SCIENCE 3RD TRIM EXAM TOPIC: WEATHERING & EROSION I
advertisement

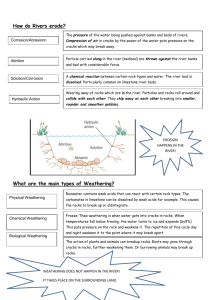
SCIENCE 3RD TRIM EXAM TOPIC: WEATHERING & EROSION I. Encircle the letter of the correct answer. 1. Refers to the process of breaking rocks into smaller pieces a) Erosion b) Weathering c) Breaking 2. It is the wearing away of land by forces such as water, wind and ice. a) Erosion b) Weathering c) Breaking 3. A type of weathering caused by water, temperature (heating & cooling), roots of trees, burrowing animals. a) Chemical Weathering b) Physical Weathering 4. . A type of weathering caused by changing the rock’s chemical composition. a) Chemical Weathering b) Physical Weathering 5. These rocks starts as either igneous or sedimentary then change due to high temperature & pressure changes, are used to build things like roofs, buildings, blackboards. a) Igneous Rocks b) Sedimentary Rocks c) Metamorphic Rocks 6. These rocks came from very hot & melted magma below the earth’s crust. a) Igneous Rocks b) Sedimentary Rocks c) Metamorphic Rocks 7. These rocks are formed when igneous rocks weather & becomes really small particles called sediments. These can be used to help build sidewalks, buildings. a) Igneous Rocks b) Sedimentary Rocks c) Metamorphic Rocks 8. The type of igneous rocks that is formed when magma buried deeply in the earth’s crust cools down slowly a) Extrusive Igneous Rocks b) Intrusive Igneous Rocks 9. The type of igneous rocks that is formed and cooled on the earth’s surface after some violent volcanic eruptions. a) Extrusive Igneous Rocks b) Intrusive Igneous Rocks II. Write PW if the agent is for Physical Weathering and CW for Chemical Weathering. _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. acids roots of trees water temperature oxygen man III. Read Weathering and Erosion notes in the notebook on the description of the agents of erosion and weathering. IV. Discuss the rock cycle. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ TOPIC: ATMOSPHERE I. Write the letter of the atmosphere being referred to. A. Troposphere B. Stratosphere _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ C. Mesosphere D. Thermosphere 1. Found beyond the mesosphere with the height of about 80 – 480 km. 2. Extends to about 50km, slightly warmer here than cooler. 3. Extends up to 10 -15 kms, this is where we live 4. Extends from 50 – 80 kms., the temperature decreases with increasing altitude. 5. It has very little water vapour that’s why it’s calm, has few clouds & no storms. 6. Main gases are nitrogen and oxygen. 7. The densest of the atmospheric layer. 8. Generally warmer but cool air is sometimes trapped beneath the warm air. 9. Where ozone layer is located. 10. It controls variation in temperature. II. Encircle the letter of the correct answer. 1. Refers to the amount of water vapour in the air. a) humidity b) condensation 2. A very large amount of air that has the same temperature & humidity. a) air pressure b) air mass c) relative humidity c) precipitation 3. Created during the day which makes the air above the land warmer while the air above the water cooler. a) land breeze b) sea breeze 4. A measure of the amount of water vapour in the air compared to the amount needed for saturation at a specific temperature. a) humidity b) condensation c) relative humidity 5. The downward force exerted by the weight of the air. a) air pressure b) air mass c) precipitation 6. The formation of liquid from water to water vapour. a) humidity b) condensation c) relative humidity 7. Happens at night when the land cools much more rapidly than ocean water, the air over the land becomes cooler than the air above the ocean. a) land breeze b) sea breeze 8. Water falling from the clouds is called ______. a) air pressure b) air mass c) precipitation 9. Measures the wind direction. a) anemometer b) barometer c) wind vane 10. Air pressure is measured by ______. a) anemometer b) barometer c) wind vane 11. Measures the wind speed. a) anemometer c) wind vane b) barometer 12. Liquid precipitation. a) snow b) rain 13. It’s formed when water vapour turns directly into ice crystals. a) snow b) rain II. True or False. Write T if the statement is true, if false write the correct answer. ___________________ 1. Snow, hail & sleet are all solid precipitation. ___________________ 2. Heated air is more dense and has low pressure ___________________ 3. Air always contain the same amount of water vapour. ____________________ 4. Air has its own weight. ____________________ 5. The colder the air, the lower the air pressure. ___________________ 6. Air molecules are closed together in high pressure than they are in an area of lower air pressure. III. Identify the storm signal descriptions. Write the letter of the correct answer. Signal No. 1 Signal No. 2 Signal No. 3 Signal No. 4 ____ 1. Strong winds of more than 185 kph, affects certain areas in at least 12 hours. ____ 2. Maximum wind speed is greater than 60 kph but not more than 100 kph, affects certain areas in at least 24 hours. ____ 3. Maximum wind speed not more than 60 kph, affect certain areas in at least 36 hours. ____ 4. Maximum wind speed of more than 100 kph up to 185 kph, affect certain areas in at least 12-18 hours. ____ 5. Winds may cause branches of small trees to be broken and to unroof small houses using light materials. ____ 6. Classes in pre-school, elementary and high school are suspended. ____ 7. Flooding, large trees uprooted, buildings severely damaged, electrical and communications are disrupted. ____ 8. Classes in all levels are automatically suspended. ____ 9. Moderate to heavy damages may be expected. ____ 10. Light to moderate damages to the communities affected. ____ 11. People are advised not to travel by sea or air. ____ 12. Forced evacuation from low-lying areas. IV. Encircle the letter of the correct answer: 1. It begins as a low pressure center over an ocean with circulating winds less than 24 km/hr or no wind at all a) intertropical convergence zone b) tropical cyclone c) monsoons 2. A short radio detecting device used in weather forecasting. a) telescope b) antenna c) radar 3. Has a speed of 60 km/hr or less. a) storm b) depression c) typhoon 4. Refers to the center of the typhoon where the winds move in counterclockwise direction in the northern hemisphere. a) eye b) head c) brain 5. Has a wind speed of more than 18 km/hr. Considered the most destructive weather disturbance due to heavy rains and violent winds. a) storm a) storm b) depression c) typhoon 6. Has a wind speed beyond 60-118 km/hr. a) storm b) depression c) typhoon 7. Formed by a low pressure area on the east and west absorbing water vapor from the ocean that causes heavy rains in the Philippines. a) southwest monsoon or habagat b) northeast monsoon or amihan 8. This monsoon begins in November that causes rains along the eastern coastal of the country bet Nov and Feb. a) southwest monsoon or habagat b) northeast monsoon or amihan V. Essay / Enumeration. A. List down 3 reminders on the following situations. 1. Before the typhoon a. ____________________________________________________________________________ b. ____________________________________________________________________________ c. ____________________________________________________________________________ 2. During the typhoon a. ____________________________________________________________________________ b. ____________________________________________________________________________ c. ____________________________________________________________________________ 3. After the typhoon a. ____________________________________________________________________________ b. ____________________________________________________________________________ c. ____________________________________________________________________________ B. Give the importance of weather forecast (p293, last line) __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ C. Read 287-288 for Precautionary Measures TOPIC: MOON & STARS I. Write the letter of the correct phase of the moon being described. A. New Moon B. Third Quarter Moon C.Waxing Crescent Moon D. Full Moon E. First Quarter Moon F. Waxing Gibbous Moon _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ 1. The moon can be seen after the first quarter but before the full moon. 2. The moon can be seen after the new moon but before the first quarter. 3. The lighted side of the moon faces away from the Earth. 4. The right half of the moon appears lighted & the left side appears dark. 5. The lighted side of the moon faces the earth. 6. The left half of the moon appears lighted & the right side appears dark. 7. The sun, earth & moon are nearly in straight line with the earth in the middle. _____ 8. The sun, earth & moon are almost in straight line with the moon in the middle. _____ 9. The moon that we see looks very dark. II. Encircle the letter of the correct answer. 1. A group of stars that form a pattern when seen from the Earth. a) comet b) constellation c) meteors or shooting stars 2. Regular rise & fall in the level of the ocean water. a) gravity b) waves c) tides 3. Streaks of light produced when a meteoroid burns up in the Earth’s atmosphere. a) comet b) constellation c) meteors or shooting stars 4. Made up of nucleus (has frozen gases, ice rocks & dust) plus tail. a) comet b) constellation c) meteors or shooting stars 5. There are ______ constellations up there. a) 68 b) 99 c) 88 6. A large cloud of gas & dust which forms into star. a) nebula b) protostar c) meteoroids 7. This small star is formed when the nebula contracts. a) comet b) constellation c) meteors or shooting stars 8. A celestial object consisting of a nucleus of ice & dust. a) comet b) constellation c) meteors or shooting stars III. Essay / Enumeration. A. Discuss origin of stars _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ B. Explain how stars differ in size, appearance, position, brightness, color and number. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________