SS9.2 Post Teacher aug12
advertisement

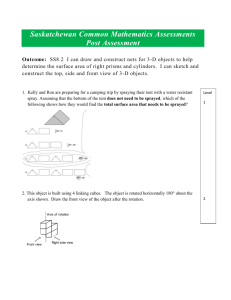
Saskatchewan Common Mathematics Assessments Post Assessment Outcome: SS9.2 Extend understanding of area to surface area of right rectangular prisms, right cylinders, right triangular prisms, to composite 3-D objects. Name: ______________________________________________________ 1. What is the area of this triangle? Level 1 2. What is the area of this cylinder? It has a radius of 5 cm and a height of 6 cm. Round off to the nearest tenth. 3. Suppose that each edge of a cube is 8 cm. Find the surface area of the cube. 2 Level 4. Determine the surface area of this rectangular prism. 3 5. This composite object is made using centimetre cubes. Determine its surface area. 6. This object is made from 3 identical right rectangular prisms. Each prism is 55 cm long and has square ends of side length 25 cm. What is the surface area of the object? 7. Determine the surface area of the object, to the nearest square centimetre. 4 Teacher Section Teacher Notes: Students will need a calculator and the following formulas: Square A=s 2 Circle A= d Rectangle A=L X W Triangle A= 1 bh bh or 2 2 Cylinder SA=2 r 2 + 2 rh Question Indicator Level Pythagorean Theorem h = a + b Answer Key: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 SS9.2 SS9.2 SS9.2 SS9.2 g SS9.2 b, c, d SS9.2 b, c, d SS9.2 b, c, d, g 1 2 2 3 3 3 4 Answer 9 cm 345.6 cm 2 384 cm 2 568 cm 2 22 cm 2 14, 750 cm 2 553 cm 2 Outcome: SS9.2 Extend understanding of area to surface area of right rectangular prisms, right cylinders, right triangular prisms, to composite 3-D objects. Description of Levels: (based on Marzano, 2007) Indicators and Learning Targets for each Level: Studentfriendly descriptions of learning targets. up to Level 1 up to Level 2 There is a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes. Prior knowledge is understood. No major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details or processes, but major errors or omissions regarding the complex processes may be present. (a) Describe 3-D composite objects from the natural and constructed world, including objects relevant to First Nations and Métis people (e.g., Mesoamerican pyramids). Terminology: rectangle, cylinder, prism, 2D/3D, surface area, area formulas (rectangle, square, triangle, circle) (a)I can describe natural and constructed 3-D objects including objects relevant to First Nations and Métis people. up to Level 3 No major errors or omissions regarding any of the information and/or processes that were explicitly taught. This is the target level for proficiency. (b) Analyze a composite 3-D object to identify areas of overlap and explain the impact of these areas on determining the surface area of the composite 3-D object. (c) Critique the statement “To find the surface area of a composite 3-D object, add together the surface areas of the individual 3-D objects from which the composite 3-D object is comprised” (d) Determine the surface area of composite 3-D objects. (e) Solve situational questions involving the surface area of composite 3-D objects. (f) Give dimensions for a single 3-D object that will have the same surface area as a composite 3-D object. (g) Approximate the surface area of a 3-D object from the natural environment using composites of standard 3-D objects such as right rectangular prisms, right cylinders, and right triangular prisms. (b)I can identify areas of overlap. (c)I can analyze the statement “To find the surface area of a composite 3-D object, add together the surface areas of the individual 3-D objects from which the composite 3-D object is comprised” (d)I can find the area of a composite 3-D object. (e)I can solve situational questions involving the surface area of composite 3-D objects. (f)I can give dimensions for a single 3-D object that will have the same surface area a composite 3-D object. (g)I can approximate the surface area of rectangular prisms, right cylinders, and right triangular prisms. up to Level 4 In addition to level 3 performance, in-depth inferences and applications go beyond what was explicitly taught.