File - Bruner`s Science Page
advertisement

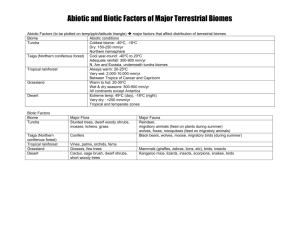
CHAPTER 1: STUDY GUIDE BIOMES AND ECOSYSTEMS ARE DIVISIONS OF THE BIOSPHERE Steps for studying for the Ch. 1 Test: 1. Re-read your notes and use your Cornell-questions to quiz yourself. 2. Re-read pages 6 – 50 of your textbook. 3. Be able to define the key vocabulary from the chapter. 4. Review your Reading Checks and Work Book, making sure all is complete. 5. Be able to answer the questions below. They are a guide for your studying. 6. Complete the online quizzes at http://www.bcscience.com/bc10/ VOCAB: Be able to define the following terms. Make VOCAB cards if • abiotic • community • • adaptations • competition • algae • ecological hierarchy • • bacteria • ecology • • behavioural • ecosystem • adaptation • habitat • • biodiversity • host • • biome • lichen • • biosphere • mutualism • biotic • niche • • climate • nutrients • • climatograph • parasitism • • commensalism • photosynthesis • you need to. physiological adaptation population predation predator prey species structural adaptation symbiosis elevation latitude terrestrial 1.1 Biomes Questions 1. What is the biosphere? 2. What does biotic mean? Give examples of biotic components in an environment. 3. What does abiotic mean? Give examples of abiotic components in an environment. 4. List, in order the divisions that scientists break the biosphere down into. 5. What is a biome? 6. How many terrestrial biomes did we focus on in class? List them. 7. List and describe the 5 factors that influence the characteristics and distribution of biomes. Which 2 are the most important? 8. What is a climatograph? Be able to read a climatograph. See the ones on pp. 16 and 17. 9. What are the three types of adaptations? Give an example of each. 10. What are the five major biomes in Canada? 11. Be able to describe the location, climate, physical features, plant adaptations, and animal adaptations, and recognize the climatographs for all eight terrestrial biomes (tundra, boreal forest, temperate deciduous forest, temperate forest, grasslands, tropical rainforest, desert, and permanent ice). 12. Which biome has the greatest variety of plant and animal species? 13. What is permafrost? In which biome does it occur? 14. What biome is also known as the coniferous forest? 15. What biome has four distinct seasons? 16. Which biomes have less than 25 cm of precipitation annually? 17. Which biomes have more than 200 cm of precipitation annually? 1.2 Ecosystems Questions 1. What is ecology? Where does the word come from? 2. What happens between abiotic and biotic components in an ecosystem? Give an example. 3. What is a habitat? Give an example. 4. List 5 abiotic components of an ecosystem and the importance of each. 5. Order and explain the difference between the biotic interactions (ecosystem, population, community, organism), within an ecosystem (from small to large scale). 6. What is symbiosis? Why is it important? 7. Name, describe and give an example of the 3 types of symbiotic relationships. 8. What is a niche? How is it different than a habitat? 9. What is competition? Give an example. 10. What is predation? How is it different than parasitism? 11. Give some examples of adaptations that predators have to help them catch prey. 12. Give some examples of adaptations that help prey avoid predators. 13. Give an example of a predator-prey relationship. How does the population of each affect the other? (Refer to Fig. 1.41 on p. 47) What will happen to the predator population if the number of prey is low? high? 14. What is the cause of most of the losses of biodiversity? 15. Why should we be concerned about the loss of biodiversity? Work book and Text Book Questions Complete all workbook pages for Ch. 1 and complete the section and chapter review from the textbook.