MATH-123 Quantitative Reasoning
advertisement

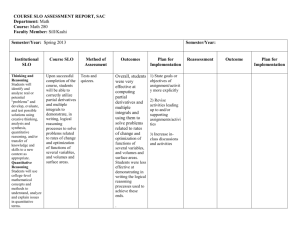
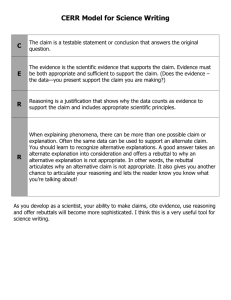
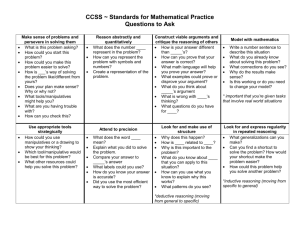
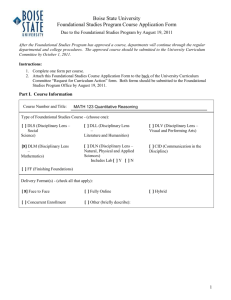
M123 Quantitative Reasoning Catalog Description MATH 123 QUANTITATIVE REASONING (3-0-3)(F, S)(DLM). Survey of quantitative reasoning skills including deductive and inductive reasoning, benchmarks, and sense of scale, applied in a conceptual way to interpretation of graphical displays, descriptive and inferential statistics, elementary probability, and exponential growth. PREREQ: MATH 25 or satisfactory placement score. Prerequisites MATH 25 or satisfactory placement score. Syllabus Statement Boise State's Foundational Studies Program provides undergraduates with a broad-based education that spans the entire university experience. MATH 123 Quantitative Reasoning satisfies three credits of the Foundational Studies Program's Disciplinary Lens-Mathematics (DL-M) requirement. It supports the following University Learning Outcomes, along with a variety of other course-specific goals: 7. Apply knowledge and the methods of reasoning characteristic of mathematics, statistics, and other formal systems to solve complex problems. MATH 123: Quantitative Reasoning is designed to introduce students to the methods of reasoning used in science and mathematics. This course helps to achieve the goals of the Foundational Studies Program by focusing on the following course learning outcomes. After successful completion of this course, you will be able to: Assess data for reasonableness Create and interpret graphical information Appreciate the statistical techniques used in studies and experiments Recognize the characteristics of exponential growth Topics covered Methods of reasoning Inductive Deductive Retroductive (Abductive or Bayesian) Number Sense or Attention to numbers Sense of scale Reasonableness and benchmark figures (numbers that experts use to judge reasonableness) Source of numbers Relationship between a thousand, million, billion, trillion Proportional reasoning Understanding Percentages Per hundred Techniques for calculator free approximations Using proportional reasoning to find approximations for non-linear behavior error issues with linearizing Non linear functions Compound interest as a introduction to exponential growth How the components of compound interest formula affect total interest earned How to make compounding you earn work for you. (You must reinvest the interest and/or dividend.) Simplifying assumptions when using financial formulas How the duration of a loan affects payment size and total interest paid Change in Area and Volume vs. change in linear dimensions Understanding Risk (Hope to Certitude) Relative frequency Absolute frequency High-risk and low-risk in context "Is one in ten thousand good or bad?" (Airplane crashes, misreading medical test result) Conditional probability Specificity vs. positive predictive value How prevalence affects positive predictive value Elementary Probability Expected value Normal Distribution Using observations How, why, and by whom was the data collected Communicating data graphically Association (correlation) vs. causation Avoid being misled Ethics