"POLITEHNICA" UNIVERSITY OF TIMISOARA SYLLABUS for the
advertisement

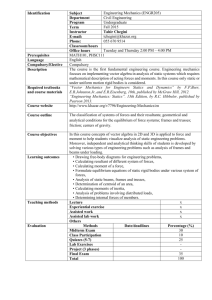
"POLITEHNICA" UNIVERSITY OF TIMISOARA SYLLABUS for the course: “MECHANICS” (“MECANICA”) FACULTY OF CIVIL ENGINEERING DOMAIN CIVIL ENGINEERING Year of study: I Semester: 2 Course coordinator: Assoc. Prof. Raul ZAHARIA Collaborators: Drd. eng. Ioan BOTH Number of hours / Examination / Credits Course Seminar Practical works Project 28 28 Fundamental In the domain Speciality Course status Compulsory: Imposed Optional Examination Credits E 4 Complementary Facultative A. COURSE OBJECTIVES The course aims to provide the students with fundamental knowledge of Newtonian mechanics, including the topics of kinematics and dynamics. The course contains the fundamental notions of classical mechanics that are used further in the “Mechanics of materials” and “Structural analysis” courses. After completion of the course, the student should be able to calculate the geometrical characteristics of cross-sections, to compute the reactions of a given statically determined structure, to determine the axial forces within a truss, to determine the displacements within a plane mechanism and to apply the principle of virtual work B. COURSE TOPICS 1. Introduction 2. A little bit of history 3. Basic notions and principles of theoretical mechanics 4. Statics (4.1 Statics of the particle; 4.2 Statics of the rigid body; 4.3. Statics of systems of rigid bodies; 4.4 Geometrical characteristics of the cross-sections for linear elements; 4. 5. Trusses) 5. Kinematics (5.1 Kinematics of the particle. 5.2 Kinematics of the rigid body) 6. Dynamics (6.1 Priciples; 6.2 Dynamics of the particle; 6.3 Dynanics of the systems of particles) 7. Principle of virtual work apllied in the analysis of civil engineering structures (7.1 Plane mechanisms with 1 DOF; 7.2 Principle of virtual work applied in the Structural Analysis) C. APPLICATIONS TOPICS 1. Dimensions, quantities and units of measurement 2. Operations with vectors 3. Equilibrium of a particle 4. Equivalent force system 5. Couple of forces 6. Static equilibrium for a plane structure (Types of forces, reactions, Simple supported beam, Cantilever, Frames, Calculation of internal forces in trusses) 7. Geometric properties of simple and composed Cross-sections (Centre of gravity, First moment of area, Second moment of area, Polar moment of inertia, Product of inertia of a cross-section, Position of principal axis) 8. Circular motion 9. Plane parallel motion. Motion of a rigid solid body with a fixed point 10. Application of the virtual work principle in the computation of the reactions for a statically determinate structure D. EDUCATIONAL METHODS EMPLOYED Course: lecturing, conversation, explication, demonstration Seminar: explication, example E. EVALUATION PROCEDURE Written exam. Two internal examiners. Five applications and three-five theoretical subjects. Mark 5 is given if all subjects are 50% covered. The exam covers 60% of the final mark, while the activity during the semester covers 40% of the final mark. Activity: Students are expected to attend and participate in every class session. The attendance will be monitored. Homework: There will be approximately one homework assignment every two weeks. F. REFERENCES 1.Beer F.P., Johnston E.R. Jr., Vector Mechanics for Engineers, McGRaw-Hill Shames I.H., Engineering Mechanics-Statics, Prentice – Hall, 1959 2. BuildRight Toolbox, BCG03 General Construction Training Package, BCG40106 Certificate IV in Building and Construction (Building), Australian Flexible Learning Framework Toolbox project developed by Holmesglen Training and Development, Holmesglen Institute of TAFE, Australian Gouvernment, Department of Education, Science and Training, Commonwealth of Australia 2007 3. Dragulescu D., Toth-Tascau M., Mecanica, Ed. Orizonturi Universitare, Timisoara, 2002 4. Feynman R., Leighton R., Sands M., Feynman Lectures on Physics: The Definitive and Extended Edition, Publisher Addison Wesley, 2005 4. Hibbler R. C., Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Dynamics, 11th Edition, Peason Prentice Hall, 2006 5. McLean W. G., Nelson E. W., Theory and problems of Engineering Mechanics, McGraw-Hill Book Company, Second edition, 1962 G. INTERNATIONAL COMPATIBILITY 1. Technical University of Liege HEAD OF DEPARTMENT Prof. Dr. Ing. Dan DUBINĂ COURSE COORDINATOR Assoc. Prof. Raul ZAHARIA