Hueneme.Math.6thgrade.Unit 1 Chaptering
advertisement

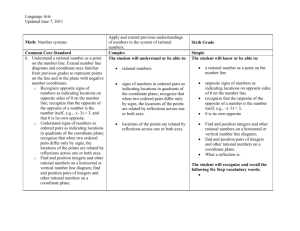
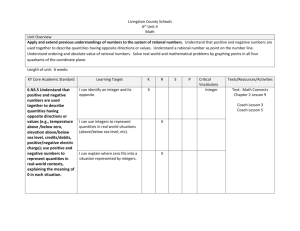
Hueneme Elementary School District Grade 6 Mathematics Unit 1 Outline: The Number System Chapter 1 of 4 Approximate Length: 7 days Enduring understanding addressed in this chapter: NUMBERS: The set of real numbers is infinite, and each real number can be associated with a unique point on the number line. Emphasized Mathematical Practices: 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 4. Model with mathematics 5. Use appropriate tools strategically Priority Standards 6.NS.5. Understand that positive and negative numbers are used together to describe quantities having opposite directions or values (e.g., temperature above/below zero, elevation above/below sea level, credits/debits, positive/negative electric charge); use positive and negative numbers to represent quantities in real-world contexts, explaining the meaning of 0 in each situation. 6.NS.6. Understand a rational number as a point on the number line. Extend number line diagrams and coordinate axes familiar from previous grades to represent points on the line and in the plane with negative number coordinates. a. Recognize opposite signs of numbers as indicating locations on opposite sides of 0 on the number line; recognize that the opposite of the opposite of a number is the number itself, e.g., –(–3) = 3, and that 0 is its own opposite. Hueneme Elementary School District Grade 6 Mathematics Unit 1 Outline: The Number System Learning Objectives Students will use a number line to represent quantities with opposite directions or values in relation to real-world contexts. Students will describe real-world examples of numbers and their opposites in relation to zero. Criteria for Success Given two numbers with opposite signs, students will plot the points on a number line and explain a real-world situation that represents the numbers in relation to zero. Students will select a pair of opposites and generate a real-world scenario representing the numbers. Relevant Essential Questions How/why is a number line useful in showing the relationship between numbers? How is (-3) related to (4)? How are positive and negative numbers related to real life? What is the opposite of an opposite? Hueneme Elementary School District Grade 6 Mathematics Unit 1 Outline: The Number System Chapter 2 of 4 Approximate Length: 9 days Enduring Understanding addressed in this chapter: COMPARISON: Numbers and measures can be compared by their relative values. Emphasized Mathematical Practices: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. Model with mathematics Priority Standards 6.NS.7. Understand ordering and absolute value of rational numbers. a. Interpret statements of inequality as statements about the relative position of two numbers on a number line diagram. For example, interpret –3 > –7 as a statement that –3 is located to the right of –7 on a number line oriented from left to right. b. Write, interpret, and explain statements of order for rational numbers in real-world contexts. For example, write – 3 oC > –7 oC to express the fact that –3 oC is warmer than –7 oC. 6.EE.8. Write an inequality of the form x > c or x < c to represent a constraint or condition in a real-world or mathematical problem. Recognize that inequalities of the form x > c or x < c have infinitely many solutions; represent solutions of such inequalities on number line diagrams. Hueneme Elementary School District Grade 6 Mathematics Unit 1 Outline: The Number System Learning Objectives Students will explain the relationship between two numbers based on their position on a number line and within a real-world context. Criteria for Success Given two thermometers, write two inequality statements to describe the relationship between the two thermometers. Relevant Essential Questions How is (-10) related to (-30)? Students will write inequalities to represent a real-world and/or mathematical problem. Given a chart showing the average depth of many of the world’s oceans, students will write two inequality statements to compare oceans. How can you use the relative values of numbers to make comparisons? Hueneme Elementary School District Grade 6 Mathematics Unit 1 Outline: The Number System Chapter 3 of 4 . Enduring Understanding(s) addressed in this chapter: Approximate Length: 9 days NUMBERS: The set of real numbers is infinite, and each real number can be associated with a unique point on the number line. COMPARISON: Numbers and measures can be compared by their relative values. Emphasized Mathematical Practices: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically Priority Standard 6.NS.7. Understand ordering and absolute value of rational numbers. c. Understand the absolute value of a rational number as its distance from 0 on the number line; interpret absolute value as magnitude for a positive or negative quantity in a real-world situation. For example, for an account balance of –30 dollars, write |–30| = 30 to describe the size of the debt in dollars. d. Distinguish comparisons of absolute value from statements about order. For example, recognize that an account balance less than –30 dollars represents a debt greater than 30 dollars. Hueneme Elementary School District Grade 6 Mathematics Unit 1 Outline: The Number System Learning Objectives Criteria for Success Relevant Essential Questions Given a set of numbers, students will identify the absolute values and provide proof for their answers using a number line. What is absolute value? How are absolute values of positive and negative numbers related to each other? Given a situation involving negative numbers (debts, elevations below sea level…) students will use absolute value to interpret the meaning. Students will use Given a listing of debts (as absolute values to make negative numbers) students comparisons. will use absolute value to determine and explain which debt is greater. Why/when is it necessary to rely on absolute value to interpret positive and negative numbers? Explain absolute value using a number line. Use absolute value to interpret meanings of rational numbers in realworld situations. How can absolute value be used to compare numbers? Type(s) of assessments recommended (SR/SCR/PT) and Possible Instructional Resources CR: On the horizontal number line, plot 7 and -7. What is the distance of each point from zero? What is the distance between 7 and -7? How does absolute value help you find the distance between 7 and 7? SCR SCR Hueneme Elementary School District Grade 6 Mathematics Unit 1 Outline: The Number System Chapter 4 of 4 Approximate Length: 10 days Big Idea(s) addressed in this chapter: ORIENTATION & LOCATION: Objects in space can be oriented in an infinite number of ways, and an object’s location in space can be described quantitatively. Emphasized Mathematical Practices: 4. Model with mathematics 5. Use appropriate tools strategically Priority Standards 6.NS.6. Understand a rational number as a point on the number line. Extend number line diagrams and coordinate axes familiar from previous grades to represent points on the line and in the plane with negative number coordinates. b. Understand signs of numbers in ordered pairs as indicating locations in quadrants of the coordinate plane; recognize that when two ordered pairs differ only by signs, the locations of the points are related by reflections across one or both axes. c. Find and position integers and other rational numbers on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram; find and position pairs of integers and other rational numbers on a coordinate plane. 6.NS.8. Solve real-world and mathematical problems by graphing points in all four quadrants of the coordinate plane. Include use of coordinates and absolute value to find distances between points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. 6.G.3. Draw polygons in the coordinate plane given coordinates for the vertices; use coordinates to find the length of a side joining points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. Apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems Hueneme Elementary School District Grade 6 Mathematics Unit 1 Outline: The Number System Learning Objectives Criteria for Success Students will identify, locate, and place pairs of integers and rational numbers on a coordinate plane. Given a set of coordinates of a town, students will place points of interest on a coordinate plane. Students will explain relationships between ordered pairs and their reflections. Given a list of ordered pairs, students will locate their reflections across one or both axes. Students will use absolute value to determine the distance between two points with a common coordinate. Students will find distance from one point of interest to another on same axis. Relevant Essential Questions Why are there four quadrants on a coordinate plane? How do you determine in which coordinate an ordered pair should be placed? How can you form a reflection with a given ordered pair? How can you use absolute value to find the distance between two ordered pairs?