MSDE Arts Literacy Team - DorchesterSuccessForAll
advertisement

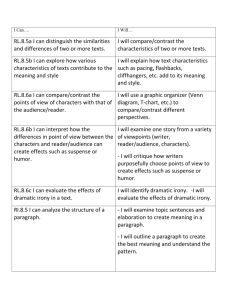
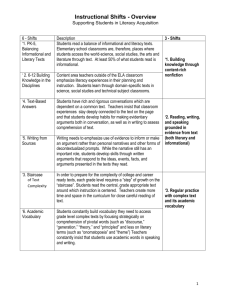
MSDE Arts Literacy Team April 14, 2013 Arts Writing Connections to Common Core Standards College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Writing, Black Core Arts Connections Writing, Red, Grades 6-8 Core Arts Connections-Writing, Blue, Grades 9-12 Cluster: Text Types and Purposes Common Core Standards 1. Write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts, using valid reasoning and relevant and sufficient evidence. Arts Writing 6-8 Grades 1. Prepare in writing an argument about an issue or topic related to a specific arts discipline. The argument might take the form of a critique, review, letter, or petition. It might assess the quality of a performance, media presentation, exhibition, or specific musical composition, dance, play, film/video, or visual artwork. Or it might address the suitability of a performance or exhibition for a particular audience or venue. Support the opinion with logical reasoning and relevant, accurate data and evidence using credible sources. Arts Writing 9-12 Grades 1. Write ARGUMENT TEXT: Text that persuades or convinces. Take a definite stand on an issue related to a specific arts discipline. Write a persuasive argument or claim that presents and defends your point of view. Your argument might take the form of a critique, review, letter, or petition. It might assess the quality of a performance, media presentation, exhibition, or specific musical composition, dance, play, film/video, or visual artwork. Or it might address the suitability of a performance or exhibition for a particular audience or venue. A sound argument: Clearly states the issue and your claim. Weighs the claims and counterclaims on both sides of the issue and points out the strong and weak points of both arguments based on accurate evidence or data from trustworthy sources. Refutes the counterclaims with logical reasoning. Uses words and phrases such as for example, therefore, however, on the other hand, to make the relationship between claims, counterclaims, reasons, and evidence absolutely clear. Finishes with a conclusion that follows MSDE Arts Literacy Team April 14, 2013 logically from your argument. 2. Write informative/explanatory texts to examine and convey complex ideas and information clearly and accurately through the effective selection, organization, and analysis of content. 2. Write informative/explanatory texts such as labels, captions, program notes, or website entries, to convey information and ideas that are accurate and relevant. 2. Write INFORMATIONAL TEXT: Text that provides information or explains. Write text that examines and conveys information clearly and accurately. The text might consist of exhibition panels and labels, program notes, story or plot synopses, performer biographies, instructional brochures, picture captions, publicity flyers, or any other arts-related text that serves the purpose of conveying information. A clear, well-organized informational text: Selects and presents facts and concepts that are accurate, pertinent, and well suited to a specific audience and purpose. Groups related facts, topics, and concepts together, perhaps using headings, captions, or graphics to make their organization clear. Develops the topic with well-chosen, clearly-worded details that might include quotations, concrete data, or definitions of domain-specific vocabulary. Uses transition words or phrases, such as in addition or next, to reinforce the organization of the text. Concludes with a statement that is a natural outgrowth of the text and may suggest further discussion. 3. Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective 3. Write a narrative that expresses real or imagined experiences or events in the form of 3. Write NARRATIVE TEXT: Text that tells a story or relates a sequence of events. MSDE Arts Literacy Team April 14, 2013 technique, well-chosen details, and wellstructured event sequences. a dance, play, video, film, or piece of music or visual art. Or write a detailed step-by-step narrative that explains the use of a specific technique or the process of creating a specific artwork. A. Using art forms and techniques inherent in dance, theatre, video/film, music, or visual art, create an original narrative or original interpretation of an existing story that uses real or imagined experiences or events. While some narratives might take the form of written stories or scripts, others might communicate primarily through movement, sound, or visual imagery. A narrative text: Introduces a problem or situation Establishes a setting or context for the story Introduces a narrator and/or characters Moves the story forward in a way that reflects the characters’ actions, thoughts, and feelings as well as the creator’s point of view using any of these devices: dialogue, large body movement, telling gestures, expressive sound, light, or visual imagery. Signals shifts in time and place and shows how one event builds upon another over time. Reflects on challenges met or unmet, problems resolved or unresolved, or lessons learned. Cluster: Production and Distribution of Writing 4. Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are 4. After identifying the intended audience and purpose of a piece of writing, produce clear coherent text that conveys pertinent B. Write a detailed step-by-step sequence of events that explains the use of a specific material, procedure, or technique used in the process of carrying out an arts-related task. 4. After identifying the intended audience and purpose of a piece of writing, produce clear coherent text that conveys pertinent MSDE Arts Literacy Team April 14, 2013 Cluster: Research to Build and Present Knowledge appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. information in an arts-related flyer, poster, program, or exhibition label. 5. Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach. 5. Develop and strengthen a piece of writing as needed by revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach until it satisfies its purpose and the needs of its audience. Seek opinions and guidance from peers, teachers and other adults. Compare the revision process with the way a dance, play, film/video, musical composition, or piece of visual art is rethought or reworked to achieve the desired result. 6. Use technology, including the Internet, to produce and publish writing and to interact and collaborate with others. 6. Use technology to explore relationships between the written word, images, and sound. Use the Internet to produce and/or distribute writing and other creative work in order to encourage interaction and collaboration among like-minded students. 7. Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects based on focused questions, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation. 7. Conduct short narrowly focused research projects to answer a given or self-generated arts-related question, drawing on several sources. Compile additional related focused questions that might serve as starting points for future explorations. 8. Gather relevant information from multiple print and digital sources; assess the credibility 8. Carry out an extended research project on an arts-related topic, gathering relevant information in an arts-related brochure, manual, program, exhibition label, flyer, poster or website. Follow guidelines described in Writing Standard 2, above. 5. Develop and strengthen a piece of writing by revising, editing, and rewriting, guided by Writing Standards 1-3, above. Seek opinions and guidance from peers, teachers, and other adults. If necessary, rethink the organization of the piece or try a new approach to the subject until the piece of writing satisfies its purpose and the needs of its audience. Compare the revision process with the way a dance, play, film/video, piece of music, or visual art is reworked to achieve the desired result. 6. Use technology to explore relationships between the written word, visual images, and sound. Use the Internet to produce and/or distribute writing and other creative work in order to encourage interaction and collaboration among like-minded students. Take advantage of technology’s capacity to link to other information and to display information flexibly and dynamically. Update work in response to ongoing feedback that might include new information, opinions, or logical arguments. 7. Conduct short narrowly focused research projects or more extended projects to answer a given or self-generated arts-related question. Draw on and synthesize multiple sources in order to demonstrate a thorough understanding of the subject under investigation. Narrow or broaden the inquiry as necessary. 8. Carry out an extended research project on an arts-related topic. Use search terms MSDE Arts Literacy Team April 14, 2013 Cluster: Range of Writing and accuracy of each source, and integrate the information while avoiding plagiarism. information from multiple print and digital sources. Use search terms effectively, and assess the credibility and accuracy of each source. Integrate the information, avoiding plagiarism, into a written report or visual, aural, theatrical, or kinesthetic presentation. 9. Draw evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. 9. Apply all grade level reading standards when selecting and using literary or informational texts as source material for writing. Seek evidence, make logical inferences, determine central ideas or themes, summarize key ideas, connect ideas, interpret symbols and key terms, analyze structure, and compare points of view. 10. Write routinely over extended time frames as well as shorter time frames in connection with the creation of artwork requiring long and short process times. Long-term writing projects may involve research, reflection, revision, and self-evaluation. Short-term writing may involve journal and sketchbook entries. 10. Write routinely over extended time frames (time for research, reflection, and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of tasks, purposes, and audiences. effectively to gather relevant information from multiple print and digital sources. Assess the credibility and accuracy of each source as well as its capacity to provide useful information and/or insights that are appropriate for the intended audience. Integrate the information, avoiding plagiarism, into a written report or visual, aural, theatrical, or kinesthetic presentation. 9. Apply all grade level reading standards when selecting and using literary or informational texts as source material for writing. Seek evidence, make logical inferences, determine central ideas or themes, summarize key ideas, connect ideas, interpret symbols and key terms, analyze structure, and compare points of view. 10. Write routinely over extended time frames as well as shorter time frames in connection with the creation of artwork requiring long and short process times. Long-term writing projects may involve research, reflection, revision, and self-evaluation. Short-term writing may involve journal and sketchbook entries.