Draws dot plots of suboptimal sequence alignments Structure, Uses geometric hashing for the topology independent comparison of proteins topology independent Author Year Zuker 1991 Bachar et al. 1993 Uliel at al Sequence Uliel et al. 1999 [36] SHEBA Structure Jung & Lee 2001 [37] Multiprot Structure, Topology independent First suggestion how a sequence comparison algorithm for the detection of circular permutations can work Duplicates a sequence in the middle; uses SHEBA algorithm for structure alignment; determines new cut position after structure alignment Calculates a sequence order independent multiple protein structure alignment Shatsky 2004 RASPODOM Sequence Modified Needleman & Wunsch sequence comparison algorithm Weiner et al. 2005 CPSARST Describes protein structures as one-dimensional text strings by using a Ramachandran Lo, Lyu sequential transformation (RST) algorithm. Detects circular permutations through a duplication of the sequence represention and "double filter-and-refine" strategy. Structure 2008 Availability Reference [34] [35] server, download [38] server [39] server [40] GANGSTA + Structure Works in two stages. Stage one identifies coarse alignments based on secondary structure elements. Stage two refines the alignment on residue level and extends into loop regions. Schmidt2009 Goenner et al. server download [41] SANA Structure Wang et al. 2010 download [42] CE-CP Structure Detect initial aligned fragment pairs. Build network of possible AFPs. Use randommate algorithm to connect components to a graph. Built on top of the Combinatorial Extension algorithm. Duplicates atoms before alignment, truncates results after alignment Bliven et al. 2010 server download [43] Table 1. Algorithms for comparing pairs of circularly permuted proteins.





![IS 788 [Process] Change Management](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009898338_1-678e0fadd3ae3f5ae562e6044e3e3804-300x300.png)