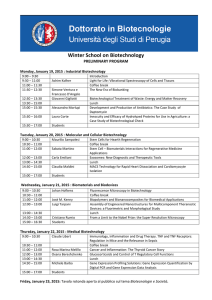
Report - G
advertisement

The Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan JSC "National Center of State Scientific and Technical Expertise" Report of optimistic scenario of directions "Biotechnology" in Kazakhstan up to 2030, developed as part of the system analysis and forecasting in science and technology Contributors to the report: The coordinator of the expert group in the direction "Biotechnology", First Vice-Rector - Vice Rector for Innovative Development of Innovative Eurasian University, Doctor of Veterinary, professor E.B. Nikitin Chairman of the expert group on the direction "Biotechnology", the representative of Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan Science Committee for the construction of an international reference laboratory in Almaty, Doctor of Veterinary, professor S.M. Mamadaliev The group expert on the direction "Biotechnology", Deputy General Director of Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan National center of Biotecnology, Ph.D, Doctor of Veterinary, Professor The group expert on the direction "Biotechnology", Head of department of the Institute of Microbiology and Virology of of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan Committee, Ph.D., professor, corresponding member of Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Kazakhstan Virology Ministry Science National The group expert on the direction "Biotechnology", Head of the Laboratory of the Institute of Plant Biotechnology of Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan Science Committee, Ph.D., Professor The group expert on the direction "Biotechnology", Doctor of Veterinary, Ph.D., Professor of Microbiology and Biotechnology Department of the Kazakh Agro-Technical University S.Seifullin. К.К. Mukanov V.E. Berezin L.K. Mamonov А.К. Bulashev The group expert on the direction "Biotechnology", Head of R.T. Omarov Department "Biotechnology" ENU. Gumilev Department, Ph.D., professor Astana, 2013 The present study aims to show the options for the development of biotechnology in Kazakhstan for the period up to 2030, and is not an attempt to anticipate the future. It is aimed at providing the foundations for strategic understanding of options for future development based on identifying key trends, opportunities and risks of the future. In the basis for constructing future scenarios key mega-trends, factors that have a significant impact on the development and implementation of scenarios and variables in the trajectory of development, which have a high uncertainty in the future, are put. A brief summary contains the basic provisions and the conclusions reached in the development of scenarios biotechnological directions in Kazakhstan for the period up to 2030 (hereinafter - the Scenario). When developing scenarios the following points were covered: 1. GLOBAL CHALLENGES, TRENDS AND FACTORS OF DEVELOPMENT 2. KAZAKH TRENDS AND FACTORS 3. THE KEY TRENDS AND FACTORS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF BIOTECHNOLOGY 4. THE CROSS-IMPACT ANALYSIS 5. ANALYSIS OF THE FUTURE MARKET IN THE WORLD AND IN KAZAKHSTAN 6. ANALYSIS OF DEVELOPMENT STRATEGIES AND PROGRAMS OF BIOTECHNOLOGY SECTOR IN THE WORLD 7. ANALYSIS OF STRATEGIES AND PROGRAMS FOR DEVELOPMENT OF THE BIOTECHNOLOGY SECTOR IN KAZAKHSTAN 8. ANALYSIS OF R & D IN THE WORLD, IDENTIFICATION OF LEADING COUNTRIES 9. ANALYSIS OF THE COMPETENCE OF R & D IN KAZAKHSTAN 10. A STRATEGY ON THE SCENARIO 11. "WILD CARDS" 12. THE SCENARIO RISKS AND THREATS 2 IMAGING THE FUTURE The President of Kazakhstan, N.A. Nazarbayev in his Address to the Nation "Strategy" Kazakhstan-2050" has set a goal of transition to the society of universal labour, based on knowledge - a healthy and prosperous nation, ensuring the prudent use of the environment and natural resources with the use of advanced, environmentally friendly technologies for the extraction and processing of minerals and raw materials, with sustainable development of the agricultural sector, ensuring availability and food security, with the introduction of safe and clean energy breakthrough projects in the field of new materials, bio and nanotechnologies, based on the rapid development of modern information and communication technologies. 2030: the best for the future of Kazakhstan in the field of biotechnology: Agrobiotechnology: • A significant proportion of diagnostic products and vaccines for veterinary medicine is produced by the bio enterprises of Kazakhstan; • On the basis of modern biotechnology drought- and salt-resistant crop varieties are developed; • Deep processing Biotechnology of agricultural products and agricultural waste will enable reception of high value added products; • Modern biotechnological methods of water and land resources provide higher yields of agricultural plants and animal productivity. Biomedical: • On the basis of cell and DNA technologies personalized medicine will be developed; • Highly effective medicines from natural sources of Kazakhstan origin were developed and implemented; • With the use of biotechnological methods ways of early diagnosis and treatment of socially significant diseases in humans and animals were improved • On the basis of DNA technology, cellular and nanotechnologies and monoclonal antibodies medicinal, preventive and diagnostic preparations of new generation were produced; • Food production of therapeutic and prophylactic and functional purposes will increase Bioecology: • The method of bioremediation is carried out in the short term recovery in output due to contamination by oil products and other non-natural pollutants from the turnover of productive land; • Bioconversion based on biotechnological processes allows to eliminate pollution by organic waste and to generate more energy. The main objective of biotechnology in Kazakhstan is the creation and implementation of high technologies and competitive biotechnological products for health and agriculture, environmental protection, food and processing industries. In the future, the development of biotechnology, we can assume the appearance of three interrelated sub-packets, based on recombinant DNA technology, embryonic stem cells and cloning, and developing the medical sciences, agriculture, environmental management and hightech engineering: 3 1. Bioengineering (biocatalysis, biosynthesis, biosensors, cell markers, in the long term living construction materials and living systems); 2. Management of the genome (the production of GM plants, GM animals, of GM microorganisms, including genetically modified antibiotics, genetically modified enzymes, yeast GM crops, biopesticides, etc.); 3. Artificial ecosystems (production of extinct organisms, the creation of new species, the creation of ecosystems). On the development of environmental technology in this scenario, the key impact will be probable Biological Diversity Act, postulating the need to maximize the genetic stock of the Earth. This will lead to significant changes in wildlife management from the creation / destruction of natural ecosystems, Mankind will go to the construction of artificial ecosystems for specific user tasks. If we manage to overcome the social tensions and resolve a large group of complex philosophical, theological and cultural issues, next stage of development: the artificial elevation of a number of species to the mind will be implemented. I. GLOBAL CHALLENGES, TRENDS AND FACTORS OF DEVELOPMENT The main challenges: Among the key challenges that determine the development of the sector in question science and technology in the world, some of the most important, affecting the social, economic, scientific and technological development of the world community can be selected. These include: Socio-economic. Population growth, particularly in developing countries; an aging population and, as a consequence, reduction of the people proportion of working age; malnutrition and hunger on a global scale; urbanization and reduction of agricultural lands; globalization in almost all areas, including trade, manufacturing and services, extraction of natural resources; income growth in developing countries, changing the world leaders in the industry in question, increased global trade and tourist flows; rising fuel prices and a decrease of mineral reserves. Environmental. Soil and water pollution as a result of human activities; increase the amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere; the growth of global climate change; reduction of arable land due to urbanization, needs of conservation, unsustainable agricultural production and soil degradation. Science and technology. The increase in the number of breakthrough scientific advances in biotechnology, molecular biology, genetics, medicine and ecology; increasing the share of hightech industries and high-tech products, development of new areas by human, polar regions, mineral resources, deep sea and space. Science and technology are seen as an integral part of economic growth by developing country governments. They are taking steps to develop their own scientific and technical infrastructure, promotion of research, expansion of the higher education system. The new global "Technological wave" could lead to a fundamental transformation of the markets of high-tech products and services, a fundamental impact on competitive advantage as the national economy and the competitiveness of its individual sectors. The factors and trends that will have a significant impact on the development of biotechnology in the world for the period up to 2030 are as follows: 1. Biopharmaceuticals 2. Biomedical 4 2.1 Molecular Diagnostics 2.2 Diagnostic tools to personalize therapy 2.3 Cell and tissue engineering for therapeutic purposes 2.4 Biocompatible materials 3. Industrial Biotechnology 3.1 Biopolymers 3.2 Biological products for industrial use 4. Bioenergy 5. Agricultural Biotechnology 5.1 Biotechnology for recycling 5.2 Food Industry Analyzing the world's major challenges and trends shaping the fields of science, technology and production in the field of biotechnology, the following factors affecting the development of biotechnology in the world are: Social Political Economic Environmental Population growth, particularly in developing countries The aging population Malnutrition and hunger on a global scale Continue to develop urbanization trends Ongoing globalization trends Growth of incomes in developing countries Change of the world market producers of biotechnology products Increased global trade and tourist flows Pollution of soil and water as a result of economic human activity The amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere increases. A continuous increase in global climate change Technological In the world shrinking arable land due process urbanization, conservation needs, unsustainable agricultural production and soil degradation are being reduced. Rising fuel prices and a decrease in reserves of fossil fuels Population growth, particularly in developing countries, causes growth of demand for food and feed. This leads to the need to improve the productivity of agricultural land and nonagricultural land is plowed. Although population growth in the past decade has slowed down, however, in absolute terms the population has increased significantly, mainly due to developing countries. Malnutrition and hunger on a global scale remains a major problem of global agricultural production. Although enough food in the world, malnutrition, hunger and insecurity of some food products continues to persist, not only in underdeveloped countries, but also among the poor in industrialized countries. 5 North America Europe Central and South America The Asia-Pacific region South Africa Poor Middle class Rich Middle East and North Africa World Picture 1 - Change the size of the middle class and the predicted distribution of population by social classes (the forecast of the World Bank) The population of western countries continues to age, and European countries face a growing demand for medical support. The most important medical problem of the near future the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases. To maintain the health of the population will be tested and implemented many biotechnological products, medical and social costs would amount to a significant portion of the national budget, reducing the investment in other sectors of the economy. The growing anxiety of the public in relation to preventive health care and nutrition, and the requirements of the meticulous quality control of products as well will lead to changes in the food industry. Faced with an abundance and variety of food products, consumers in developed countries are very demanding with regard to the products they are buying. More and more increasing consumer interest in food technology. The trends of urbanization and more technological equipment of agriculture continue to develop. This area is controlled by the commercial sector of agriculture and stimulate the process of standardization and consolidation. The system of agricultural production involves fewer people. Life sciences continues to grow rapidly both in fundamental and in applied field. The exponential growth of biological information contained in databases of genes and proteins, will continue, although in the next decade, growth of new products use on the basis of these databases unlikely is to be as rapid. In medicine, genomics information will allow to develop new strategies for the treatment of diseases and identify new drugs. In agriculture, this technology will lead to the emergence of new products and technological means, including biosensors and diagnostic tools in order to increase agricultural productivity. US and European countries are leaders in the field of biotechnology, including the medical and agricultural. At the same time, there is a rapid growth of biotechnology in some developing countries, primarily in China, India and Brazil. It does not exclude a change of "key players" in the near future. Acute water problems will come not only regionally, but also internationally. Obviously, the supply of fresh water will be used primarily for drinking and to a lesser extent for agriculture. The quality of fresh water in the world will decline. The world community will put the problem of water conservation, the use of new agricultural technologies and technology of zero tillage. The amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere increases. Global climate changes continue to increase. International 6 efforts are focused on slowing down and mitigate such effects. Rising levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will increase because of rapid industrialization in many developing countries, especially in China. The response to global warming can only be a change in agricultural production schemes and energy policies. CO2 emissions - the developing countries (UN data, million. t.) CO2 emissions - developed countries (UN data, million. t.) 14 000 12 000 10 000 2005 8 000 6 000 4 000 2 000 2000 1995 1990 0 Picture 2 - Dynamics of carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere Rising fuel prices and a decrease in reserves of fossil fuels will be one of the most important problems for US agriculture. Concerns over the depletion of fossil fuels, coupled with the costs of technological progress have led to the need for biofuels. High energy prices are forcing the United States to use synthetic fertilizers that provokes prolonged decline in the viability of new agricultural lands, which are dependent on huge amounts of fertilizer. In the world arable lands are reduced due to urbanization, conservation needs, unsustainable agricultural production and soil degradation. This will undoubtedly affect the volume of agricultural production, leads to plowing new arable land, poorly adapted for use, and the extinction of species in these areas, especially in developing countries. Picture 3 - The scale and degree of degradation of arable land in the world Increased global trade and travel flows significantly increase the risk of new diseases and causes more rapid spread of diseases in plants, animals and people. The modified agricultural systems, reduction of areas for agricultural production, global warming creates new conditions for the emergence of new agricultural diseases. The treatment of human infectious diseases, including AIDS, malaria, tuberculosis and influenza is one of the major problems of the new century. According to FAO (WHO), as a result of an unprecedented increase in average temperatures in Europe due to global warming, Europe is the rapid spread of 7 "exotic" diseases that were previously typical only for tropical countries of the tropical belt. It is found that the disease is now transferred primarily mosquitoes, which in large quantities penetrate Europe in airplanes, commercial vessels and with a load of goods as well. II. KAZAKH TRENDS AND FACTORS In Kazakhstan the most important are the following factors: The aging population Environmental pollution The increasing demand for food Increasing probability of the emergence of new diseases Problems of water and natural resources The ongoing globalization trend The growth of global climate change, including by increasing the amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere increases. The loss of arable land due to urbanization, conservation needs, unsustainable agricultural production and land degradation Decrease in inventories of fossil fuels, the continuing upward trend in world prices for oil and gas. In addition, the specific Kazakh factors can be selected: Rising incidence of socially significant diseases of humans and animals The growing number of genetic diseases in humans Problems associated with the use of water resources Withdrawal of rotation of arable land due to the influence of anthropogenic factors. In many respects, the major trends existing in the Republic of Kazakhstan, correspond to the world trends, although there is a certain specifics related to the geographical location of the country, geopolitical features, state of the economy and social system. There is a growing population while increasing the proportion of older people in the general age structure of society - according to the Kazakh Statistics Agency, Kazakhstan's population could reach 24 million. Inhabitants over 65 in 2050 will be 9%. At the same time there is an increase in the incidence of cardiovascular, cancer and chronic diseases, which requires improving the health care system and meet the demand of pharmaceuticals. Kazakhstan has rich plant resources that can be a source for drugs of natural origin. In this regard, promising is the development of biotechnology, aimed at generating and manufacturing pharmabioceuticals from natural sources. There is an increase in demand for food and in general the products of agriculture. While the upward trend in imports of food products in the food market of the country will continue until 2015, Kazakhstan, with its vast land resources, has great opportunities for increasing agricultural production and agricultural exports. The development of the domestic sector Agro biotechnology can not only help to reduce food imports and overall agricultural production in the republic, but will dramatically increase the share of agricultural exports, leading to a substantial strengthening of the economy. By virtue of the neighborhood with the countries of disadvantaged epidemic and epizootic situation in Kazakhstan the danger of the penetration and spread of dangerous infectious diseases, that requires not only 8 the improvement of the system of epidemic and epizootic control, but also the creation and production of domestic vaccine, diagnostic and prophylactic drugs to combat infectious diseases of humans and animals. The development of this area of biotechnology is also very promising, both in terms of increasing biosafety of the country and due to the possibility of development of domestic sector pharmabioceuticals and output them to other markets, especially neighboring countries. A significant problem for many regions of Kazakhstan is environmental degradation. This phenomenon is due not only to global climate change and the state of water and air as well, but with significantly increased human activities, including the extraction of minerals and the active use of land in agricultural production. Ecological problems in Kazakhstan are among the most acute and require timely solutions. The development of bio-ecology, including the creation and implementation of biological products for the treatment environment, environment restoration of damaged ecosystems, improve soil fertility, etc. is a very promising trend for the country. Development of alternative sources of energy is one of the leading trends. A significant role in this regard plays a biofuel made from renewable raw materials, including agricultural waste and food industries. The development of biotechnology direction in Kazakhstan will help to reduce dependence on petroleum production, and will help to improve the environmental situation in general. Therefore the most promising directions of biotechnology for the development of Kazakhstan are the following: - Agrobiotechnology - Biomedical - Bioecology - Bioenergy. III. KEY DIRECTIONS FOR DEVELOPMENT OF "BIOTECHNOLOGY" IN KAZAKHSTAN. TRENDS AND FACTORS The main global and Kazakhstan factors, that have a significant influence on the development of biotechnology in Kazakhstan, were classified as follows: Social 1. Population growth, particularly in developing countries 2. Population aging 3. Increasing demand for food 4. The possibility of the development of new and "forgotten" Diseases 5. Increase the incidence of socially significant diseases of humans and animals 6. Increase in the number of genetic diseases in humans 7. Continue to develop the trend of urbanization Political Economic 8. Ongoing globalization trends 9. Growth of income in developing countries 10. Change the world market producers of biotechnology products 11. Increased global trade and tourist flows Environmental 12. Contamination of soil and water as a result of human activities 13. The lack of water resources 14. The amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the 9 Technological atmosphere is increasing - global climate change Process 15. The loss of arable land due to urbanization, conservation needs, unsustainable agricultural production and soil degradation 16. Rising fuel prices and a decrease in reserves of fossil fuels Future directions of "Biotechnology" in Kazakhstan Society Economy Technology •Population growth, particularly in developing countries •The aging population •The increasing demand for food •The possibility of the development of new and "forgotten" diseases •Increased incidence of socially significant diseases of humans and animals •The growing number of genetic diseases in humans •Continue to develop the trend of urbanization • Reduction of arable land due to urbanization, conservation needs, unsustainable agricultural production and soil degradation • Rising fuel prices and a decrease in reserves of fossil fuels Politics Environment • income growth in developing countries • change of the world market producers of biotechnology products • increased global trade and tourist flows • Availability of unique flora - source of natural medicinal compounds • Soil and water pollution as a result of human activities • Lack of water resources • The amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is increasing - global climate change • The ongoing globalization trends Picture 4 - Trends and factors of biotechnology development in Kazakhstan IV. Cross-impact analysis The key factors for the development of biotechnology in Kazakhstan are the following factors: Global climate change; Soil and water pollution as a result of human activities; The increasing demand for food; The aging of the population; The loss of arable agricultural land and soil degradation; Population growth, particularly in developing countries. Below is a ranking of the factors influencing the development of biotechnology in Kazakhstan, according to the degree of uncertainty and importance. 10 Contamination of soil and Population growth, water as a result of human particularly in developing activities countries The amount of carbon dioxide Increasing demand for food and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is increasing - Rising fuel prices and a decrease in reserves of fossil fuels global climate change The loss of arable land due to urbanization, conservation needs, unsustainable agricultural production and soil degradation The possibility of the development of new and "forgotten" Diseases Population aging Increase the incidence of socially Lack of water resources Growth of number of genetic diseases of people Change the world market producers of biotechnology products significant diseases of humans and animals Availability of unique flora - The degree of influence Growth of income in developing countries source of natural medicinal Increased global trade and tourist flows compounds Continue to develop the Ongoing globalization trend of urbanization trends The level of uncertainty Picture 5 - Ranking the factors that will have a decisive impact on the future development of biotechnology The mutual influence of factors on the direction development of "Biotechnology" is shown in Picture 6. On the basis of analysis of world and Kazakhstan trends and factors influencing the development of biotechnology, the following basic requirements of the development of biotechnology in the Republic of Kazakhstan can be determined: AGROBIOTECHNOLOGY: Import substitution of diagnostic products and vaccines for veterinary use; Withdrawal drought- and salt-tolerant crop varieties, based on the techniques of modern biotechnology; Improving Biotechnology deep processing of agricultural products and agricultural waste; The introduction of modern biotechnological methods of water and land resources; BIOMEDICINE: Development and introduction of personalized medicine; Development and introduction of drugs from natural sources; Improved methods of early diagnosis and treatment of socially significant diseases in humans and animals; Development of medical, preventive and diagnostic preparations of new generation on the basis of DNA technology, cellular and nanotechnologies and monoclonal antibodies; Expansion of biotech industries in the field of healthy nutrition 11 Population growth, particularly in Contamination of soil and water as a result of human activities developing countries Population aging Lack of water resources Malnutrition and hunger on a global scale The amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is increasing global climate change The possibility of the development of new and "forgotten" Diseases Increase the incidence of socially significant diseases of humans and animals Increase in the number of genetic diseases in humans Continue to develop the trend of urbanization The loss of arable land due to urbanization, conservation needs, unsustainable Growth of income in developing countries agricultural production and soil degradation Rising fuel prices and a decrease in reserves of fossil fuels Availability of unique flora source of natural medicinal compounds Change the world market producers of biotechnology products Global trade and economic policy Increased global trade and tourist flows Picture 6 - Network sociogram of factor relationship for the future direction of "Biotechnology" Note: The strength of the relationship (line) among all factors (node) is represented by the line type (solid - the most durable connection; interrupted - average interconnection; point - little correlation). BIOECOLOGY: Restore bioremediation method of retiring productive land due to contamination by oil products and other non-natural pollutants; Bioconversion of organic waste on the basis of biotechnological processes. V. ANALYSIS OF EXISTING AND FUTURE MARKETS IN THE WORLD AND IN KAZAKHSTAN IN BIOTECHNOLOGY DIRECTION On the market of biotechnology, at least two segments of the market operate today - lowcost and high-cost biotechnology. The first of these are the markets of developed countries in Western and Eastern Europe and markets in the US, Canada and Japan as well. The second are the markets of the developing world, i.e. Asia, Latin America and Africa. By type of marketed product to the high costs of biotechnology segment of the market are the most expensive, rare and high-end their types. Primarily, these are some subsections of medical and industrial biotechnology, environmental biotechnology, biocatalysis, biogeotechnology, biosafety and bioethics, biotechnical Instrumentation and biocriminology and military biotechnology. For low-cost segment of the biotech market the most primitive, effective and relatively cheap their species (compared to the cost of expensive biotech) should be included. To them, first of all, we can include some subsections of agricultural and food biotechnology, biotechnology in forest products, environmental biotechnology, biogeotechnology of energy and 12 new materials, in some way - Industrial and medical biotechnology, biocatalysis and biogeotechnology (the last two segments - least of all) Today the global market for biotechnology products is estimated at nearly 163 billion dollars. The main market segments are the products for the food industry and agriculture - 45 billion. USD., Pharmaceutical products - 26.8 billion. USD., Enzymes and preparations for the manufacture of detergents - 21 billion dollars, partly pharmaceutical cosmetics made from natural vegetable or animal raw materials, the market volume of which is 40 billion dollars. Table 1 - Market segmentation of biotechnology bln. USD Category Pharmaceutical preparations Biotechnology Bioindustry in total 2011 % 797,7 289,1 20,3 1 107,1 13 72,1 26,1 1,8 100% Production of pharmaceuticals is 72.1% of the total market share. The share of biotechnology, in turn, is 26.1% of the market. The remaining 1.8% of the market apply to the bioindustry. The global market for pharmaceuticals, biotechnology and bioindustry has shown a relatively high level of growth in the period from 2007 to 2011. It is expected that the market will continue to grow with approximately the same performance during the study period until 2016. The total market revenue of global pharmaceuticals, biotechnology and bioindustry in 2011 was a US $ 1 107 billion., The average annual rate (CAGR) is 6.7% between 2007 and 2011. Segment of pharmaceutical production in 2011 is the most profitable of US $ 797.7 billion., I.e. 72.1% of all revenues in the industry. Biotechnology segment in 2011 amounted to US $ 289,1 bln., i.e. 26.1% of the total industry. It is expected that the market for pharmaceuticals, biotechnology and bioindustry accelerates average annual rate (CAGR) of 6.8% for the five-year period from 2011 to 2016, that will lead to a turnover of US $ 1 535,7 billion by end of 2016. Regionally, the main actors of the market of pharmaceuticals, biotechnology & Bio industry are the countries of American continent (44%) and Europe (27.4%). America Europe Asia and the Pacific Rest of the world Source: MARKETLINE Picture 7 - The regional market segmentation of biotechnology US lead in the development of biotechnology, and by a considerable margin from other countries. About 70% of global sales and volume of R & D in biotechnology accounts for the country. United States is the world's largest producer and exporter of Agro-biotech products. Currently sale of seeds of genetically modified plants, such as corn, soybeans, cotton, canola, potatoes, rice and sugar beet is implemented. The US market of pharmaceuticals, biotechnology and bioindustry has around 3 500 companies. The list of the largest companies include: Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Johnson & Johnson and Pfizer. It is worth noting that the market in the US is highly concentrated: the largest 50 companies account for more than 80 percent of income. Among the major pharmaceutical manufacturers, which are located outside the United States can be noted: Bayer (Germany), GlaxoSmithKline (UK), Novartis and Roche Holding (Switzerland) and Sanofi (France). Pfizer Inc. is a leading player in the global pharmaceutical, biotechnology and bioindustry, the company's share is 5.2% of the total market turnover. Johnson & Johnson with a share of 4.5% is on the second place. 14 The rest Source: MARKETLINE Picture 8 - The main actors in the world biotechnology market Companies engaged in biotechnology, occupy a little less than 1/10 of the list of 500 largest companies in the world (45 of 500). The main mass (24 of 45) accounted for the most profitable and most advanced to date trend of biotechnology - Biopharmaceuticals. The vast majority of companies - giants falls into this area (positions 12 - 21 on the list) and is owned by the United States. It should be noted that the list of 45 companies involved in biotechnology, the US owns 29, Japan - 3, Switzerland - 3, France - 3 UK - 2, Germany - 2, Netherlands - 1, Denmark - 1, Israel - 1. Russia's share in world production of biotechnological products is less than 1%, or about 20-25 bln. rubles, of which about 70% comes from the production of pharmaceuticals. Kazakhstan market of biotechnological products is part of the world market. Consumer goods, manufactured from the products of biotechnology are present in Kazakhstan, however, the domestic production base is quite weak and does not allow for large-scale release of competitive products on the world market. Industrial production of biotechnological products in Kazakhstan is presented in the form of production of certain types of test systems, vaccines, biological dairy products, feed additives, crop protection products and alcohol. To date, production of genetically engineered drugs is not virtually established, while there are original domestic developments past or passing phase of preclinical and clinical studies. 15 Kazakhstan's share in the market of biotechnology today is practically zero. Industrial production of biotechnological products in Kazakhstan presented in the form of production of certain types of test systems, vaccines, biological dairy products, feed additives, crop protection products and alcohol. Manufacturers of these products are in the Scientific Research Institute for Biological Safety Problems of Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Kazakh Scientific Center for Quarantine and Zoonotic Diseases named after M.Aykimbaeva of Ministry of Health of Kazakhstan, small biotech companies of Stepnogorsk, LLP"Biocom", Ltd. Research and Production Enterprise "Antigen" and other enterprises. However, it should be noted that the production of biological products in the above organizations do not meet the standards of GMP. So now topical for Kazakhstan is to organize the production of biotechnological products, in accordance with the standards of GMP. Currently, its own production of medicines in Kazakhstan is 11% (including vaccines 1.1%), veterinary drugs 78% (mainly the production of drugs from imported substances), while the remaining products are imported into the country. The country carried out the organization of production of generic drugs and the modernization of existing and new facilities in accordance with international standards GMP as well. Currently, the market share of generic drugs is the main consumer of drugs in Kazakhstan - about 85%, and market innovative drugs - no more than 15%. Analysts expect 2030 global market for pharmaceuticals, biotechnology and bioindustry will grow to more than $ 2 billion and, accordingly, will increase by 65% compared to the latest data from 2011. Average annual growth rate in the period from 2012 to 2030 will be approximately 6.8%. According to analysts, the financial indicators published by the largest players in the pharmaceutical market for Q1-Q3 2012 indicate further growth of the industry as a whole. Growth is noticed on the main markets of pharmaceuticals industry and in emerging markets as well. $ billion of grouth % of grouth Year Picture 9 - Market Forecast: 2012-2016 Expert estimates of biotechnology development forecast in the next 15-20 years, the allow to make following conclusions on the implementation of the investment policy in biotechnology today. Particularly at this stage of the organization of production only highly profitable products, which has developed a stable purchasing power is relevant. Taking this into consideration the priority projects for investment are producing of: - Amylolytic enzyme preparations for the brewing of liquor and food industries, production of proteolytic enzymes used in the production of detergents of «Bio» and other purposes; 16 - Complex processing of microbial biomass to produce products of protein and nucleotide nature for medicine, food industry, etc.; - Enzymatic preparations for recycling food industry, production of meat, milk, alcohol, etc.; - Medical and veterinary drugs, including diagnosis and treatment of a number of heavy and infectious diseases; - Probiotic preparations of bifidumbacterin and laktobakterina type; - Feed additives for livestock, biological plant protection; - Bacterial fertilizers, vermiculture; - Preparations for cleaning and bioremediation of contaminated soils, water, and oilproducing companies for the petroleum sector. In the coming years it is projected to expand significantly the use of biotechnology in important areas of the economy, as the fine chemistry (biocatalysts, organic synthesis products), mining (biogeotechnology, bioremediation of soils), semiconductors (new material), information technology (microelectronic systems, bioinformatics tools , devices based on biological principles biocomputers). The most promising, and due to the economically attractive, collecting a fair amount of investment in the various countries of the world are the biotechnological production of new energy, new materials, ecobiotechnology, biocatalysis, Biogeotechnology, biotechnology instrumentation, biotechnology criminalistics. VI. ANALYSIS OF STRATEGIES OF BIOTECHNOLOGY IN THE WORLD Because biotechnology is used in various industries and affects many spheres of human life, in the world the following "color" classification of biotechnology was adopted: Red biotechnology is biotechnology associated with providing health and potential correction of its genome, and production of biopharmaceuticals (recombinant proteins, enzymes, antibodies) as well; Green biotechnology is aimed at the development and creation of genetically modified (GM) plants resistant to biotic and abiotic stresses, defines modern methods of agriculture and forestry; White Biotechnology is industrial biotechnology that combines the production of biofuels, biotechnology, and food, chemical and petrochemical industry; Grey Biotechnology is related to the environmental management, bioremediation; Blue Biotechnology is associated with the use of marine resources and raw materials. "Red" biotechnology. The total volume of the biopharmaceutical market in 2030 is estimated at 350 billion dollars. The fastest dynamics of the growth in sales is expected for the preparations of monoclonal antibodies, their sales are expected to grow to 37 billion dollars in 2010 to 90 billion dollars in 2015. "White" biotechnology. The modern world market of food ingredients is estimated at 24 billion dollars in 2030, its volume will increase to 48 billion dollars. 17 Chemical Industry Food industry Medicine Agriculture Biotechnology Environment protection Power Industry Picture 10 - Biotechnology in the modern world "Green" biotechnology. The most priority is the production of biological products for the crop, feed additives for farm animals, veterinary biologics and the development of new varieties of useful plants and animals, using modern genetic and biotechnological method as well. The main types of biological products for agriculture are enzymes for feed, biological plant protection and plant growth stimulants, silos ferment and veterinary medicines for livestock as well. "Grey" biotechnology. The most promising methods to protect the environment of the new generation are biological treatment methods. The global market for biological treatment methods of hydrocarbon-contaminated areas by the end of 2012 amounted to about 6.3 billion dollars. The global market leader in terms of biological remediation technology use of biological remediation of oil waste and oil products is the United States. "Blue Biotechnology". The global market of marine biotechnology in 2010 amounted to 3.7 billion US dollars; by 2030 6.8 billion US dollars are projected. (http://regionalliance.com/biotehnologia.html) The patents relate to the unrealized shape of biotech market object. In Picture 33 the share and the growth of international patents in biotechnology in countries-leaders in the field of economy are reflected. Share and growth in the number of international patents in biotechnology in the countries Share Growth: 19952005 Japan USA Germany United Kingdom Canada China South Korea Sigapore India Brazil Picture 11 - Percentage growth in the number of international patents in the field of biotechnology Analysis of the number of patents in different branches of bioindustry in the period from 1982 to 2011 shows that the largest number of patents fall on enzymes (78 940), transgenic plants (4658), transgenic animals (3061), cytokines: interferons and interleukins (1677), and methods for cleaning the environment (1368). The Japanese government announced biotechnology as a "strategic industry" and a 18 national priority. First, major Japanese corporations did not have their own personnel, and the first studies were carried out in collaboration with US universities and companies. Currently, these corporations have acquired the necessary experience and conduct their own molecular biotechnology development, creating genetically engineered foods. Of great importance for the development of biotechnology in Japan is close cooperation between the public and private sector; in the implementation of certain biotechnological programs a number of ministries is involved. Along with the US and Japan, biotechnology is developing rapidly in Western Europe. Consideration of the biotechnology development in the EU has shown that this direction is their strategic priority. Biotech medicines of major US companies and purchased feed for animals and food for humans derived from genetically modified plants were admitted to the EU market. Biotechnology Development Programs financed by the governments of Western European countries, are focused on the implementation of targeted programs or achievement of specific business goals, unlike the United States, where government efforts are directed mainly at supporting basic research and enterprise and private sector organizations are developing with little or no financial support from the state. VII. ANALYSIS OF THE STRATEGY OF BIOTECHNOLOGY IN KAZAKHSTAN In Kazakhstan, the research and development and production of biotechnology products are not well developed. Currently, in the Republic of Kazakhstan 10 research programs in biotechnology, biomedicine, bio-safety and environmental protection are being implemented. About 30 scientific institutions subordinated to the Ministry of Education and Science, the Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Agriculture are engaged in the Research on various aspects of biotechnology in Kazakhstan. The program FIID biotechnology is marked as one of five "sectors of the economy of the future" and the task of increasing the share of biotechnology industry in total exports to 1% by 2015 is set. Currently, a "Concept of development of biotechnology in the Republic of Kazakhstan till 2025"is being developed, the aim of which is the creation of the Republic of Kazakhstan innovative bio-industry, based on the large-scale introduction of modern biotechnology in the key sectors of the economy. As part of a number of scientific and technical programs of scientific organizations of Kazakhstan 30 test systems for the diagnosis of infectious animal diseases were created 25 vaccines were developed. Domestic test systems for diagnosing infectious diseases based on PCR, recombinant antigens, and monoclonal antibodies were developed. Technology of lactic ferments, enzyme preparations, ferments for silage feed, feed additives for farm animals were created. Biologics to protect plants from disease and pest control of crops were developed. Efficient biological products for the purification of oil-contaminated soil and increase crop yields were created. 19 Review of strategic plans of individual line ministries for the period up to 2015 showed that a situation where the domestic market of biotechnological products is already occupied by foreign multinationals, creating a total dependence on imports, it is particularly observed in the pharmaceutical industry. A similar situation is predicted in agriculture, bio-energy, food and processing industries. In the Strategic Plan of the Ministry of Industry and New Technologies of the Republic of Kazakhstan for 2011-2015, approved by the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan from February 8, 2011 № 102 it is stated that the problems in the pharmaceutical industry, mainly related to the "narrow" range of products, non-conformity with international standards of GMP and the imperfection of the legal framework governing the development of the industry. In the Strategic Plan of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan for 20112015, approved by the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan on February 25, 2011 #183 low level of manufacturing base for production of medical immunobiological preparations, particularly diagnostics, test systems, and others is marked. Currently, sectorial programs, indirectly affecting the biotechnology issues are implemented by individual ministries, among them: The program for development of agriculture of the Republic of Kazakhstan for 2013-2020 "Agribusiness - 2020", which aims to create conditions for improving the competitiveness of agribusiness entities of the Republic of Kazakhstan; State Program for Development of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan "Salamatty Kazakhstan" for 2011-2015, approved by the Government of The Republic of Kazakhstan dated August 4, 2010 № 791; The program for the development of the pharmaceutical industry of the Republic of Kazakhstan for 2010-2014, approved by the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated November 29, 2010 № 1113. In 2010, the share of domestic production of pharmaceutical products according to the Kazakh Statistics Agency in terms of value is 13.7% . According to the Customs Control Committee of Ministry of Finance of Kazakhstan for 11 months of 2010, exports of pharmaceutical products amounted to 2.2 billion tenge or 15.4 million US dollars, imports of pharmaceutical products amounted to 118.5 billion tenge or 806,5 million US dollars. A major obstacle to the rapid development of biotechnology in the Republic of Kazakhstan is the lack of a state strategy for the development of biotechnology and bioeconomy, proper coordination and management of this important area of activity at the state level. The work carried out within individual departments, is not enough to force an interdisciplinary and intersectoral nature of the area. This interdisciplinary and, therefore, from a management perspective Interdepartmental - creates certain difficulties in the planning and coordination, and most importantly - leads to an underestimation of the importance of biotechnology. Based on the above, the main problems for the development of biotechnology in Kazakhstan are: - The lack of public policies; - Imperfection of the legislative framework; - Lack of government support measures of bioindustry; - Lack of a clear inter-agency coordination; - The lack of mechanisms to ensure the demand for biotechnology products and its implementation. Thus, the solution of the above problems requires the adoption of comprehensive measures of state regulation of the biotechnology industry, including 20 the improvement of the regulatory framework, the development of inter-state programs, the creation of economic incentives to encourage investment and innovation in the field of biotechnology. VIII. ANALYSIS OF R & D IN BIOTECHNOLOGY, IDENTIFICATION OF WORLD LEADERS Save US world leadership in terms of investment in R & D is accompanied in the first decade of the XXI century by strengthening the scientific and technological strength of competitors, especially China, Japan, South Korea and other countries. The most dramatic jump in R & D financial support to strengthen positions in the sphere of high technologies is marked in China, occupied in 2009 the second place in the world in terms of R & D funding (1.7% of GDP) and the first place in terms of exports of high-tech products. Increasing investment in R & D, including from the budget, continued in the context of the global crisis of 2008-2009, when the United States and other countries have been forced to freeze or cut public funding for a number of budget lines in the fight against an unprecedented budget deficits. In the period of 2007-2010 public expenditure on R & D increased in almost all OECD countries, and many of them have increased not only in absolute terms but also relative to GDP. In the years of crisis in terms of government spending relative to GDP, several countries, including the United States, overcame significant bar of 1%. Thus, by the beginning of the second decade of the XXI century, the United States continued to outpace other countries in terms of total R & D scale financial support, as well as public spending on R & D relative to GDP. However, it should be noted that the share of total expenditure in GDP (2.7%) of the United States is much smaller than countries such as Sweden (3.6%), Korea (3.4%), Japan (3.3%) and Denmark (3.0%). The trend towards the loss of the United States position in terms of total spending on research and development relative to GDP is observed in the last century. In 1996, the United States on this indicator occupied the 5th place, in 2006 - the eighth after Israel, Sweden, Finland, Japan, Korea, Switzerland and Iceland, and in 2009 gave way to Germany, Austria and Denmark. At the same time to stimulate research activity business measures were strengthened by the use of the tax mechanism. In addition to the increase in direct budget financing, the strategic direction of the state policy of the United States and other developed countries in the field of R & D activity is to promote innovative private companies that encourage the development of research centers and educational institutions. Tax and other incentives for R & D are used in many countries around the world. According to the OECD, they are widely used in South Korea, Japan, Canada, as well as in a number of countries, non-OECD countries, such as Brazil, China, Singapore and others. High capital- and knowledge-intensive biotechnology industry defines key factors for sustainable US leadership in the global development of biotechnology: the high volume of industry funding; a large number of specialized educational and research institutions; significant resources of skilled personnel; a long history of entrepreneurship in the country. US biotechnology sector currently includes 2370 of specialized R & D companies and the general thrust of 6213 companies, including 386 public companies with a market capitalization of about 360 billion USA dollars. Revenues of public biotechnology companies in the United States between 1998 and 2007 increased from 20 to 65 billion United States dollars, spending on research and development - from 10 to 26 billion USA dollars. 21 Table expenditures - Key Indicators of funding "dozens" of leading countries in terms of total R & D Countries Total R & D costs, million dollars (2000) PPP * Total R & D spending,% of GDP * Government expenditure on R & D, % of GDP ** United States 311 210,1 2,7 27,7 China 125 747,6 1,7 24,6 Japan 113 151,6 3,3 15,6 Germany 62 372,8 2,8 27,8 Korea 38 272,8 3,4 24,8 France 36 828,4 2,1 38,4 Great Britain 32 308,8 1,9 29,3 Canada 19 564,1 1,9 31,3 Italy 18 710,4 1,3 48,3 Australia 15 390,2 2,2 38,4 * – 2009 ; ** – 2008 Source: OECD estimates based on Research and Development Database, August 2011. Наиболее часто встречаемые объекты исследований, результаты которых публикуются в мировой печати, представлены на рисунке 12: The United States is a leader in research and development in biotechnology. Almost all US universities and large biotech companies develop cutting-edge developments in the field of biotechnology. In recent years, Russia is making great efforts for the development of biotechnology. In 2012 a comprehensive program of development of biotechnology in the Russian Federation for the period up to 2020 was adopted. Indicators of the program are the volume of production of biotechnological products in 2020 800 billion rubles; the share of imports in consumption by 2020 will be 40%; the share of exports in the production of less than 25% and the yield on the level of production of biotechnological products in Russia in the amount of approximately 1% of GDP by 2020 and the creation of conditions for the sector to achieve volumes of at least 3% of GDP by 2030. The most frequent objects of research, the results of which are published in the world press, are shown in Figure 12: Microbial cells of nutrients Gold nanoparticles Tissue engineering The search for new medicines Biofuel Biodiesel Biosensor Escherichia coli Pharmaceutical Research Human Genome Renewable biomass Proteins Analysis of the genome Stem cells Picture 12 - The most frequent objects of research in the field of biotechnology 22 As can be seen from the picture, the most researched subjects are stem cells. Genomic analysis and research in the field of proteins are the most common phrases field. Production of biomass, biofuels also has a significant biotechnology research. The following picture (13) shows the distribution of biotechnology research within countries. Picture 13 - The activity of the countries in biotechnological research As can be seen from these drawings, the US, UK and Germany are the countries most involved in research in the field of biotechnology in the world. IX. ANALYSIS OF COMPETENCE OF R & D IN KAZAKHSTAN In Kazakhstan, the volume of development and production of biotechnology products is not well developed. The country has almost no biotechnological production of pharmaceutical substances, ingredients for the food industry, raw materials for the chemical industry, biofuels. There is poor use of modern biotechnology in agriculture, mining, energy. Industrial production of biotechnological products in Kazakhstan is presented in the form of production of certain types of test systems, vaccines, biological products dairy, feed additives, crop protection products and alcohol. To date, production of genetically engineered drugs is not virtually established, while there are past or passing phases of preclinical and clinical studies, original domestic developments (recombinant erythropoietin). Kazakhstan imports most sought-after drugs and biopharmaceuticals. The market of biological products is increasing every year, for example, in 2016 the projected demand for antituberculous drugs in Kazakhstan will be at 1 948 million tenge, and insulin - 1 423 million tenge. Vaccine market in Kazakhstan is relatively capacious, such as annual vaccination against hepatitis B covers 3.7 million people. The scientific organizations of Kazakhstan created a collection of cultures of microorganisms, which is bio resource base for the production of microbiological preparations and biologically active substances, was created by the scientific organizations of Kazakhstan. A number of vaccines and diagnostic test systems for veterinary was created. The technologies of lactic ferments, enzymes, starter cultures for silage fodder and fodder additives, biological products to improve crop 23 yields and protect plants from disease, biologics for the treatment of oil-contaminated soil were developed. In Kazakhstan in the period from 2006 to 2012 the dynamic growth of the number of research programs in the field of biotechnology, financed from the state budget totaling more than $ 3.5 billion tenge was marked. In 2009-2011 5 research programs with total funding over three years to 3.2 billion tenge were implemented. Currently, the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan is the coordinator of 9 research programs in biology and biotechnology for 2012-2014, approved by the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated March 12, 2012 # 318: 1) Bioremediation of disturbed ecosystems during oil production in Kyzylorda region; 2) The use of biotechnological methods of reproduction of fertility of saline soils in the Aral Sea region; 3) Development of technology and organization of pilot production of microbial preparations for agriculture and the environment; 4) Brucellosis in cattle: monitoring the epidemiological situation, the development of diagnostics and prevention; 5) Epizootological monitoring the circulation of infectious diseases in the saiga population inhabiting the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan, and the development of prevention methods; 6) Creation of genetic passport for certain groups of the population of Kazakhstan, based on the use of DNA technology; 7) Create, save, keeping and use of microbial resources in the Republic of Kazakhstan; 8) Establishment of Biotechnology drugs, dietary supplements and specific foods and other materials on the basis of cultural, introduced and wild species of flora of Kazakhstan; 9) Development of domestic genome-proteome and cell technologies for medicine, agriculture and environmental protection in Kazakhstan. Table - Scientific and technical programs in biotechnology of 2009-2011 №№ 1. 2. Name of programs Total funding volume (thousand tenge) The development and use of genetic engineering and cell technologies in medicine, 1 602 600,0 agriculture, environmental protection, food and processing industries for 2009-2011 Scientific and technical support of state regulation of turnover GM facilities in the Republic of Kazakhstan for 2009-2011 853 000,0 3. Updating, studying and maintaining collections of plants, animals, microorganisms and unique genetic banks for the conservation of biodiversity of Kazakhstan » 2009-2011 224 625,0 4. Environmental assessment and bioremediation of disrupted ecosystems in oil areas 2009-2011 268 496,0 5. "Development and implementation in selective practice the molecular breeding genetic and bioengineering methods for rapid creation of new high-yielding crop varieties to further strengthen the country's food security” for 2009-2011 333 326,0 24 The fourth chromosome Biosensor bacteria Cellulolytic Res earch The strains of Bacillus Thurigiensis The nuclear genome Biomass Proteins Picture 14 - The most commonly used objects of Kazakhstan biotechnology researchers, published abroad EurAsEC interstate target program "Innovative Biotechnology" in 2012-2014 is in progress, in which 26 research projects are implemented. Review of strategic plans of individual line ministries for the period up to 2015 has shown that today there is a situation when the domestic market of biotechnological products is already occupied by foreign multinationals, creating a total dependence on imports, it is particularly observed in the pharmaceutical industry. A similar scenario is predicted in agriculture, bio-energy, forestry and the food industry. In Kazakhstan, there is a number of promising developments in biotechnology. Biomedicine. Recombinant human erythropoietin in tablet form used inside, is currently under II Phase of clinical research. Molecular genetic tests for drug-resistant of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Genetic tests for the diagnosis and prognosis of breast cancer, colorectal cancer, stomach cancer. Diagnostic tests for determining the individual doses of drugs that reduce the risk of thrombosis. PCR test for the quantitative determination of hepatitis B and C, polyoma, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus; The cell counter drug burn "Fibrosprey" for treatment of burns. Agricultural biotechnology. New high-yielding varieties of spring wheat Severyanka, Alem, Steppnaya-15/, Shygys, Golden, Ak-Orda, Kazakhstan-20, resistant to drought and diseases. New varieties of rice "Bakanassky" and "Madina" zoned in Almaty and Kyzylorda regions. New high-yielding potato variety "Capital", resistant to fusarium. Insecticidal biologics "Bioturin" and "Bitoksiturin" for the control of insect pests of agricultural and forest crops. Vaccines against 25 infectious diseases of animals. 30 diagnostic test systems for veterinary medicine. Leaven ‘Lac Forces' silage feed 25 Food Biotechnology. Lactic starter for yoghurt-based consortium of cultures Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus lgaricus Sour cream yeast culture based on Lactococcus cremoris. Environmental biotechnology. Biologicals Ekobak, Bakoyl and Terraklin, past production testing on the territory of oil fields in the purification of oil-contaminated soils. Biogeotechnology. A consortium of microorganisms for heap leaching of gold from refractory ores that are resistant to higher content of toxic substances (copper, arsenic), technology allows the year round heap leaching under harsh continental climate, increases gold recovery by 40-50%, compared with traditional technologies, reduces sulfuric acid consumption by 20-30%; A consortium of microorganisms for in-situ leaching of uranium, the technology eliminates the need for expensive chemical oxidants and intensifies uranium mining by 30-40%, compared with the standard technology weak acid leaching. About 30 organizations subordinate to the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Agriculture, are currently engaged in research on various aspects of biotechnology in Kazakhstan. 10 research programs in biotechnology, biomedicine, bio-safety and environmental protection are Implemented. In this sector more than 2.8 thousand people are employed. Training in the country on a specialty "Biotechnology" is performed in 19 high schools. Thus, in Kazakhstan, certain aspects of fundamental and industrial biotechnology are being developed through a number of programs and research projects financed from the national budget. However, the measures implemented is not enough, it is necessary to develop a publicprivate partnership for the implementation of promising biotechnology projects. It is necessary to make decisions on a wide range of issues in a very short time. An active state policy in the field of biotechnology will solve the following problems: providing high quality medical care to the population and reducing dependence on imports of essential medicines; providing the population with quality food products of domestic production; the successful solution of environmental problems and the development of alternative energy from renewable resources; significant progress throughout the economy on an innovative way of development; the rise of economically depressed regions, including through the emergence of biotechnology clusters. X. Strategy for Actions on the scenario It should be stated that the Republic of Kazakhstan is far behind the leading countries in the scale of the development of biotechnology, especially in the development of proper industrial biotechnology. The contribution of Kazakhstan into the world of biotechnology today is a few hundredths of a percent. The country has almost no biotechnological production of pharmaceutical substances, ingredients for the food industry, raw materials for the chemical industry, biofuels. Virtually there is no use of modern biotechnology in agriculture, mining, energy. In addition, in Kazakhstan biotechnology has not been identified as an industry. There are no FEA and NACE codes, which would be related to biotechnology. 26 A major obstacle to the rapid development of biotechnology in the Republic of Kazakhstan is the lack of a state strategy for the development of biotechnology and bioeconomy, proper coordination and management of this important area of activity at the state level. The work carried out within individual departments, is not enough to force an interdisciplinary and inter-sectoral nature of most of the region. The main problem is that biotechnology is cross-sectoral discipline. This interdisciplinary and therefore from a management perspective - Interdepartmental - creates certain difficulties in the planning and coordination, and most importantly - leads to an underestimation of the importance of biotechnology by specialists and officials, both at the time it was with the progressive computerization and other integrated disciplines. Based on the above, the main problems for the development of biotechnology in Kazakhstan are: The lack of public policies; The imperfection of the legislative framework; Lack of clear inter-agency coordination. The solution of the above problems requires the adoption of comprehensive measures of state regulation of the biotechnology industry, including the improvement of the regulatory framework, the development of inter-state programs, the creation of economic incentives to encourage investment and innovation in the field of biotechnology. Below is a SWOT state analysis of biotechnology in the Republic of Kazakhstan indicating weighty relations of mutual influence at the moment. SWSWOT-analysis of biotechnology development in Kazakhstan and the assessment of its elements STRENGTHS WEAKNESSES 1. Willingness to modernize the sector and voiced public support (4); 2. The main priority areas of biotechnology in the country are identified (3); 3. Intellectual and material basis for the development of modern biotechnology is developing (3); 4. The entry of the industry in the State program of forced industrial-innovative development of Kazakhstan (4); 5. The presence of the National Center for Biotechnology Research Institute and several research groups specializing in research in the preparation of biological products, cellular, molecular and genetic engineering (4); 6. The presence of a large corporate business commodity - potential investors (2); 7. International cooperation with countries with developed biotechnology industry is established (4); 8. There are domestic world class biotechnology developments (3). 9. The presence and the possibility of a new qualified specialists in the field of cell and genetic engineering (4) 10. Involvement of leading scientists from foreign countries to train masters and doctors of philosophy in specialty "Biotechnology" (3) 11. The allocation of public grants under the program "Bolashak" training for Biotechnology (MS and Ph.D.) and training specialists in modern methods of biotechnology (3) 27 1. Lack of qualified training in the field of biotechnology (4); 2. obsolete material and technical basis of scientific organizations (4); 3. Insufficient use of research and production of modern biotechnological methods of cell and genetic engineering (3); 4. The prevalence of public procurement in the acquisition of foreign products to the detriment of the original mass generics (3); 5. Inadequate funding of R & D (4); 6. Lack of a creative relationship with well-known research centers in foreign countries (2); 7. Departmental fragmentation of research in the field of biotechnology (4) 8. Lack of interest from enterprises, government mechanisms of tax, tariff and fiscal incentives for companies developing and implementing in domestic production of scientific developments in the field of biotechnology (5) 9. The low proportion of specialists of scientific and industrial organizations-trained and advanced training in the leading scientific centers of foreign countries (3) 10. Weak competitiveness of Kazakhstan's biotech products and their low range of the global market, low export potential of the bio enterprises of Kazakhstan due to non-compliance with international GMP standard (4); 11. Underdeveloped state 12. Availability of completed domestic biotechnological developments in the field of medicine, veterinary medicine, agriculture and the environment, corresponding to world standards (4) 13. Implementation of research programs in the field of biotechnology, financed from the state budget, including international participation (4) 14. Availability of all the necessary prerequisites and capacities (availability of energy resources and biological resources, fresh water, the beginning of the development of scientific schools, training of qualified personnel, etc.) to become one of the world leaders in some areas of biotechnology (4); 15. The political stability of Kazakhstan and the favorable geographic location (4); 16. Accelerating the pace of development of the national economy, increasing investment attractiveness of the Republic of Kazakhstan at the international level (4); 17. Availability of investment sites for the implementation of innovative projects (2) POSSIBILITIES 1. The ability to produce generic drugs for the expiration of the patent, the production of innovative drugs based on the technology transfer (4); 2. Purchase of (transfer) technology (3); 3. The increase in world demand for biotechnology products, steady growth in the global market demand for eco-friendly food products (4); 4. A decision by means of biotechnological issues such as the development of depressed areas, employment of the use of renewable raw materials and others. (4); 5. Attracting foreign investment (3); 6. The development of venture capital funds in Kazakhstan (3); 7. The interest of foreign investors in establishing enterprises on deep processing of agricultural products in the Republic of Kazakhstan (3) 8. Use in the world of cellular technologies and genetic engineering methods in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of human and animal diseases (4) 9. The possibility of increasing crop yields through the inclusion in the selection process of new forms of plants with high quality products, resistant to pests and diseases (4) 10. Production of innovative products based on technology transfer (3) strategy of biotechnology and bioeconomy (5) 12. Biotechnology is not selected as an independent branch (3) 14. The difficulty of access to credit oriented biotech companies (4) 15. Dependence on imported raw materials and packaging materials (3) THREATs 1. Dominant position SУГРОЗ of biotech companies in the EU, India, Turkey on the of Kazakhstan Ы Republic TH market (5); 2. The low population density (3). 3. Dependence on imported biotechnology products (5); 4. The increase in imports of biotech products (4); 5. The rapid development of the biotechnology industry in India and China (5); 6. Loss of intellectual property for the benefit of other countries (4); 7. Continued global trend to limit the consumption of GMOs (4); 8. The threat of loss of export niches in the environmentally friendly products (4); 9. The threat of drain of highly qualified specialists in the field of biotechnology (4); 10. The stagnation of the development of biotechnology in Kazakhstan without removing it in a separate branch (5) Based on the competencies of Kazakhstan for the period up to 2030, independent development of scientific programs is possible for directions "Agrobiotechnology", "Development and introduction of drugs from natural sources", "The development of new medicines, preventive and diagnostic preparations of new generation on the basis of DNA technology, cellular and nanotechnologies and monoclonal antibodies," "Bio-ecology". Joint research with the world's leading research centers is desirable to carry out in the directions "Bioenergy", "The expansion of biotech industries in the field of healthy nutrition." Technology transfer (purchase) of advanced technologies and their adaptation with respect to the Republic of Kazakhstan will be preferred for development and implementation of methods for personalized medicine. 28 A possible mechanism for the development High Development of methods for the implementation of personalized medicine Bioenergy Mostly self-development The expansion of biotech industries in the area of healthy eating Medium The strategic significance Low Conducting joint research in Agricultural biotechnology collaboration with leading centers of the world Development and implementation of drugs from natural sources Transfer of technology Development and implementation of new drugs, preventive and diagnostic drugs of the new generation of DNA-based technologies, nanotechnology and cell monoclonal antibodies and knowledge Bioecology In the short term In the medium term In the long term Picture 15 - Matrix of priority directions of innovation and technological development in the field of biotechnology Opportunities for Kazakhstan on the further development of biotechnology: • Treatment for most known diseases • A new paradigm in agriculture; providing a complete solution to the problems of food and drinking water • Decision of the existing environmental problems • A new stage of spiritual development of mankind . The solution with the implementation of water saving technologies. In terms of the above: • Biotechnology will improve the ecological situation of the environment and efficient use of renewable resources, industrial raw materials. • Industrial biotechnology will help to develop the various branches of production in an economically and environmentally sustainable manner. • The energy derived from biomass, would fill the shortage of electricity, especially in the agricultural sector. • Industry will be innovative and competitive in the sustainable cooperation between the scientific community and the industrial area. • Green biotechnology will contribute significantly to the efficient production of biomass feedstocks. • The development of the biopharmaceutical sector will ensure domestic demand in vital medicines. • Large-scale use of genetic tests will ensure the development of personalized medicine. • Cell and tissue engineering technologies will be used in regenerative medicine and transplantation. 29 • Recombinant proteins, monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, and diagnostic tools will provide a new generation of problem-solving early diagnosis and treatment of many infectious and cancer, including social diseases. Based on the conducted analysis a long list of key products and services in the biotechnology sector in Kazakhstan until 2030 was compiled. Agrobiotechnology Product (service) Technologies Improved animal breeds that have increased productivity and resistance to adverse environmental factors Cell engineering technologies to create commercially valuable species of animals that have increased productivity and resistance to adverse environmental factors Recombinant DNA technology to create a commercially valuable species of animals, with increased productivity and resistance to adverse environmental factors Technology of animal cloning Improved plant varieties that have increased productivity and resistance to adverse environmental factors Cell engineering technologies to create economically valuable plant varieties with increased productivity and resistance to adverse environmental factors Recombinant DNA technology to create economically valuable plant varieties with increased productivity and resistance to adverse environmental factors Technology of micropropagation plants Insecticidal biologics for the control of insect pests Technology of isolation and cultivation of entomopathogenic microorganisms Technology of design entomopathogenic preparations Microbial and enzyme preparations for use in agriculture, Technology for production of microbial and enzyme food and light industry preparations Cleaning technology of microbial and enzyme preparations Technology of preservation of microbial and enzyme preparations Technology of biocatalysis Supplements to improve the structure of the diet of farm Technology of cultivation of unicellular organisms animals, birds and fish producers of protein and amino acids Biotechnology of edible protein from unicellular production Biotechnologyof production of amino acids from singlecelled Modern vaccines for the prevention of the most common, Technology of screening and selection of microorganism particularly dangerous and exotic diseases in humans and strains animals Technology of modification of the genome of microorganisms Technology of creation of a whole-cell and whole virus vaccines Technologies of creation of subunit vaccines Modern test systems for rapid diagnosis of the most common, particularly dangerous and exotic diseases in humans and animals Technologies for producing highly purified antigens Technologies for producing high affinity antibody preparations Technology of diagnostic biochips 30 Genetically engineered diagnostic technology Technologies of creation of associations of probiotic microorganisms for food processing New systems for food products of high nutritive value Technologies of creation of functionally active food and functional probiotic food supplements Fermentation technology of food raw material of low value Biomedicine Product (service) Technologies Autologous and artificial organs and tissues that are based Technology of Cell and tissue engineering for use in on cell and tissue engineering regenerative medicine and transplantation Highly effective treatment of socially significant diseases (diabetes, myocardial infarction, cancer and others.) Technology of selection of stromal stem cells Technologies of creation and accumulation of cytokines Technologies for producing anticancer antibodies Effective medicines from natural sources Biotechnology of obtaining drugs from natural raw materials Antagonists drugs, preventive and diagnostic preparations Technologies of genetic engineering vaccines of new generation Monoclonal Antibody Technology Technology of immunoassay and immunochemical analysis Technology of immunoglobulin therapeutic drugs DNA microchip diagnostics technology Genetic passports for certain groups of the population of Kazakhstan with a view to defining the role and the importance of genetic factors in predisposition to the development and multifactorial hereditary diseases. Genetic diagnosis and multifactorial hereditary diseases; Technology of genetic mapping Technology of genetic sequencing Technology of multifactorial and genetic diagnosis of hereditary diseases Bioecology Product (service) The strains of microorganisms for remiditatsii environmental objects and restore soil fertility Technologies Biotechnological methods of rehabilitation of the environment, restoration of soil fertility Bioenergetics Product (service) Biofuels Microbial fuel cells Technologies Technologies for energy production from renewable bioengineered sources For the scenario of the development of biotechnology it is expected to involve the following participants: 1) Creating innovative and educational consortium "Biotechnology" 2) Public Association "Kazakh Society of Biotechnology" as a dialogue platform. 31 Biotechnology creating breeds that have increased productivity and resistance to adverse environmental factors Genetic diagnosis and multifactorial hereditary diseases Antagonists drugs, preventive and diagnostic Technologies for producing food products of high preparations of new generation nutritive value and functional probiotic food Insecticidal biologics for the control of insect pests Supplements to improve the structure of Effective medicines from natural sources the diet of farm animals, birds and fish Genetic passports for certain groups of the population of Kazakhstan with a view to defining the role and the importance of genetic factors in predisposition to the development and multifactorial hereditary Biofuels diseases. The strains of microorganisms for the rehabilitation of the Modern vaccines for the prevention of the most environment and restoration of soil common, particularly dangerous and exotic fertility Autologous and artificial organs and diseases in humans and animals tissues that are based on cell and tissue Highly effective treatment of socially significant diseases engineering Modern test systems for rapid diagnosis of (diabetes, myocardial infarction, cancer and others.) the most common, particularly dangerous and exotic diseases in humans and animals Picture 16 - The image of the future of biotechnology in Kazakhstan 3) Scientific institutions, universities - National Center for Biotechnology Research Institute for Biological Safety Problems, Microbiology and Virology, Plant Biology and Biotechnology, animalogii problems, problems of Biology and Biotechnology, Molecular Biology and Biochemistry of M.A. Aitkhozhin, General Genetics and Cytology, Experimental Biology of F. Muhamedgalieva, Kazakh Research Institute of processing of agricultural products, RSE (Republican State Enterprise) "Republican Collection of Microorganisms", universities Kazakh National University. Al-Farabi, ENU of L.N. Gumilev, KazNAU, KazATU of S.Seifullin, Nazarbayev University, the Medical University of Astana, Karaganda State Medical University, Semey State University named by Shakarim, Innovative University of Eurasia, other research organizations and universities; 4) The representatives of the competent authorities (Ministry of Agriculture, Ministry of Industry and New Technology of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan Ministry of Health, Ministry of Environmental Protection and others.); 5) State-owned companies (JSC "KazAgroInnovation", JSC "KazMunaiGas", JSC "Kazatomprom" and etc.); 6) Development Institutes (JSC "Samruk-Kazyna" Development Bank of Kazakhstan, JSC "Investment Fund of Kazakhstan", JSC "National Agency for Technological Development" JSC "Small Entrepreneurship Development Fund", National Center for Investment Promotion "Kazinvest" Parasat JSC and others.). 7) Business structures (small, medium-sized biotech enterprises, National Union of Entrepreneurs "Atameken", Association of Business Women of Kazakhstan, etc.). 32 XI. "WILD CARDS" AND "WEAK SIGNALS" OF BIOTECHNOLOGY The main characteristics of the wild cards are low probability (or high uncertainty if the probability score cannot be obtained) and high impact. Nevertheless, the effects of the wild-card should not be sharp over time. This means that the time of exposure (and breaking effect) can be either long or short. "Wild cards" in the field of biotechnology include: Prevention of aging Revolutionary results in biotechnology prevent mental and physical aging. The impact on human society are enormous, individually and structurally, for example, people are faced with the idea of the possibility of living forever, moreover, prolongation of life brings the transformation of social systems. Regenerative medicine: from the artificial skin to patches for the heart First of all it is worth noting the establishment of various substituents skin sheets, which are used in the clinic for the treatment of burns and chronic skin lesions. Advances in this area will allow to use skin grafts containing genetically modified cells. This will eliminate genetic defects, to improve their engraftment and even set up a system for the synthesis of hormones necessary for the body. Medicines from natural sources Although more than 50 thousand secondary metabolites have been already characterized, this represents only about ten percent of the biosynthetic capacity of plants. And except plants biologically active substances are synthesized and accumulated in the bacteria, fungi, marine organisms, insects and even amphibians. Modern drug discovery programs include simultaneous automated testing for the presence of a plurality of extracts variety of biological activities. Antibodies deliver the drug directly into the tumor Delivery of medication directly into the tumor allows for enhanced drug effect and minimize unwanted side effects on other tissues and organs. Treatment of genetic diseases Various media are used to deliver genetic material inside human cells and its integration into the genome, for example, artificial liposome nanoparticles or cationic emulsion. For cancer treatment vector systems based on the elements of the viral genome, allowing the murderer to enter gene directly into the tumor, which is a result of the very beginning to produce cytotoxic proteins, were developed. Decoding the genome in one day Advances in the understanding of how genes and their encoded proteins are responsible of the disease will help to pick up a set of medicines, are much more effective to cope with a specific ailment, rather than individual drugs Treatment of severe disease - an attack on multiple targets The strategy of the modern treatment of the most severe diseases include simultaneous exposure to multiple targets - molecular stages of the pathological process. Advances in the understanding of how genes and their encoded proteins are responsible for the disease will help to pick up a set of medicines are much more effective to cope with a specific ailment, rather than individual drugs. A stem cell - a doctor within the patient Scientists predict the broadest perspective to his method: patient with infarction or fracture admits to the hospital, receives medication stimulating his 33 stem cells, after which they themselves "repair" damaged organs. The synthesis of genes for pharmaceutical industry Many biotech companies provide services of automatically synthesis of gene sequences encoding pharmaceutical proteins, adapted for the biotechnological expression systems. The average cost of synthesis is about 0.4 dollars per couple. Proper medication - for each patient Patients, according to their genetic and epigenetic (not determined by genes) features will be grouped so that the physician could predict the characteristics of the disease and to apply the appropriate treatment with minimal risk and side effects. Proteomics - key to diagnosis An important aspect is the development of complex panels of biomarkers allowing with more certainty to detect the presence of disease. Besides malignancies, biomarkers for cardiovascular, pulmonary, gastrointestinal and many other diseases are actively studied. "Weak signals" of Biotechnology are imprecise and early signs of the important developments in the external and internal factors. Weak signals tend to become stronger over time and become strong. "Weak signals" of biotechnology include: Preparation of human organs grown in pigs; Universal flu vaccine; Viral therapy of several types of cancer; Microrobots able to clear plaque in the vessels; Biological artificial heart; Transplant a human brain into a new body, grown synthetically; Creation of biological civilization, where all the main commodities grown; Creation of crops that can fix atmospheric nitrogen without the participation of microorganisms. XII. RISKS AND THREATS TO THE SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF SCENARIO Biotechnology, as it is known, has a pronounced interdisciplinary character. In this regard, the pessimistic developments in the future may be in the case if the funding of Kazakhstan science until 2015 will remain below 1% of GDP. Currently, the figure is 0.26%. Departmental fragmentation of research in the field of biotechnology could also have a negative role in the scenario. Scientific and technological risks: • The emergence of fundamentally new diseases • A new class of environmental problems • Bioterrorism and eco-terrorism • Black markets of Technologies and Bioresources • Conflicts between the subjects of biotech development and nation-states . The acute problem of drinking, irrigation and industrial water 34 Socio-economic risks: Absence Risks (lack of) funding of scientific research and business projects in the field of biotechnology. The scenario provides funding for business projects in the field of biotechnology through budgetary and extra-budgetary funds. Insufficient revenue budget base and the bad conditions of the capital market, which cannot be predicted with great accuracy, can lead to underfunding of business projects. In this case, the actual results of the scenario will be worse than expected results. Reduction of the absence risks (lack) of funding should be through the implementation of the scheme of public-private partnerships for major projects. Risks of the regulatory framework and infrastructure. The risk is associated with the lack of study of the regulatory framework in biotechnology and the lack of built system of cooperation between science and business that may impede the achievement of the planned results. Risks associated with inefficient management the scenario. The risks are caused by the following probabilities of events: the inefficient use of resources, disruption of the timing of activities, a manifestation of unaccounted factors in the implementation phase of the scenario. To reduce these risks will allow increased monitoring of the implementation of the planned measures, the improvement of the mechanism of managing the implementation of the scenario and, in the case of identifying factors that can adversely affect the course of the scenario, timely adjustment of the planned activities. The risks of a negative attitude to the scenario on the part of governments, the public and the media. To reduce these risks will allow carrying out clarification of the basic concepts, goals and ideas of the activities, the structure of expenditure in order to achieve public understanding and acceptance of the measures proposed. Planned work in this direction should be conducted with the involvement of the scientific environment and direct participants in the scenario. Risks of poor quality of the competition to participate in the Scenario and examination of the results of the competition. To reduce the risks will enable the control of compliance stated policy to the real situation in competitions and examinations, as well as the establishment of a monitoring system involving other non-governmental organizations and the public. An additional way to reduce risks should be maximum coverage and transparency of decision-making process regarding the inclusion in the scenario of various participants. In general, for the development of biotechnology in Kazakhstan a bright future is opened, but to reach it, it is necessary to overcome serious obstacles. 1. In the area of investment. In recent decades, there is a gradual stabilization of the state support of basic biotechnology research on the background of a lack of funding from the private sector. The reasons hindering private investment, are well known, and the main reason is a major uncertainty. The most important sources of uncertainty of investors are irrational public policy and public distrust. The main purpose of the private sector is a new product market launch and maximizing the firm's profits. It is necessary to create a State-level incentive mechanisms, including financial and tax to attract private capital to the biotechnology industry research and production. 35 2. In the field of public policy. The EU is pursuing a policy that hinders the development of biotechnology and barriers to trade in food products, produced with the use of Agri. The current European system of regulation severely restricts the use of GM plants seeds of crops that affect the interests of European companies in the global market of agricultural chemistry. 3. In the field of public perception. Despite the favorable prospects, with the introduction of new transgenic products, biotechnology companies will continue to face challenges. It is necessary to change the current atmosphere of distrust, even opposition from consumers through public advocacy. One of the main risks of biotechnology development for Kazakhstan is the competition from the countries of Central and South-East Asia and the countries of the Customs Union against the backdrop of the backlog from the world level in the field of biotechnology. Bioindustry in the world is developing rapidly, and in 10-15 years solutions and products suitable for mass and widespread implementation will be found. If by this time in Kazakhstan conditions for the development of the bioeconomy will be created, the country will be among the beneficiaries and owners of new technologies. If the existing skepticism persists today, Kazakhstan will be only consumer in the global technology market and will be forced to expend enormous resources on the import of new industries. The scale of this technology imports can be comparable with the import of industrial technologies in the 30s of the last century. Lingering in the development and implementation of biotechnology for a variety of industries and markets, Kazakhstan industry risks being below the modern technological structure that develops in the world the past 15-20 years. In the medium term this could lead to systemic degradation of a number of industrial sectors, as nor development in the world markets nor reproduction of a competitive manufacturing base would be possible without the use of biotechnology. 36