Literary Terms
advertisement

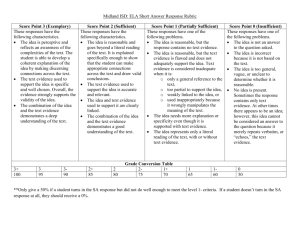
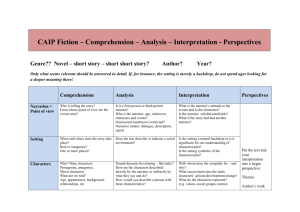
Literary Terms 1. Allegory-a story, poem, or picture that can be interpreted to reveal a hidden meaning, typically a moral or political one. (Two meanings Literal /symbolic). 2. Alliteration-a stylistic device in which a number of words, having the same first consonant sound, occur close together in a series. But a better butter makes a batter better. 3. Allusion-an expression designed to call something to mind without mentioning it explicitly; an indirect or passing reference "an allusion to Shakespeare" 4. Analogy- a comparison between two things, typically on the basis of their structure and for the purpose of explanation or clarification. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Antagonist- a person who actively opposes or is hostile to someone or something; an adversary. Aphorism- a pithy observation that contains a general truth, such as, “if it ain't broke, don't fix it.” Conflict-serious disagreement or argument, typically a protracted one. Connotation-an idea or feeling that a word invokes in addition to its literal or primary meaning Denotation-the literal or primary meaning of a word, in contrast to the feelings or ideas that the word suggests. 10.Diction- the accent, inflection, intonation, and speech-sound quality manifested by an individual speaker, usually judged in terms of prevailing standards of acceptability; enunciation. 11.Euphemism- The term euphemism refers to polite, indirect expressions which replace words and phrases considered harsh and impolite or which suggest something unpleasant. 12.Foreshadowing- be a warning or indication of (a future event). 13.Genre- a specific type of music, film, or writing. Your favorite literary genre might be science fiction, and your favorite film genre might be horror flicks about cheerleaders. 14.Hyperbole-exaggerated statements or claims not meant to be taken literally. 15.Imagery-visually descriptive or figurative language, especially in a literary work. 16.Irony-opposite of what you expect Verbal-saying the opposite of what you mean Situational-twist at the end of the story Dramatic-audience knows what is going to happen 17.Metaphor- direct comparison between two things 18.Mood- the atmosphere or pervading tone of something, especially a work of art. 19.Oxymoron-a figure of speech in which apparently contradictory terms appear in conjunction Ex. Jumbo Shrimp 20.Personification- inanimate objects are given human characteristics 21.Point of View-) the narrator's position in relation to the story being told. 1st person- I/We-seen through main characters eyes 3rd person- The third person point of view is a form of storytelling in which a narrator relates all action in third person, using third person pronouns such as "he" or "she." Omniscient- All knowing-narrator knows characters in entirety Unreliable-is a narrator who can't be trusted. Either from ignorance or self-interest, this narrator speaks with a bias, makes mistakes, or even lies. 22.Prose- All writing other than poetry 23.Protagonist- the main character 24.Rhetorical Question- a figure of speech in the form of a question that is asked in order to make a point rather than to elicit an answer. 25.Satire- the use of humor, irony, exaggeration, or ridicule to expose and criticize people's stupidity or vices, particularly in the context of contemporary politics and other topical issues. 26.Simile- Comparison using “like or as” 27.Symbolism- he use of symbols to signify ideas and qualities by giving them symbolic meanings that are different from their literal sense. 28.Theme- Central message or moral of the story 29.Thesis- Claim. Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. 30.Tone- the general character or attitude of a place, piece of writing, situation, etc. 31.Static character- stays the same throughout the story 32.Dynamic character- changes and grows throughout the story 33.Round character- a character in fiction whose personality, background, motives, and other features are fully delineated by the author. 34.Flat character- are two-dimensional in that they are relatively uncomplicated and do not change throughout the course of a work. 35.Direct characterization-the process by which the personality of a fictitious character is revealed by the use of descriptive adjectives, phrases, or epithets. 36.Indirect Characterization-the process by which the personality of a fictitious character is revealed through the character's speech, actions, appearance, etc.