Topic 3: Battle for the Biosphere
advertisement

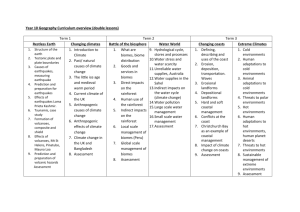
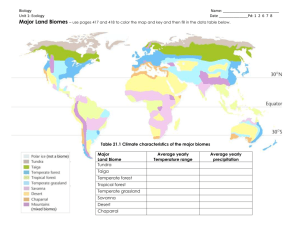
Topic 3: Battle for the Biosphere What you need to know: How to describe the distribution of Biomes across the Earth’s surface How climate (temperature and precipitation) influences the distribution and types of Biomes How local factors, such as altitude, also influences biome distribution How the biosphere provides important services to humans How the biosphere provides goods (resources) that humans use How goods and services support human life on Earth How humans are directly degrading biomes by their actions, such as deforestation A named example of biome degradation How global climate change is affecting biomes Why humans need to conserve biomes and biodiversity How to define sustainable and unsustainable Why humans need to use biomes more sustainably in the future How global actions and agreements could help make this possible Examples of global actions and agreements How local and national management could conserve biomes Examples of local and national management What is the Biosphere? The biosphere is the part of the Earth’s surface that is inhabited by living things. A biome is a large ecosystem. Climate (temperature, Rainfall and sunshine) determines what animals and plants live in a biome. Examples of Biomes include: Tropical rainforest Deserts Deciduous Coniferous forest Tundra Biomes are different in different parts of the world because of the difference in climate. Lines of latitude travel in rings around the Earth. The equator is a line of latitude Latitude has an effect on climate so often biomes change as you travel north or south. The Sun’s rays are more intense at the Equator leading to hotter temperatures in the Tropics. Apart from temperature, rainfall and sunshine there are local factors which can change a biome. Local Factors that change biomes Distance from coast - Near the coast land is Geology - Limestone bedrock creates dry soil cooled by the sea, decreasing the average conditions as it does not retain water. temperature Altitude - Temperature decreases by 10C for Distance inland - Inland areas isolated from every 100m gained in altitude. the sea suffer from low rainfall. Task: Describe how local factors affect the growth of rainforests (4 marks) The biosphere life-support system The biosphere acts as a life-support system for the planet, helping to regulate the composition of the atmosphere, maintaining soil health and regulating the hydrological (water) cycle. Plants absorb carbon dioxide and produce oxygen instead Dead leaves and plants add nutrients to the soil. Insects and animals burrow, helping the soil breath Trees and other plants slow the flow of rainwater to rivers acting as a natural flood control What goods and services can be provided by the Tropical Rainforest? Goods are products which can be removed from the forest. This can be done in a sustainable way (this means without damaging the forest). Services are things which the forest does for the biosphere, these are usually processes that the forest helps to run that benefit life on the planet. Goods and their benefits Food (berry, nut and fruit picking or larger scale cereal production. Wheat and corn are increasingly used for the production of biofuels as well Medicines (Many Raw materials (The biosphere naturally occurring provides raw materials for industrial substances act as activities. E.g, wood for the medicines and construction of houses and boats) remedies) as fuel) Services and their benefits Water control (Forests Atmosphere (Forests removes Carbon dioxide intercept rainwater on their leaves. This slows the water down in getting from the to the river. This reduces atmosphere and this reduces global the risk of flash floods. warming) Nutrient Cycle (Leaf litter from dying plant leaves are broken down by termites and fungi on the forest floor. This releases nutrients into the soil to help make the soil fertile and allow other plants to grow) Ecotourism (natural resources for people to enjoy in a sustainable way) Task: Describe some of the goods and services the biosphere provides humans with (4 marks) Task: Describe two services that the biosphere provides and explain why they are important What is a Tropical Rainforest? Found mostly in a band around the equator. Here the concentrated Sun’s rays heat the moist air causing it to rise. Heavy rainfall is the result and a climate with near perfect all year growing conditions. The climate graph shows a constantly high temperature (red line) and generally very high levels of rainfall (blue bars). The rainforest has great biodiversity – this means it has a great variety of different types of plants and animals. E.g. the Amazon rainforest What impacts are humans having on the Tropical Rainforest Human Activity Logging Effects/Impact Commercial logging destroys the forest and animal habitat. Often several trees are destroyed in the process of cutting down and removing one tree. Commercial intensive farming requires massive areas of land to be Conversion to deforested. Either plantations of crops such as soya and coffee farmland are grown or the land is used for grazing cattle for beef. Mining cuts away whole hillsides. Opencast mining destroys the Mining surface. Transport to and from the mine also causes pollution. Case Study: Carajas Scheme, Amazon. Road building Allows access to previously inaccessible parts of the forest. This can then lead to deforestation for logging or farming. Population growth Population of Brazil has increased from 60 million in the 1960s to nearly 200 million today putting huge pressure on the Amazon, e.g. more room for houses and farm land Pollution and Main threat comes from increased Carbon Dioxide. Rainforest frogs Climate Change have disappeared in large numbers due to temperature change. All forms of deforestation have an impact on the processes that take place on the forest. The removal of trees reduces the leaf litter falling onto the forest floor, which in turn will reduce the amount of nutrients that enter the soil. This therefore reduces the soils ability to allow new plant growth (The nutrient cycle will no longer work). Case Study – Amazon Rainforest Task: Describe the impacts that human activities are having on the Amazon (4 marks) How can we sustainably mange biomes? Sustainability – the ability to keep something going at the same rate or level. The current generation of people should not damage the environment in ways that will threaten future generations’ environment Unsustainable - unable to be kept going at the same rate or level Sustainable management means to make use of a resource in a way that: Protects it for future generations to enjoy. Benefits and trains local people. Is environmentally friendly. To make use of the goods that the tropical rainforest provides we must sustainably manage it. Strategy Ecotourism Sustainable Management Strategies Benefits This encourages tourists to visit a biome such as a rainforest. However, the aim of the holiday is to promote environmental awareness. Local people run the resort so earn money and learn new skills. The resorts are often small so have only a minimal impact on the environment. Case Study Santa Lucia, Tropical Rainforest in Ecuador. National Parks These are conservation areas which are set up in valuable or rare environments. They have very strict rules about what can be built by the landowners and residents of the park and what industry can take place in the park. Tourists are encouraged to visit and learn about the area. Peak District, UK. Global management: Wetlands (area where water is the primary factor controlling the environment and the associated plant and animal life) Local management: Biodiversity Action Plans (BAPs), e.g. Community Forests The Ramsar Convention (a global treaty) has achieved real success, protecting wetlands everywhere from unsustainable over-exploitation. Wetlands are among the world’s most ecologically productive environments. They are also an important source of water for people. Severn Estuary Together, the twelve Community Forests were able to help to improve the health, well being and quality of life of over half of England's population The Community Forests have planted over 10,000 hectares of new woodland and provided sustainable living spaces for thousands of people and animals. Greenwood Forrest, Nottinghamshire Task: Choose a local example of biosphere management. Explain the methods used to make it more sustainable (4 marks)