Week 3 - Arteries + Veins - PBL-J-2015
advertisement
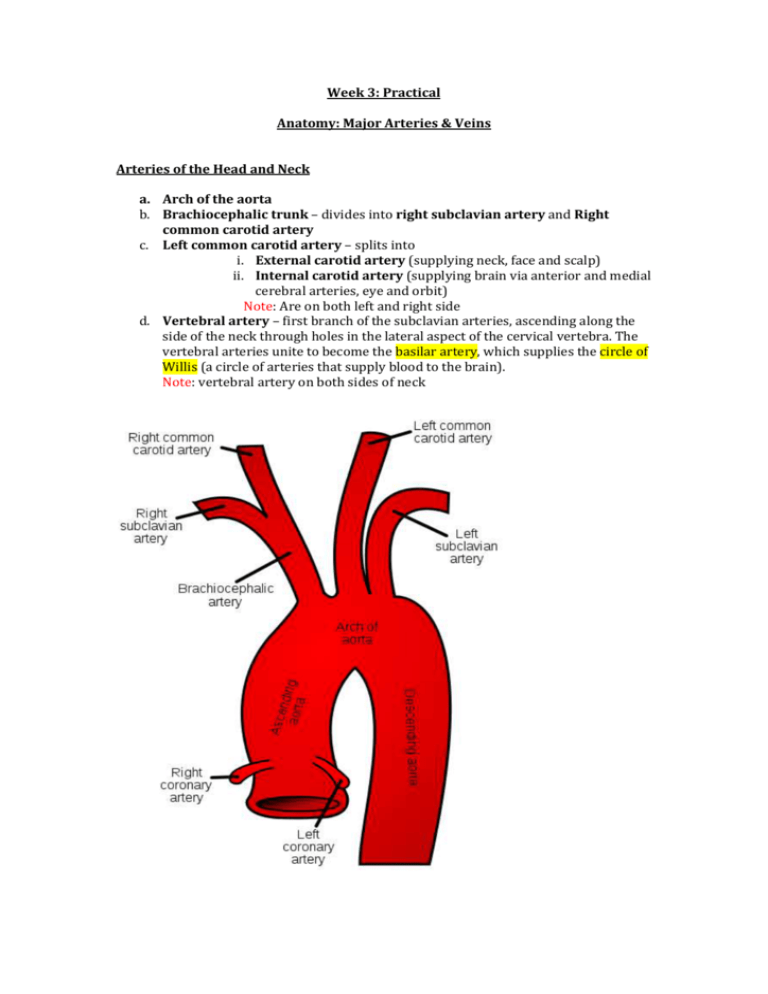
Week 3: Practical Anatomy: Major Arteries & Veins Arteries of the Head and Neck a. Arch of the aorta b. Brachiocephalic trunk – divides into right subclavian artery and Right common carotid artery c. Left common carotid artery – splits into i. External carotid artery (supplying neck, face and scalp) ii. Internal carotid artery (supplying brain via anterior and medial cerebral arteries, eye and orbit) Note: Are on both left and right side d. Vertebral artery – first branch of the subclavian arteries, ascending along the side of the neck through holes in the lateral aspect of the cervical vertebra. The vertebral arteries unite to become the basilar artery, which supplies the circle of Willis (a circle of arteries that supply blood to the brain). Note: vertebral artery on both sides of neck Veins of the Head and Neck a. External jugular vein – drains structures of the face and scalp, empties into subclavian vein. b. Internal jugular vein – receives blood from brain, face and neck and joins the sublclavian vein c. Subclavian vein – continuation of the axillary vein, joins with internal jugular vein to form brachiocephalic vein d. Brachiocephalic vein – formed by union of internal jugular and subclavian veins e. Superior vena cava – formed by union of left and right brachiocephalic veins and empties into right atrium of heart Note: All veins above, except superior vena cava, are on both sides Arteries of the Upper Limb a. Right Subclavian artery – arises from brachiocephalic trunk and supplies bllod to the right arm b. Left subclavian artery – arises directly from aortic arch and supplies blood to left arm c. Axillary artery – continuation of subclavian artery and branches off to provide blood to various upper limb tissues d. Brachial artery – continuation of the axillary artery. Provides main blood supply to arm. Divides into two major branches: i. Radial artery – smaller terminal branch of brachial artery, coursing along lateral forearm and ending in deep palmar arch of hand ii. Ulnar artery –larger terminal branch of brachial artery, coursing along anterior forearm and ending in the superficial arch of the hand. Note: All the branches from Axillary artery Veins of the Upper Limb a. Cephalic vein – arises from lateral side of the arm, drains into axillary vein b. Basilic vein – arises from medial side of the arm, drains into brachial vein c. Meidan cubital vein – connects cephalic and basilic vein Arteries of the Lower Limb a. Femoral artery – on anterior thigh, between anterior superior iliac spine and pubic symphhysis b. Popliteal artery – continuation of the femoral artery in the politeal fossa behind the knee. Supplies blood to knee joint and muscles in thigh + calf. Divides into two major branches: i. Anterior tibial artery – smaller terminal branch of poplital, coursing the anterior compartment of the leg and supplying blood to anterior leg and dorsal foot ii. Posterior tibial artery – coursing posterior compartment of leg and supplying blood to posterior leg and plantar surface of foot. Terminates by dividing into medial and lateral plantar arteries. c. Dorsalis pedis artery – continuation of anterior tibial at the ankle joint, it is lateral to the tendon on flexor hallicus longus. Veins of the Lower Limb a. Great saphenous vein – travels along medial thigh to empty into femoral vein b. Small saphenous vein – quite a large vein, superficial, courses up posterior leg, drains into politeal vein c. Popliteal vein- located behind knee and runs alongside popliteal artery. Formed by the union of anterior and posterior tibial veins d. Femoral vein – continuous with the popliteal vein into the thigh. Drains deep thigh muscles and femur Femoral Triangle • Is an anatomical feature of the anterior, medial thigh. • It is bound by three anatomical parts 1. Inguinal ligament – superior 2. Medial border of abductor longus muscle – medially 3. Medial border of sartorius muscle – laterally • The floor comprises of the pectineus and abductor longus muscle medially & iliopsoas muscle laterally • The roof is formed by the fascia lata • The contents of the femoral triangle: Femoral nerve Femoral artery Femoral vein Note: vein is most medial and nerve is most lateral Cubital Fossa • Is a triangular anatomical area on the anterior elbow • It is bound by: 1. Brachioradialis – laterally 2. Pronator teres – medially 3. Imaginary horizontal line between the medial and lateral epicondyles – base/superior • The floor comprises of the brachialis and supinator muscles • The roof is formed by the deep fascia (reinforced bicipital aponeurosis) • The contents of the cubital fossa are (from lateral to medial): Radial nerve (sometimes not included in cubital fossa) Biceps brachii tendon/muscle Brachial artery Median nerve With Radial Nerve