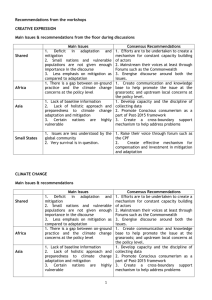
IPCC reports - Earth and Atmospheric Sciences
advertisement

IPCC—Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change www.ipch.ch (info extracted from this web page). The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) was established by the United Nations Environmental Programme (UNEP) and the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) in 1988 to assess the scientific, technical and socio-economic information relevant for the understanding of human induced climate change, its potential impacts and options for mitigation and adaptation. The IPCC has completed three full assessment reports, guidelines and methodologies, special reports and technical papers. For more information on the IPCC, its activities and publications please see the IPCC homepage. AR4: Assessment Report 4 WG1: Physical science basis. 2007 table of contents. Summary for Policymakers Technical Summary Frequently Asked Questions (extracted from chapters below) ------------------------1 Historical Overview of Climate Change Science 2 Changes in Atmospheric Constituents and in Radiative Forcing 3 Observations: Surface and Atmospheric Climate Change 4 Observations: Changes in Snow, Ice and Frozen Ground 5 Observations: Oceanic Climate Change and Sea Level 6 Palaeoclimate 7 Couplings Between Changes in the Climate System and Biogeochemistry 8 Climate Models and their Evaluation 9 Understanding and Attributing Climate Change 10 Global Climate Projections 11 Regional Climate Projections ------------------------Uncertainty Guidance Note for the Fourth Assessment Report WG !!: Impacts, adaptations and vulnerability This is the Working Group II website. In its reports, Working Group II assesses the scientific, technical, environmental, economic and social aspects of the vulnerability (sensitivity and adaptability) to climate change of, and the negative and positive consequences for, ecological systems, socio-economic sectors and human health, with an emphasis on regional sectoral and cross-sectoral issues. Working Group II is guided by a Bureau, which is chaired by Osvaldo Canziani (Argentina) and Martin Parry (UK). Working Group II also has a Technical Support Unit (TSU) to help direct the production of reports. The TSU is housed in the Hadley Centre of the UK Met Office. More on the organisation of Working Group II and information for contacting members of the TSU is available on this website. Introduction to the Report Summary for Policymakers Technical Summary Chapter 1: Assessment of Observed Changes and Responses in Natural and Managed Systems Chapter 2: New Assesment Methods and the Characterisation of Future Conditions Chapter 3: Fresh Water Resources and their Management Chapter 4: Ecosystems, their Properties, Goods and Services Chapter 5: Food, Fibre, and Forest Products Chapter 6: Coastal Systems and Low-Lying Areas Chapter 7: Industry, Settlement and Society Chapter 8: Human Health Chapter 9: Africa Chapter 10: Asia Chapter 11: Australia and New Zealand Chapter 12: Europe Chapter 13: Latin America Chapter 14: North America Chapter 15: Polar Regions (Arctic and Antarctic) Chapter 16: Small Islands Chapter 17: Assessment of Adaptation Practices, Options, Constraints and Capacity Chapter 18: Inter-Relationships Between Adaptation and Mitigation Chapter 19: Assessing Key Vulnerabilities and the Risk from Climate Change Chapter 20: Perspectives on Climate Change and Sustainability Cross-Chapter Case Studies Appendix I: Glossary Appendix II: List of Contributors to the WGII AR4 Appendix III: List of Reviewers of the WGII AR4 Appendix IV: Acronyms Index WG III: Mitigation of climate change Draft reports available Technical Summary (2.1 MB) Chapter 1: Introduction (312 KB ) Chapter 2: Framing Issues (590 KB) Chapter 3: Issues related to mitigation in the long-term context (2.5 MB) Chapter 4: Energy Supply (2.9 MB) Chapter 5: Transport and its infrastructure (1.2 MB) Chapter 6: Residential and commercial buildings (854 KB) Chapter 7: Industry (664 KB) Chapter 8: Agriculture (1.2 MB) Chapter 9: Forestry (1.3 MB) Chapter 10: Waste management (561 KB) Chapter 11: Mitigation from a cross-sectoral perspective (844 KB) Chapter 12: Sustainable Development and mitigation (677 KB) Chapter 13: Policies, instruments, and co-operative arrangements (897 KB) Glossary, Abbrevations, Chemical Symbols (206 KB) AR4 Synthesis Report - Outline of Topics Observed changes in climate and its effects (WG 1, 2) Past climate change including palaeoclimate aspects Effects of past climate change on natural systems and society Causes of change (WG 1, 2, 3) Natural and human-related factors Feedbacks, via the carbon cycle and otherwise Climate change and its impacts in the near and long term under different scenarios (WG 1, 2, 3) Future climate change Vulnerabilities Hazards, risks and opportunities Water, agriculture, ecosystems, human well-being and development Regional implications Implications of timescales, inertia, and lags Risks of abrupt or irreversible changes Adaptation and mitigation options and responses, and the inter-relationship with sustainable development, at global and regional levels (WG 2, 3) Adaptation - past experience and options and policies (including costs/benefits, cobenefits, and spillover effects), extent, limits, effectiveness and enhancement, sectoral and regional considerations, current, medium-, and long-term Mitigation - past experience and options and policies (including costs/benefits, cobenefits, and spillover effects), extent, limits, effectiveness and enhancement, sectoral and regional considerations, current, medium-, and long-term Relationship between adaptation and mitigation options Technology: timing, development, transfer, environment and integration issues International cooperation The long term perspective: scientific and socio-economic aspects relevant to adaptation and mitigation, consistent with the objectives and provisions of the Convention, and in the context of sustainable development Costs, benefits and avoided damage and risks at global and regional levels and under different scenarios Timing of mitigation and equity implications Relationship between adaptation and mitigation Technology flows and development Broader environment and integration issues Robust findings, key uncertainties