b. IntroSocialSciences - Suicide Analysis
advertisement
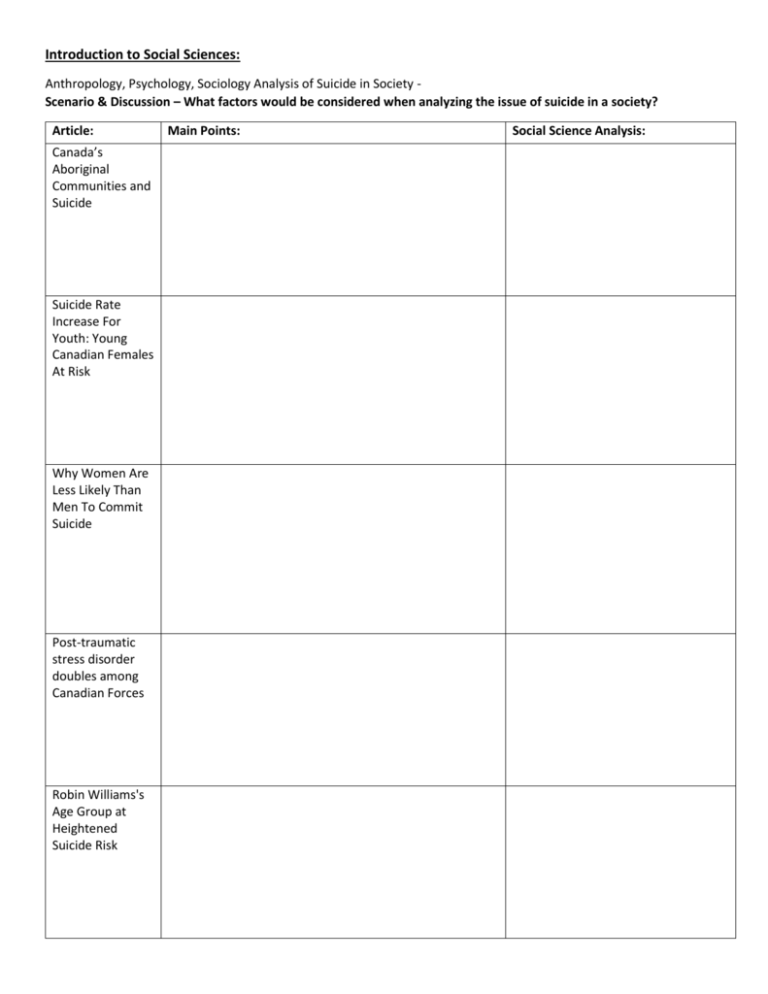
Introduction to Social Sciences: Anthropology, Psychology, Sociology Analysis of Suicide in Society Scenario & Discussion – What factors would be considered when analyzing the issue of suicide in a society? Article: Canada’s Aboriginal Communities and Suicide Suicide Rate Increase For Youth: Young Canadian Females At Risk Why Women Are Less Likely Than Men To Commit Suicide Post-traumatic stress disorder doubles among Canadian Forces Robin Williams's Age Group at Heightened Suicide Risk Main Points: Social Science Analysis: Anthropology: • • • • • • • • • • Anthropology is the scientific study of the origin, the behaviour, and the physical, social, and cultural development of humans. Anthropologists seek to understand what makes us human by studying human ancestors through archaeological excavation and by observing living cultures throughout the world Aim to describe what it means to be human Study of human life throughout history Anthropologist study how humans think, live, communicate, produce, and interact with their social and physical environment Anthropology study both the differences/similarities of people and their respective cultures Study of the lives/cultures of human beings, alive or dead Physical anthropologists want to know where humans as a species come from, how our bodies evolved to their present form, and what makes humans unique. Linguistic anthropologists study human languages and how language affects and expresses culture. Cultural anthropologists study and compare cultures of living people in different cultural settings around the world Psychology: • • • • • • • Psychology is the study of the human mind and its mental states. It includes the study of characteristics of temperament and behaviour of a person or group Psychologists aim to describe, predict, and control behaviour and mental processes. Early in the 20th Century, psychologists began to develop psychoanalytic theories as a new approach to therapy, based on Sigmund Freud’s work. These theories are based on the belief that unlocking the unconscious mind is the key to understanding human behaviour and relationships. Behavioural psychology is another branch of psychology that was common in the first half of the twentieth century. It is based on the belief that psychologists need empirical evidence, obtained through experimentation, to understand and change human behaviour. Clinical psychology became an important concept in the second half of the century. It developed out of the patient relationship idea of therapy. Clinical psychologists believe that the client should be very involved in his or her own recovery, rather than relying only on the therapist’s interpretation of the issues. This approach empowered the client in a way not previously practised. The word cognition refers to the mental processes in the brain. So cognitive psychology is the study and application of how the brain learns. Unlike behaviourists, cognitive psychologists believe in and consider mental states, such as beliefs, motivations, and desires. However, cognitive psychology is often coupled with behavioural psychology to create methods of treating people with some mental illnesses and neurotic disorders. Sociology: • • • • • • • • Sociology is the study of human social life, groups, and societies. It also involves studying the behaviour of individuals and groups, as well as social institutions. Sociologists study such areas as gerontology, politics, culture, economy, religion, and crime. They examine organizations, social movements, collective behaviour, social institutions, and social identities. A society is a large group of people who live in the same area and who share a distinctive culture and institutions. This group provides protection, stability, security, and identity to its members. Sociologists attempt to answer key questions about why certain social behaviours exist and how different societies function. They study individual behaviour within the context of groups, the behaviour of groups, and a society as a whole to understand the complex world around us, investigate existing problems, and examine issues. Sociologists study the interactions among people living together in a society and their actions, beliefs, and behaviours in order to understand the society. Sociologists also compare and contrasts human interactions and behaviours between different societies. They examine a wide range of issues and topics to investigate problems and developing issues, including the following: gender roles, criminal behaviour ethnicity, family structure, social institutions, sexuality, social classes









