File
advertisement
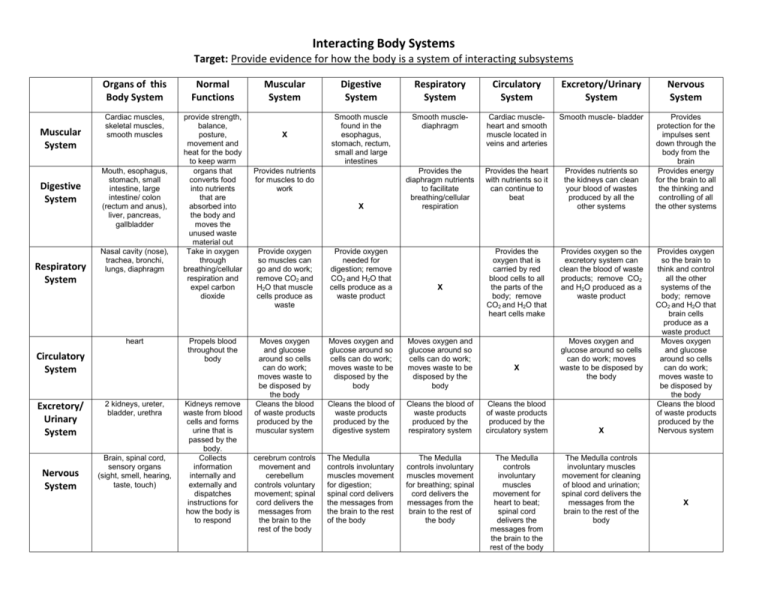
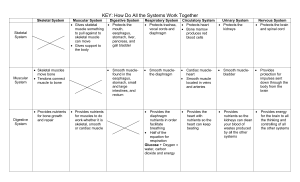
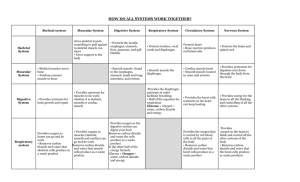
Interacting Body Systems Target: Provide evidence for how the body is a system of interacting subsystems Muscular System Digestive System Respiratory System Organs of this Body System Normal Functions Cardiac muscles, skeletal muscles, smooth muscles provide strength, balance, posture, movement and heat for the body to keep warm organs that converts food into nutrients that are absorbed into the body and moves the unused waste material out Take in oxygen through breathing/cellular respiration and expel carbon dioxide Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine/ colon (rectum and anus), liver, pancreas, gallbladder Nasal cavity (nose), trachea, bronchi, lungs, diaphragm heart Circulatory System Excretory/ Urinary System Nervous System 2 kidneys, ureter, bladder, urethra Brain, spinal cord, sensory organs (sight, smell, hearing, taste, touch) Propels blood throughout the body Kidneys remove waste from blood cells and forms urine that is passed by the body. Collects information internally and externally and dispatches instructions for how the body is to respond Muscular System X Digestive System Respiratory System Circulatory System Excretory/Urinary System Nervous System Smooth muscle found in the esophagus, stomach, rectum, small and large intestines Smooth musclediaphragm Cardiac muscleheart and smooth muscle located in veins and arteries Smooth muscle- bladder Provides the diaphragm nutrients to facilitate breathing/cellular respiration Provides the heart with nutrients so it can continue to beat Provides nutrients so the kidneys can clean your blood of wastes produced by all the other systems Provides protection for the impulses sent down through the body from the brain Provides energy for the brain to all the thinking and controlling of all the other systems Provides the oxygen that is carried by red blood cells to all the parts of the body; remove CO2 and H2O that heart cells make Provides oxygen so the excretory system can clean the blood of waste products; remove CO2 and H2O produced as a waste product Provides nutrients for muscles to do work X Provide oxygen so muscles can go and do work; remove CO2 and H2O that muscle cells produce as waste Provide oxygen needed for digestion; remove CO2 and H2O that cells produce as a waste product Moves oxygen and glucose around so cells can do work; moves waste to be disposed by the body Cleans the blood of waste products produced by the muscular system Moves oxygen and glucose around so cells can do work; moves waste to be disposed by the body Moves oxygen and glucose around so cells can do work; moves waste to be disposed by the body Cleans the blood of waste products produced by the digestive system Cleans the blood of waste products produced by the respiratory system Cleans the blood of waste products produced by the circulatory system The Medulla controls involuntary muscles movement for digestion; spinal cord delivers the messages from the brain to the rest of the body The Medulla controls involuntary muscles movement for breathing; spinal cord delivers the messages from the brain to the rest of the body The Medulla controls involuntary muscles movement for heart to beat; spinal cord delivers the messages from the brain to the rest of the body cerebrum controls movement and cerebellum controls voluntary movement; spinal cord delivers the messages from the brain to the rest of the body X X Moves oxygen and glucose around so cells can do work; moves waste to be disposed by the body X The Medulla controls involuntary muscles movement for cleaning of blood and urination; spinal cord delivers the messages from the brain to the rest of the body Provides oxygen so the brain to think and control all the other systems of the body; remove CO2 and H2O that brain cells produce as a waste product Moves oxygen and glucose around so cells can do work; moves waste to be disposed by the body Cleans the blood of waste products produced by the Nervous system X