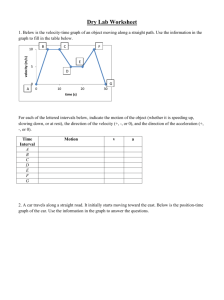
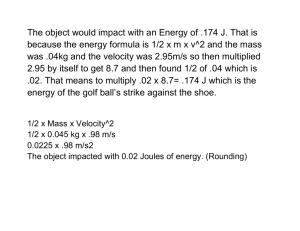1 Key Concepts
advertisement

Key Concepts 1 Name__________________________ Key Concepts 1. Conversion factors can be used to convert from one unit to another. 2. Velocity is a change in position divided by time. 3. Acceleration is a change in velocity divided by time. 4. The slope of a position-time graph equals velocity. Vocabulary Conversion Factor A ratio of units that is equal to one. (1 kg / 1000 g). Magnitude Size. Resultant A vector that represents the sum of 2+ other vectors. Delta Change in a quantity. Final minus initial. Velocity Fastness and direction. Vector. Speed Fastness with no direction. Scalar. Vector A quantity with magnitude and directional information. Scalar A quantity with magnitude but no directional information. Instantaneous Speed The speed at a certain time. Acceleration Change in velocity / time. Velocity Change in position / time. Translation Motion in a straight line. Rotation Spinning motion. Linear Relation One variable depends on the other directly. y = 3 x Quadratic Relation One variable depends on the square of the other. y = 3 x2 Inverse Relation One variable increases when the other decreases. y = 1 / x Example 1. A car travels 30 meters north then 10 meters south. This takes 5 seconds. Speed = dist / time = 40/5 = 8 m/s. Velocity = disp / time = 20/5 = 4 m/s north. Example 2. Mr. Blount runs one lap (400 m) around the track in 40 seconds. Speed = dist / time = 400/40 = 10 m/s. Velocity = disp / time = 0/40 = 0 m/s. Write the key concepts. 1. ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. ______________________________________________________________________________ Write the definitions. 5. Conversion Factor 6. Magnitude 7. Resultant 8. Delta 9. Velocity 10. Speed 11. Vector 12. Scalar 13. Instantaneous Speed 14. Acceleration 15. Velocity 16. Translation 17. Rotation 18. Linear Relation 19. Quadratic Relation 20. Inverse Relation Example 1. A car travels 30 meters north then 10 meters south. This takes 5 seconds. 21. What is the speed? ______________________________________________________________ 22. What is the velocity? _____________________________________________________________ Example 2. Mr. Blount runs one lap (400 m) around the track in 40 seconds. 23. What is the speed? ______________________________________________________________ 24. What is the velocity? _____________________________________________________________