Paeds rashes fact sheet
advertisement

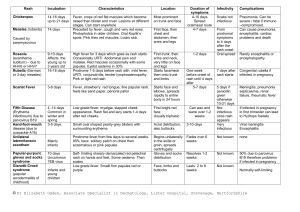
Paeds Rashes Kawasaki disease Epidemiology: infants and children effected; 85% <5yrs, 30% <1yr; peak occurrence 18-24/12; most common cause of acquired paediatric heart disease; incr in Asian / Blacks; 9-20:100,000 medium sized vessels (inc. coronary, renal, hepatic, Pathophysiology: Generalised systemic vasculitis of splanchnic) of unknown cause (likely post-infectious, due to super Ag bacterial toxins) Diagnostic Criteria 1) Fever >5 days (abrupt onset; in 100%) 2) 4 out of 5 of following within 3/7 of rash: can have <4 if echo shows CAD; those <6m old may have incomplete presentation (2-3 criteria) a. Bilat non-exudative bulbar conjunctival injection (with perilimbic sparing) – present in 80% b. Pharyngeal oedema / red cracked lips / strawberry tongue – present in 90%; lasts 2-3/52; dry, crack and fissure by 6/7 c. d. e. Cervical lymphadenopathy – present in 60-98%; usually solitary, unilateral, >1.5cm Diffuse erythema and swelling of hands and feet during acute phase (predilection for perineum, usually accompanies onset of fever; erythema, oedema) periungal desquamation during convalescent phase (after 23/52); present in 85-95% Polymorphous generalized rash – present in 99% May also get arthritis (35%), hepatitis (40%), AP, D+V, urethritis is sterile pyuria (70%), asceptic meningitis (25%), pericardial effusion / arrhythmia (20%), gallbladder hydrops (<10%), carditis and CCF (<5%; usually resolves by 6-8/52) Phases: Acute febrile phase: weeks 0 - 2; myocarditis (25%; resolves alone), pericarditis (resolves alone), pericardial effusion (rarely large), valvular dysfunction, LV dysfunction (50%), arrhythmias; MI (1%); conduction defects (20%); coronary arteritis begins Subacute phase: weeks 2 -3 Convalescent phase: weeks 4 - 6 Symptoms: fever for 1-2/52; tachycardia out of proportion to fever, gallop rhythm Ix: ECG: non-specific ST-T waves changes (in 7%) CXR bloods (anaemia for age, decr alb, incr plt, incr WBC, incr ALT, incr ESR and CRP ++, decr alb), ASOT / anti-DNAase B urine (sterile pyuria) echo (perform at initial presentation at 2/52 at 6/52 at 1yr; may not need to do initial echo if present <10/7 with normal ECG) Complications: Coronary artery aneurysms (20% untreated children) occur in 2nd – 4th week (can be as early as 3/7 or be delayed 6-8/52; RF for development: male, <1yr, >5yrs, fever >10/7, decr alb / Hb, clinical signs of cardiac involvement); stenosis, thrombosis; MI is leading cause of death; 75% fatalities occur within 6/52; children <6/12 at incr risk of developing cardiac complications so have lower threshold for diagnosis in this group; mortality <1%; excellent prognosis if trt within 10/7 and normal echo Treatment: Supportive care IVIG 2g/kg over 12hrs symptomatic improvement in 90%, prevents aneurysm in 95% (decr risk of heart Scarlet Fever abnormality from 20% to 3-5% if given in 1st 10/7); if ongoing fever, may require 2nd dose; aim to commence early than D5 High dose aspirin 30-50mg/kg/day until fever gone 3-5mg/kg OD for 6-8/52 helps prevent thrombosis; no evidence that it prevents the formation of aneurysms; must continue on low dose therapy indefinitely if develop aneurysms, otherwise stop at 6/52 Corticosteroids if refractory to above treatment Cause: Group A beta-haemolytic strep erythrogenic toxin Incubation: 2-4/7 (ie. Short) Sx: Acute onset fever, sore throat, headache, V, AP exanthem develops over 1-2/7 Red tonsils and pharynx covered in exudates Tongue white coating through which red hyptertrophied papillae project (white strawberry tongue) white coating disappears after 4-5/7 red strawberry tongue Bright red / haemorrhagic spots on soft palate. After 12-48hrs Red, finely punctate 1-2mm blanching papules (rough sandpaper) on neck, axillae and groin Rapidly spreads to trunk and extremities. Linear petechial eruptions in antecubital and axillary folds (Pastia’s lines). Fades at 6/7. Desquamates at 2/52, on hands and feet 1st. Facial flushing and circumoral pallor. Complications: OM, sinusitis, rheumatic fever, post-strep GN Ix: ASOT, swab Trt: Penicillin 10/7 Measles Cause: RNA myxovirus Epidemiology: rare in immunised; now mostly seen in older patients; highly infectious (90% susceptible close contacts will become infected) Incubation: 7-18/7 (av 10/7); 14/7 between exposure and rash; patient infectious from 5/7 before rash to 4/7 after rash Case definition: 3-4/7 URTI rash 1. Fever >38 (ie. High) 2. Rash: fever always present at time of onset of rash; behind ears and at hairline spreads from head to feet, inc palms and soles; erythematous maculopapular, red blanching confluence esp on face copper-brownish hue as resolves desquamates after 3/7; lasts 1/52 3. 1 of cough / coryza / conjunctivitis / Koplick spots (white, bluish-white 1mm spots with red base on buccal mucosa; appear 1/7 before rash); may have generalised lymphadenopathy; may be diarrhoea Complications: OM (2.5%), pneumonia (4%; responsible for 50% deaths); encephalitis (0.1%; onset 1-2/52 after disease; mortality 10-15%; permanent neuro damage in 40%); subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (can occur 410yrs later, progressive mental deterioration and death); myocarditis, nephritis, hepatitis, pericarditis, keratitis Ix: swab for PCR (will be +ive within few days, when serology may still be negative; also useful in immunocomp); blood for serology (IgM = infection, levels peak at 7-10/7; IgG = immunity; may be negative if <4/7 from onset fever, need to do rpt after 1/52, remains +ive for 3/12, sens 100%, spec 98%); double bag specs and don’t send through lamsen Trt: Supportive; need infection control measures; notifiable disease; no school / child care for 5/7; admit if: poor PO intake, resp compromise, CNS complications Prophylaxis: Exposed if: enter same room within 2hrs of infected person leaving Non-immune if: not had 2x MMR and born after 1969, from 6/12 to 1st vaccine, if >4yrs and not had 2nd vaccine, pregnant, immunocomp, or prem <28/40 Offer MMR if <72hrs (not if pregnant); if immunocomp / pregnant / >72hrs, consider Ig HSP Epidemiology: 2:1000; more Asian / Indian; usually 4-6yrs (2-11yrs) Cause: Allergic vasculitis, follows URTI, IgA mediated; assoc with infection, drugs, vaccines; may be post Grp A strep Pathology: Small vessels (skin, GIT, kidneys, jts) Sx: Palpable purpura on buttocks and legs (extensor surface) – presenting Sx in 50%; maybe also erythematous, urticarial, echymoses, petechaie AP (+N+V+D; in 60-80%; diffuse and colicky; occurs after rash; 50% have blood in stool; 5% get acute GI haemorrhage; 3% get intussusception) Migratory polyarthralgia (66-80%; presenting Sx in 25%; usually resolves after 24-48hrs; in gravity dependent jts) Renal failure (in 20-50%) – nephritic syndrome; ESRF in <1% Generalized oedema (eg. Feet; often painful) Ix: Haematuria and proteinuria in 90%; urine, FBC (plts normal), U+E Complications: Nephritic / nephrotic syndrome, ARF (<1%), HTN; if proteinuria = more severe and needs FU; Intussusception (5%); bowel perf Trt: Usually resolves in 3-4/52; supportive; monitor BP and urine for 6/12; IVF if ill; NSAIDS; Consider prednisone 1mg/kg for 2/52 (if abdo, jt or scrotal disease; may prevent renal complications (2% get long term renal impairment); helps jt pain, abdo pain, oedema) Admit if: Abdo, renal complications; symptomatic relief Notes from: Dunn, Starship Guidelines Paeds Rashes How to Describe a Rash Palpable lesions Papules <0.5cm Nodules >0.5cm Vesicles <0.5cm, clear fluid Pustules Yellow fluid PurpuraPurple; palpable / non-palpable Non-palpable lesions Macules Alterations in circumscribed area of skin Pigmentation Assessment History Fever, systemic symptoms, prev immunizations, human/animal contacts, travel, bites/stings, drugs, food, environmental exposure Initial location of rash, pattern and timeframe of development, initial Morphology Examination Vitals Undress – scalp, ears, neck, MM, skinfolds, digits, web interspaces, palms, soles Morphology, location, distribution ENTEROVIRUSES Echovirus 9, Coxsackievirus A9 Transmission Fecal-oral, oral-oral, RS-oral Sx Non-specific febrile illnesses, RTI, GI Sx, meningitis; variety of rashes Maculopapular rash beginning on face and neck, extending to trunk and feet; may be lesions on buccal mucosa and soft palate (resemble Koplik spots); maybe petechiae, vesicles, urticaria Duration 5/7 Enterovirus (hand, foot and mouth disease) Sx Fever, anorexia, malaise, sore mouth 1-2/7 later, oral lesions then cutaneous lesions Oral lesions: painful 4-8mm vesicles on erythematous base on buccal mucosa, tongue, soft palate, gingiva ulcerate Cutaneous lesions: 3-7mm red papules grey vesicles on palms and soles (may be dorsum of feet and buttocks) heal in 7-10/7 Trt Hydration, analgesia, mouthwash Coxsackievirus (herpangina) Sx Fever, mouth pain, oral ulcers Similar ulcers to hand, foot and mouth; but no skin lesions RUBELLA Incubation Sx Trt 12-25/7 1-5/7 fever, malaise, headache, sore throat irregular pink macules and papules on face, spreading to neck, trunk and arms; coalesces then clears Forchheimer spots: pinpoint petechiae on soft palate that coalesce Suboccipital and posterior auricular lymphadenopathy Supportive ERYTHEMA INFECTIOSUM (FIFTH DISEASE, SLAPPED CHEEK) Sx Trt Abrupt appearance of rash fiery red rash on cheeks; diffuse erythema of closely grouped tiny papules on erythematous base; edges slightly raised; circumoral pallor; sparing of eyelids and chin; lasts 4-5/7 1-2/7 after face rash nonpruritic macular/maculopapular erythema on trunk and upper limbs spreads; lasts 1/52; spares palms and soles; fades with central clearing Assoc with fever, malaise, headache, sore throat, cough, coryza, N+V+D, myalgia Supportive HERPES Transmission Sx Trt HSV-2 genital, HSV-1 oral Herpes labialis, gingivostomatitis – painful umbilicated vesicles unroof and crust over Eczema herpiticum – break out on area previously affected by eczema Herpetic whitlow – distal fingers Consider sexual abuse Oral acyclovir; supportive CHICKENPOX Sx Trt Pruritic generalized vesicular exanthem with mild systemic symptoms; starts on trunk / scalp as faint red macules vesicular in 24hrs, on erythematous base dry and crust; widespread, palms and soles spared; may occur on MM Supportive if uncomplicated; cleanse lesions to prevent 2Y infection; antivirals only if immunocompromised ROSEOLA INFANTUM (SIXTH DISEASE) Sx Trt Abrupt onset fever lasting 3-5/7, cough, coryza, anorexia, abdo discomfort fever settles appearance of rash over 1-2/7. Erythematous, blanching, macular/maculopapular eruption, discrete rose / pale pink 2-5mm lesions; most on neck, trunk and buttocks; can also involve face and arms. No MM involvement. Lasts 1-2/7 fades rapidly. Supportive IMPETIGO Cause Sx Trt Staph aureus, beta-haemolytic strep Lesions on face, neck, and extremities; usually no systemic Sx Nonbullous: small erythematous macules and papules thin walled vesicles pustules rupture golden yellow crust smooth red surface underneath; may become confluent; local adenopathy Bullous: local; toxin causes separation of skin and bullae; thin walled bullae 0.5-3cm, filled with clear-yellow fluid, rupture easily Staph scalded skin syndrome: systemic; malaise, fever, irritability, tender skin; extensive areas of exfoliation; Nikolsky sign +ive Nonbullous: topical; oral only if severe SSSS: inpatient, IVABx; may require admission to burns unit ERYSIPELAS Cause Sx Trt Group A beta-haemolytic strep Fever, chills, malaise, vomiting Local redness, heat, swelling; raised indurated border; well demarcated Penicillin SCABIES Sx Trt Severe pruritis; generalized eruption of linear burrows, papules, pustules, vesicles; mostly affect hand, feet, groin; excoriation from scratching Permethrin ERYTHEMA TOXICUM Sx Trt Erythematous macules 2-3cm on face, trunk, extremities; central 1-3mm pustules None SEBORRHOEIC DERMATITIS Sx Trt NAPPY RASH Greasy yellow/red scales, mostly on scalp; not pruritic Mineral oil Contact dermatitis: erythematous macular/papular with well demarcated borders; trt with hygeine Candidal dermatitis: erythematous papular / pustular lesions; scaling around margins; satellite lesions