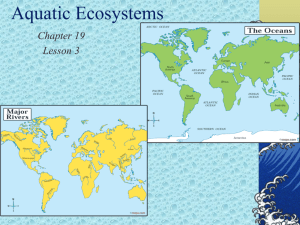
(water) Biomes
advertisement

15.4 & 15.5 POWERPOINT NOTES MARINE, ESTUARY, AND FRESHWATER ECOSYSTEMS 1. Water (aquatic) Biomes Include _________________ (saltwater) and _________________ biomes. Make up the largest ecosystem on earth. More than 70% of the earth’s surface is covered by water, and more organisms live in ____________________ than live on ______________________. Water biomes are typically more stable than land biomes. The temperature varies less because of the ability of water to absorb and hold __________. 2. Factors Affecting Water Biomes Amounts of available _________________ and carbon dioxide. Temperature and _____________________. Amounts of dissolved _________________ and suspended particles. 3. Aquatic (water) Biomes ____________________ (saltwater) ____________________ 4. KEY CONCEPT :Marine ecosystems are global. 5. Marine (saltwater) Oceans, Intertidal Zones Hold large quantities of solar ___________________ Help to stabilize the earth’s ____________________ Contain a constant supply of nutrients and dissolved salts Much of the photosynthesis on earth is carried out by __________________ near the surface of the oceans and coastal waters. Light penetrates through water to a depth of 30 meters. Photosynthesis does not occur at greater depths. 6. Ocean/saltwater This is by far the world’s _________________ and most _________________ biome. Water temperature and depth are key factors that determine the many different characteristics of oceanic creatures. There are 3 main types of ocean biomes… Temperate oceans Tropical oceans _________________________ 7. The ocean can be divided into zones. Ocean _______________ can be determined by their distance from shoreline and water depths. 8. The _______________ _____________ harbors more biomass than any other zone. Plankton make up most of the biomass. ______________________ ______________________ 9. KEY CONCEPT Freshwater ecosystems include ________________ as well as flowing and standing water. 10.Freshwater Less than 3% of the Earth’s water is fresh water. Ponds, Swamps, Lakes, Streams, and Rivers will vary by: 15.4 and 15.5 PP NOTES BIOLOGY Page 2 Size Speed of current ______________________ Concentration of dissolved gasses and suspended particles Rate of change Like the marine biome, freshwater biomes are home to a __________________ range of plants and animals. Temperature and depth play a key role in determining what types of life can be found in freshwater ecosystems. There are 3 types… Rivers and ____________________ Ponds and ____________________ ______________________ 11.Freshwater ecosystems include moving and standing water. A _________________________ is a region of land that _______________________________________________________________________. Ecosystems may be different along a river’s course 12.Wetlands are among the most productive ecosystems. provide a ______________ for many species filter ________________ water renew underground water supply Some animals have adaptations suited to the freshwater they inhabit. 13.Ponds and lakes share common features. All lakes “turn over” periodically. Turn over happens due to changes in _______________________. In both autumn and spring, surface water flows downward and bottom water flows upward. The upwelling brings up ___________________. 14.Estuaries are dynamic environments where rivers flow into the ocean. An estuary is a ________________________ ___________________ body of water. mixture of fresh water with ________________ water Chesapeake Bay Louisiana bayous 15.Estuaries are highly productive ecosystems. Estuaries provide a protected _________________ for many species. birds migration spawning grounds 16.Estuaries are primarily threatened by ________________development.