Name Evolution Unit B 1.3 1. When did Darwin publish his book on
advertisement

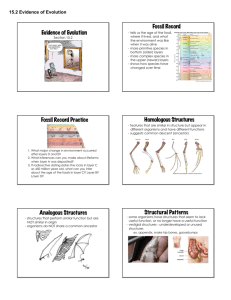
Name ___________________________ Evolution Unit B 1.3 1. When did Darwin publish his book on evolution? __1859___________________________ 2. Darwin’s work is still considered the Theory of Evolution? A scientific theory is a statement based on __observation____and ______experiment__. pg. 29___________ 3. What happens if continued observation and experiment support a theory’s statement? __It is widely accepted___________ 4. A theory that has been widely accepted is used to __explain _____ and_predict_____ natural __phenonmena_____________. 5. Using the chart on pg 29, what three areas do scientists use as evidence for evolution? __fossil_______evidence, _biological_____evidence, and __genetic_______ evidence. 6. Darwin gathered many specimens of fossils__that caused him to think that species appear to have a __common______ ancestor. 7. What is a common ancestor? _an early form of an organism from which several later forms have descended_______ 8. Which main idea in the theory of evolution does the idea of a common ancestor support? ______natural selection_________________________________________________________ 9. True or False:. Scientists comparing modern plants and modern algae to fossil algae would say they all share a common ancestor. 10. What kind of evidence do scientists returning to the Galapagos Islands today find to support Darwin’s ideas? _________fossil and biological evidence_________________________________________________ 11. These scientists study the _structure_______ and the ___development_________ of living things. 12. What conclusions do these scientists come to through their observations?__ __Modern organisms are related to earlier specimens___________________________ 13. Evidence for evolution can also be observed within the _physical__ structures of adult organisms such as vestigial_____ organs and ___homologous____structures with different functions. pg___________ 14. _Vestigial__ organsr are physical structures that were fully developed and __functional____ in an _earlier group__ of organisms but are reduced and __unused_ in ____later___ species. pg.______ 15. Give an example of a vestigial organ. ____pelvic bones in a whale- ancestor used to walk, human appendix-???_____ 16. Researchers use vestigial organs to show that modern organisms having these organs are _related _____ to a ____common_____ ancestor. ( NOT IN BOOK)-Similar structures with different functions are called HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES. 17. Scientists have compared the anatomy of living things and noticed that many different species share ___similar ___structures_____. Look at pg 31. Describe how some scientists compare similar structures. a lizard’s __leg______, a bat’s _wing_______ and a manatee’s ___flipper__ 18. Do they have a similar function? __No___________ 19. However, even though these structures are used differently, some scientists believe this similarity in structure indicates that these organisms shared a _common__ancestor________. 20. What process caused the variations in form and functions of these homologous structures? __natural selection______________. 21. What factors influence natural selection? different __environments_______,; different__pressures_______________. . 22. Scientists also observed similarities in the early development of different organisms as an _embryo_____ and the study is embryology. 23. See page 32. What organisms are being compared? __chicken________, _rabbit_______, and a ___salamander___________. 24. As the organism continues to develop, what happens to the similarities? _________They begin to change to distinct characteristics_______________ 25. The key to understanding how traits are passed from one generation to the next lies in the study of__DNA_____, which is the ___genetic __ _material___ found in all cells. 26. What else does DNA contain? __the code that a cell uses to put together all the materials it needs to function properly.______ 27.What is the code in DNA made of? __4 sub units called bases__ 28.What letters represent the bases in DNA? ___Adenine, Guanine, Thymine and Cytosine._____ 29. What is a gene? _a segment of DNA that relates to s specific trait or function in an organism____________________ and each gene has a particular _sequence____ of bases. pg.____________ 30. What is a clock gene and its function? _a gene in mammals that relates to the function of walking and sleeping________ 31. What do evolutionary scientists believe concerning the similarities in the sequences between two organisms? _________The more matches in the sequences the more closely they are related.__________ 32. Even though the two organisms appear so different, much of the __functioning ____ of their __cells__is similar. On a separate sheet of paper draw a graphic organizer showing Evidences of Evolution. Use the words biological, genetic, homologous structures, vestigial structures, embryology, and fossils,