Grade-6-Unit-1-Plan-Rational
advertisement
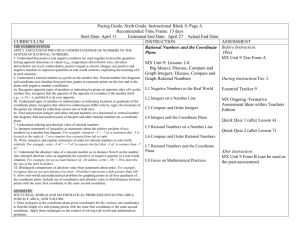
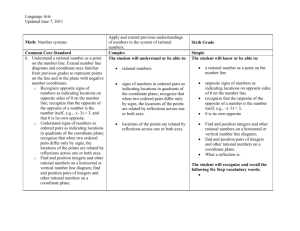
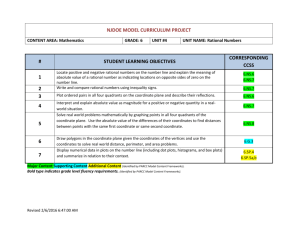
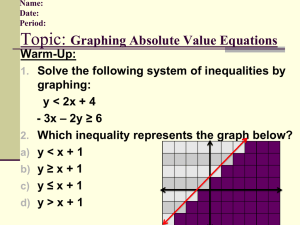
6th Grade Mathematics UNIT 1: Rational Numbers and Absolute Value Unit 1/ Rational Numbers and Absolute Value/ 15 days Students will apply and extend their previous understandings of numbers to the system of rational numbers (fractions, decimals, integers). They will develop an understanding of the meaning of integers in the real-world context Big Ideas/Enduring Understandings Positive and negative numbers are often used to solve problems in everyday life. Rational numbers are points on a number line Numbers in ordered pairs indicate locations in quadrants of the coordinate plane Negative numbers are used to represent quantities that are less than zero. Absolute value is a measure of distance from zero Absolute value is useful in ordering and graphing positive and negative numbers. Guiding Questions: What are positive and negative numbers? How do we compare rational numbers? Can a negative number have a greater absolute value than a positive number? How do we represent rational numbers on a number line? How do we graph ordered pairs to solve problems? NYS Common Core Standards for Mathematics: Mathematical Content6.NS.5 Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite directions or values (e.g., temperature above/below zero, elevation above/below sea level, credits/debits, positive/negative electric charge); use positive and negative numbers to represent quantities in real-world contexts, explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation. 6.NS.6 Understand a rational number as a point on the number line. Extend number line diagrams and coordinate axes familiar from previous grades to represent points on the line and in the plane with negative number coordinates. 6.NS.7 Understand ordering and absolute value of rational numbers. 6.NS.8 Solve real-world and mathematical problems by graphing points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. Include use of coordinates and absolute value to find distances between points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. 6.G.3 Draw polygons in the coordinate plane given coordinates for the vertices; use coordinates to find the length of a side joining points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. Apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. Mathematical Practices 1: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them 2: Reason abstractly and quantitatively 3: Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others 4: Model with mathematics 5: Use appropriate tools strategically 6: Attend to precision 1 6th Grade Mathematics 7: Look for and make use of structure 8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning Content Skills Fractions Decimals Integers Absolute value Graphing coordinates Distance Locate rational numbers on a number line Locate ordered pairs on the coordinate plane Order and compare rational numbers Interpreting absolute value in real-world scenarios Vocabulary/ Key Terms Integers Rational numbers Opposite numbers Positive and negative numbers Absolute value Inequality Number line Coordinate grid x-axis and y-axis Origin Quadrants Ordered pair/ coordinate x-coordinate andy-coordinate ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE Initial Assessment Diagnostic test for prior skills needed Formative Assessments: Checks for Understanding Short- and Extended-Response questions used throughout the unit. Reflections Formative Assessment Tasks Summative Assessments: 1. Quizzes 2. Interim assessments 3. Unit test 4. Performance Tasks TEACHING PLAN Teaching and Learning Activities: 2 6th Grade Mathematics Lesson 1: Positive and negative numbers are used to describe amounts having opposite values Lesson 2: Positive and negative numbers show amounts in real-world situations and they explain the meaning of zero in those situations Lesson 3: A rational number is a point on a number line which shows positive and negative numbers Lesson 4: Opposite signs of numbers indicate places on opposite sides of 0 on the number line Lesson 5: Signs of numbers in ordered pairs indicate locations In quadrants of the coordinate plane Lesson 6: Ordering positive and negative numbers Lesson 7: Absolute value of rational numbers Lesson 8: Distance between points in the coordinate plane Culminating Activities: Performance tasks Essential question as a post-assessment. Reflections Set goals for improvement Unit test Resources Needed: a. b. c. d. e. Connected Mathematics Project 3 – Grade 6 Impact Mathematics Course 1 Rulers Graph Paper Chart Paper CALENDAR 3 6th Grade Mathematics Time Spent on Standard Standards 3 days 6.NS.5 Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite directions or values (e.g., temperature above/below zero, elevation above/below sea level, credits/debits, positive/negative electric charge); use positive and negative numbers to represent quantities in realworld contexts, explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation. 3 days 6.NS.6 Understand a rational number as a point on the number line. Extend number line diagrams and coordinate axes familiar from previous grades to represent points on the line and in the plane with negative number coordinates. 3days 6.NS.7 Understand ordering and absolute value of rational numbers. 3 days 3 days Topics To Cover CMP3 Unit: Comparing Bits and Pieces (Investigation 3) Rational Numbers Absolute value Graphing 6.NS.8 Solve real-world and mathematical problems by graphing points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. Include use of coordinates and absolute value to find distances between points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. 6.G.3 Draw polygons in the coordinate plane given coordinates for the vertices; use coordinates to find the length of a side joining points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. Apply these techniques in the context of solving realworld and mathematical problems. 3 days 4