ENGR 3340 – Fundamentals of Statics and Dynamics Required
advertisement

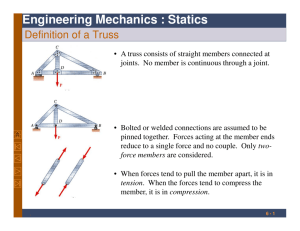
INTER AMERICAN UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO BAYAMON CAMPUS SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ENGR 3340 – Fundamentals of Statics and Dynamics Required Catalog Description: Analysis of force systems. Application of equilibrium law for particles and rigid bodies. Structural analysis including internal forces and friction. Calculation of centers of gravity, centroid and moment of inertia. Kinematics and kinetics analysis of particles and rigid bodies. Discussion of vibratory systems. Pre-requisite(s): PHYS 3311 – Physics for Engineers I Textbook: Hibbeler, R.C., Engineering Mechanics-Static and Dynamics, 12th. Ed. Prentice Hall, 2010. Suggested References: Beer, F.P. and Johnston, E.R., Vector Mechanics for Engineers - Statics and Dynamics, 9th Ed., McGraw-Hill, 2009. Bedford, Anthony and Fowler Wallce., Engineering Mechanics - Statics and Dynamics, 5th Ed., Prentice Hall, 2007. Meriam J. L.,Kraige L. G., Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Dynamics, 6th Ed., John Wiley & Sons, 2008. Electronic references of Statics and Dynamics, from http://www.engnetbase.com/ Course Objectives Upon successful completion of the course, the student will be able to: 1. Understand the fundamental concepts of statics and dynamics. 2. Apply the different methods and the mathematics involved in the solution of engineering problems. 3. Distinguish between particles and rigid bodies and their analysis. 4. Draw free-body diagrams. 5. Solve equilibrium problems using the equations of equilibrium. 6. Calculate the moment of a force. 7. Reduce a simple distributed loading. 8. Calculate position, displacement, velocity and acceleration of a particle. 9. Analyze the accelerated motion of a particle. 10. Use principles of work and energy for basic dynamic analysis. 11. Use principles of impulse and momentum for basic dynamic analysis. 12. Solve vibrations problems. Topics Covered Lecture Topic* 1. Introduction: General Principles 2. Statics of Particles-2D 3. Statics of Rigid Bodies-2D 4. Introduction to Center of Gravity and Centroids 5. Introduction to Structural Analysis 6. Statics of Particles-3D 7. Statics of Rigid Bodies- 3D 8. Dynamic of Particles: Kinematics 9. Dynamic of Particles: Kinetics 10. Dynamic of Rigid Bodies: Introduction to Kinematics and Kinetics of Rigid Bodies 11. Introduction to Vibrations *Schedule is subject to change Class/Lab Schedule: Three credit hours. Forty-five hour lecture per term (Expressed in hours per term according to the General Catalog description). Grading Policy Grades are reported according to the following standard grading system: A (90-100), B (80-89), C (70-79), D (60-69), F (0-59) Contribution of Course to Meeting Professional Component Three credit hours of engineering science and two credit hours of engineering design. Relationship of Course to Program Outcomes** a b c d e f g h i j k **The numbers and letters correspond to the Program Educational Objectives and Program Outcomes of mechanical engineering, respectively. Revised by: Prof. Jorge Diazgranados Jimenez, Date: 2/9/16 Supporting Services or Special Needs Students requiring additional services or special assistance must request these at the beginning of the course or as soon as they learn that they need them, through the appropriate register in the Coordination Office of Student Services located on the Student Affair Office. Honesty, Fraud and Plagiarism (General Student Regulations, Chapter V) The lack of honesty, fraud, plagiarism and any other inadequate behavior in relation to academic work constitute major infractions sanctioned by General Student Regulations. Major infractions, according to General Regulation Students, may result in suspension from the University for a definite period of time greater than one year or the permanent expulsion from the University, among others sanctions.