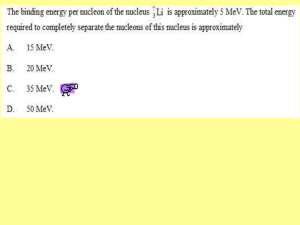CHAPTER 19. Nuclear Chemistry True — False (choose one
advertisement

CHAPTER 19. Nuclear Chemistry True — False (choose one) ___1. ___2. ___3. ___4. ___5. ___6. Radioactivity was discovered by Wilhelm Roentgen. The atomic number of 66 30 X is 36. 226 An atom of 88 Ra has a total of 314 nucleons. Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of radiation from the nucleus of an atom. The radioactive process is not affected by changes in physical state or temperature. The nature of the radioactivity exhibited by a radioactive element depends on the form or compound in which the element exists. ___7. The principal emissions from the nucleus of disintegrating natural radionuclides are known as alpha rays or particles, beta rays or particles, and gamma rays. ___8. All atoms with atomic numbers greater than 83 are radioactive. ___9. In two half-life periods of time a radioactive substance will decay completely (100%) into another element. ___10. Radionuclides of the same element have the same half-lives. ___11. All particles and rays emanate from the nucleus in radioactive changes. ___12. A positron has a positive charge of + 1. ___13. The half-life of radionuclides can vary from millionths of a second to billions of years. ___14. The longer the half-life of a radionuclide, the faster it decays. ___15. If the half-life of Ra-226 is 1620 years, the amount remaining from 1000 g of Ra-226 at the end of 4860 years is 125 g. ___16. As the temperature of a radionuclide increases, its half-life decreases. ___17. The following symbols all represent an alpha particle: He2+ or 24 He. ___18. A beta particle is written as -10 e. ___19. A balanced nuclear reaction has the same number and kinds of atoms on both sides of the equation. ___20. When alpha, beta, or gamma radiation is emitted from a nucleus, the residue remaining is a different element. ___21. In order for an element to change into another element (transmutation) the number of protons in the nucleus must change. ___22. Alpha disintegration of a radionuclide results in the formation of a new element with an atomic number four less than the starting element. ___23. The half-life of Ra-226 is 1620 years. ___24. When an atom emits a beta particle as a result of nuclear decay, the number of protons in the atom increases. 207 ___25. The loss of one alpha and two beta particles from 211 84 Po leaves 84 Po. 235 ___26. The disintegration of 247 96 Cm to 92 U involves the loss of four alpha and four beta particles from the nucleus. 235 ___27. The disintegration of 247 96 Cm to 92 U involves the loss of three alpha and two beta particles from the nucleus. ___28. The gamma ray has the greatest penetrating ability of the three principal emissions from the nucleus. ___29. Radioactivity is due to an unstable ratio of neutrons to protons in an atom. ___30. The three naturally occurring radioactive disintegration series all end with a stable nuclide of lead. ___31. The stable end product of the natural disintegration series of U-238 is Pb-206. ___32. A transmutation reaction must involve a change in the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. ___33. The first artificial transmutation was accomplished by Ernest Rutherford in which he converted 147 N to 187 O. ___34. The bombardment of stable nuclei with atomic particles to form unstable nuclei, which are radioactive, is called induced or artificial radioactivity. ___35. Artificial radionuclides do not have specific half-lives like natural radionuclides. 4 1 30 ___36. The symbol for the missing particle in the equation 27 13 Al + 2 He ? + 0 n is 15 p. ___37. The unit of measurement of radioactivity is the curie, which corresponds to the amount of radiation produced by 1 gram of pure radium. ___38. A Geiger counter operates on the basis that radiations from a radioactive source are able to ionize molecules, forming ions and creating a flow of a detectable electric current. ___39. Two or more neutrons are released during a nuclear fission reaction. ___40. In nuclear fission a heavy nuclide splits into two or more smaller nuclides. ___41. Most nuclides formed as a result of nuclear fission are radioactive. ___42. The neutrons released during nuclear fission are necessary to sustain a nuclear chain reaction. ___43. The major components of a nuclear power plant are nuclear fuel, a central system to regulate the heat generated, and a cooling system, which returns the heat from the nuclear reactor. ___44. A nuclear reactor is a special furnace that produces energy by a controlled nuclear chain reaction. ___45. Nuclear fusion is the process of uniting the nuclei of two light elements to form one heavier nucleus. ___46. Helium may be produced by the fusion of hydrogen isotopes. ___47. The energy from nuclear fusion reactions is derived by the conversion of mass into energy. ___48. The difference in mass between the mass of a nucleus and the total mass of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus is called the mass defect. ___49. The binding energy of a nucleus is the energy equivalent of the mass defect of the nucleus. ___50. The smaller the mass defect of a nucleus the greater the binding energy. ___51. The equivalence between mass and energy is expressed by E = 1/2mv2. ___52. The elements following uranium are called transuranium elements. ___53. Almost all the known transuranium elements are radioactive. ___54. Alpha, beta, and gamma radiations are classified as ionizing radiations and can damage or kill living cells. ___55. Strontium-90 is a hazardous radionuclide because it deposits in the bones like calcium and its radiation may cause leukemia and bone cancer. ___56. Nuclear radiation may damage the structure of the genes, which can then have an effect on the genetic of future generations. ___57. Radioactive tracers are compounds containing a radionuclide whose reactions in a chemical or biological system can be traced or followed using radiation detection instruments. ___58. Radiocarbon age dating is based on a diminishing ratio of C-14 to C-12 in a previously living species. ___59. Radioactivity was first discovered by Antoine Henri Becquerel. ___60. A thin sheet of paper will normally block beta radiation. ___61. When a nucleus emits an alpha particle or a beta particle, it always changes into a nuclide of a different element. ___62. When an atom loses a beta particle from its nucleus, a different element is formed, having essentially the same mass and atomic number one greater than the starting element. ___63. A radioactive disintegration series shows the succession of alpha and beta emissions by which naturally occurring radioactive elements decay to reach stability. ___64. The energy from nuclear fission can be harnessed to produce steam, which can drive turbines and produce electricity. ___65. The high energy released from nuclear fusion gives other nuclei enough kinetic energy to sustain a chain reaction. ___66. Cancers are often treated by gamma radiation from CO–60, which destroys the rapidly growing cancer cells. ___67. Protracted exposure to low levels of any form of ionizing radiation can weaken the body and lead to the onset of malignant tumors. ___68. A positron has the mass of an electron and the electrical charge of a proton. ___69. Transmutation is the changing of a nuclide of one element to a nuclide of another element. ___70. Rem is the unit of radiation that relates to the biological effect of absorbed radioactive radiation. ___71. A Geiger counter measures ionizing radiation. ___72. An alpha particle is a negatively charged particle with a mass number equivalent to that of a proton. ___73. Cesium-137 spontaneously decays to emit beta particles and to form barium-137. The half-life of the cesium isotope is about 30 years. It will take approximately 150 years before 97% of the cesium in a particular sample has decomposed. ___74. An isotope of uranium undergoes a fission reaction when bombarded with neutrons. The mass number of the ? 141 92 uranium isotope used must have been 238. 10 n + 92 U 56 Ba + 36 Kr + 3 10 n. ___75. Atoms of all elements have at least one neutron in the nucleus. ___76. These nuclear particles are listed in order of increasing ability to penetrate matter: alpha, beta, and gamma. ___77. After the duration of three half-lives, 1/6 of any radioactive sample will still be radioactive. indirectly related. ___78. Half-life and the stability of a nuclide are ___79. A critical mass is required to sustain a chain reaction in a nuclear fission. ___80. Gamma radiation is affected by electromagnetic field.