Monday - How about those Cells!
advertisement

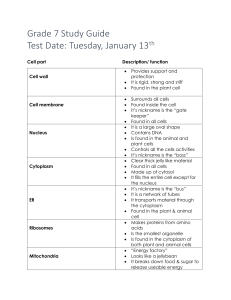
Monday Lesson Plan: Plants vs. Animal Cells Organization and Development of Living Organisms Sunshine State Standards: SC.912.L14.2, SC.912.L14.3 Goal: 1. For students to distinguish the differences and similarities between plant and animal cells. 2. To develop an understanding of structure as in relates to function of the different parts in plant and animal cells. Book: Essentials of Cell Biology (Unit 1.1 / Unit 3.5) http://www.nature.com/scitable/ebooks/essentials-of-cell-biology-14749010 Introduction: Today we are going to dive into the world of cells. We’re going to start off by defining some major components of cell biology. Then, we will further dissect each topic to gain a better understanding of cells as they relate to topics such as animals, plants, and even you! Step one: Define major components of cell biology with the class, as a group activity. Defining terms: Three main components of any cell (prokaryotic/eukaryotic): 1. Plasma membrane: Defines the boundary of the cell. 2. Cytoplasm: Semi-fluid contents of the cell, includes ribosomes. 3. DNA: contains the cell’s genetic information. Prokaryotic Cell: A cell that is lacking a true nucleus that is bound by a membrane. They are simplistic forms of life that make up bacteria and archaea. Eukaryotic Cell: A cell that has a true membrane-bound nucleus along with membrane- bound organelles. They are more complex forms of life than prokaryotic cells and make up all protists, fungi, plants, and animals. Step two: Assign students into groups of four or five. Instruct them to take turns reading unit 1.1 and 3.5. Step three: Have the class come together as a whole group and hold a group discussion about the reading to answer any questions the students may have. Step four: Hand out worksheets and have the students work individually to complete them. Go over the answers next class as a review to the topic. Name: ____________________ Date: ______________ Use the word bank to place the organelles of cells into a column: Plant cell, Animal cell, or both. **Internet Safety Reminder**: While using the EBook, do not click on any advertisements as they can distract you as well as cause harm to computer. Do not give any personal information on ANY website. Word Bank Plasma membrane lysosomes Large, central vacuole Plant Cell Nucleus Chloroplast cell walls Animal Cell Golgi apparatus Mitochondria Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes Cytoplasm peroxisomes Both Answers: Plant cell (chloroplast, cell walls, large central vacuole, peroxisomes, cytoplasm, nucleus, plasma membrane, ER, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, Mitochondria) Animal cell (lysosomes, peroxisomes, cytoplasm, nucleus, plasma membrane, ER, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, Mitochondria) Both (peroxisomes, cytoplasm, nucleus, plasma membrane, ER, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, Mitochondria). Match the organelle with the correct function. Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Cell walls Cytoplasm Lysosomes Peroxisomes Chloroplast Nucleus Mitochondria Large central vacuole Plasma membrane Provides support and protection to cell organelles. Carries materials through the cell and aids in the production of proteins Constructs proteins Contains the heredity material of the cell Utilizes the sun’s energy to produce sugar for plants Breaks down large food molecules into smaller ones and digests old cell parts: Intracellular digestion Breaks down sugar molecules to produce ATP (energy) Support, protects, allows diffusion to occur Controls what enters and exits the cell Stores food and water Receives, packages, and distributes proteins and lipids Oxidation of molecules Answers: Ribosomes constructs proteins. Endoplasmic reticulum carries materials through the cell/aids in making proteins. Golgi apparatus Receives, packages, and distributes proteins and lipids. Cell walls support, protects, and allows for diffusion to occur. Cytoplasm Provides support and protection to cell organelles. Lysosomes Breaks down large food molecules into smaller ones and digests old cell parts: Intracellular digestion. Peroxisomes Oxidation of molecules. Chloroplast Utilizes the sun’s energy to produce sugar for plants. Nucleus Contains the heredity material of the cell. Mitochondria Breaks down sugar molecules to produce ATP (energy). Large, central vacuole stores food and water. Plasma membrane Controls what enters and exits the cell. Conclusion: Through completing this lesson plan students will gain an understanding into the world of cells. Students will acquire a lot of new information through this lesson. This is why the lesson plan was mixed with learning styles. At the beginning of the lesson, the teacher is lecturing the students on some key components of cell biology (teacher-centered learning). After the mini lecture, students get into groups and read more in depth on cells, their organelles, and the differences and similarities of plants and animal cells (studentcentered). The class comes together to have a large group discussion about the reading (student-centered). Additional E-books: http://www.dedicatedteacher.com/cells-learning-about-science-for-grades-4-12-mark-twainmedia-ebook/carson-dellosa-publishing/CSD404050EB/pd/ http://www.rempub.com/ebooks-category/all-about-cells-student-learning-guide-ebook http://www.freebookcentre.net/biology-books-download/Structure-and-Function-of-MajorCell-Components.html http://www.freebookcentre.net/biology-books-download/Cells-and-Cell-Function.html http://www.freebookcentre.net/biology-books-download/Essentials-of-Cell-Biology.html