UNIT 3 Exam Population Biology An ecosystems carrying capacity
advertisement
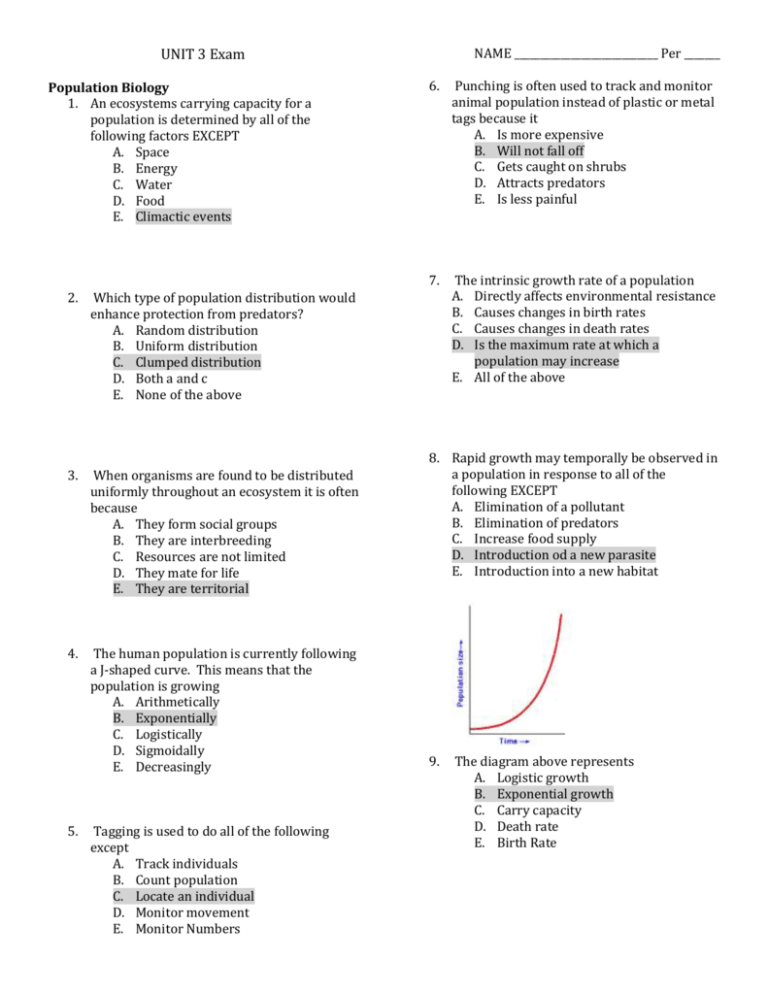
NAME ____________________________ Per _______ UNIT 3 Exam Population Biology 1. An ecosystems carrying capacity for a population is determined by all of the following factors EXCEPT A. Space B. Energy C. Water D. Food E. Climactic events 2. Which type of population distribution would enhance protection from predators? A. Random distribution B. Uniform distribution C. Clumped distribution D. Both a and c E. None of the above 3. When organisms are found to be distributed uniformly throughout an ecosystem it is often because A. They form social groups B. They are interbreeding C. Resources are not limited D. They mate for life E. They are territorial 4. The human population is currently following a J-shaped curve. This means that the population is growing A. Arithmetically B. Exponentially C. Logistically D. Sigmoidally E. Decreasingly 5. Tagging is used to do all of the following except A. Track individuals B. Count population C. Locate an individual D. Monitor movement E. Monitor Numbers 6. Punching is often used to track and monitor animal population instead of plastic or metal tags because it A. Is more expensive B. Will not fall off C. Gets caught on shrubs D. Attracts predators E. Is less painful 7. The intrinsic growth rate of a population A. Directly affects environmental resistance B. Causes changes in birth rates C. Causes changes in death rates D. Is the maximum rate at which a population may increase E. All of the above 8. Rapid growth may temporally be observed in a population in response to all of the following EXCEPT A. Elimination of a pollutant B. Elimination of predators C. Increase food supply D. Introduction od a new parasite E. Introduction into a new habitat 9. The diagram above represents A. Logistic growth B. Exponential growth C. Carry capacity D. Death rate E. Birth Rate 10. A population of rabbits, introduced to an island, has rapid growth for a few years; then its growth slows. The population becomes stable because A. The carrying capacity has been reached B. Environmental resistance declines C. Immigration is reduced D. R declines E. Bergman’s principal takes effect Population Dynamics 11. Developing countries tend to have an ________ age structure diagram A. Rectangular shaped B. Inverted triangle C. Pyramid shaped D. Square E. Round 12. The following is an example of an animal that exhibits R reproductive strategies. A. Cows B. Rabbits C. Elephants D. Humans E. Kangaroos 13. An animal that has K reproductive strategies does all of the following except A. Have a few, large offspring B. Adults are typically large in size C. Give some type if parental care D. Reach reproductive maturity early E. Stabilize near carrying capacity 14. If a population age structure diagram looks like a pyramid, the population is A. Expanding B. Shrinking C. Remaining the same D. Will expand for one generation E. Slowing A C B C 15. Using the figures above, choose the statement that best describes population A. A. This is a developed nation B. Women have access to education C. Women have access to family planning D. Birth rates are above replacement level fertility E. The population will double in two years 16. Population B represents a population that is A. Growing quickly B. Growing slowly C. Stable D. Declining E. Not enough data to tell 17. At current growth rates, which country will probably be the most populous in the world after 2050? A. China B. Brazil C. India D. Indonesia E. United states 18. Which of the following statements about China’s one child policy are incorrect? A. It has resulted in male dominance B. It has created a larger middle class C. Families are given economic incentives to have less children D. China uses less resources as a result E. Chinas population has begun to stabilize 19. Education of women has a direct correlation with A. Lower birth rates B. Higher birth rates C. Economic decline D. Economic gain E. Woman’s health 20. ___________ is an example of a developing country and ____________ is and example of a developed country. A. U.S., Russia B. China, Denmark C. China, India D. U.S., China E. France, China Population Size and Impacts 21. At the start of a study there were 200 spotted salamanders in an old-growth forest patch in northern California. Over the next year a biologist tracking the salamanders saw that 25 new salamanders hatched and 5 died. Thus r for this year was _______ A. 0.1 B. 5 C. 20 D. 25 E. 200 22. The most critical factor in controlling human population growth is A. Controlling reproductive lifespan B. Decreasing the age of first birth C. Degreasing the average number of births per woman D. Decreasing infant death E. Increasing overall wellness for the human race. 23. A population of river otters has a growth rate of r=.2 per year. If the population started at 50 individuals and there is no migration, how many would you expect after one year? A. 10;2 B. 52;54 C. 60;70 D. 60;72 E. 70;90 24. The total fertility rate is an estimate of A. The number of children that will survive to adulthood. B. The number of years a typical infant will live C. The number of children each woman will have D. The number of births her 1000 people per year E. The percentage of woman in a population that are able to have children 25. If a population of 100 birds increases to 120 birds the following year, r= ________ A. .16 B. .20 C. 1.2 D. 2 E. 20 26. Population growth rates are high in developing countries because A. Infant mortality rates are low B. Women tend to have children late in life C. Family planning is common D. Children are often an important economic advantage E. All of the above 27. Which developed country has the fastest population growth rate today? A. France B. Denmark C. Nigeria D. United States E. Russia 28. At present, Earths human population is A. Stable B. Declining C. Increasing exponentially D. Increasing at a constant rate E. Increasing at about 10% a year 29. U.S. citizen have a large ecological footprint because of their high consumption of A. Food B. Lumber C. Energy resources D. Space E. All of the above 30. Using the rule of 70, a population growing at 10% would double in A. 7 years B. 10 years C. 15 years D. 17 years E. Not enough information provided 31. A countries impact on the environment is influences by I. Population II. Technology III. Affluence A. I B. II C. III D. I and III E. I, II and III 32. Choose the answer that best represents replacement level fertility A. 0.5 B. 1.5 C. 2.0 D. 2.5 E. 3.0 33. All of the following are true about Tuberculosis EXCEPT: A. Many people world wide are infected white not all have developed the disease B. The disease in associated with airborne transmission C. Symptoms of the disease include weakness and coughing up blood D. The disease primarily affects the stomach E. Inappropriate use of antibiotics led to antibiotic resistant strains of the disease 34. A metropolitan region of 100,000 people has 2,000 births, 500 deaths, 200 emigrants and 100 immigrants over a 1 year period. Its population growth rate is A. 1.2 percent B. 1.4 percent C. 1.6 percent D. 1.8 percent E. 2.0 percent 35. A pathogen of an emergent virus that lives in hundreds of species of birds and is transmitted by mosquitos is A. Malaria B. Avian Flu C. West Nile D. Ebola E. Yersinia pestis Ecosystem Diversity 36. What is most significant when determining the diversity of an ecosystem? A. The number of organisms present B. The number of species present C. The amount of land the ecosystem covers D. The amount of precipitation an ecosystem receives E. The interactions between producers and consumers 37. Which of the following measures of biodiversity takes into account the number of species present and the relative abundance of the species present? A. Shannon’s index B. Species richness C. Species evenness D. Biodiversity index E. Hardy –Weinberg Index 38. In the diagram shown, which pair of organisms have the closest evolutionary relationship? A. Leopard and Lamprey B. Tuna and Turtle C. Tuna and Leopard D. Turtle and Salamander E. Lamprey and Turtle 39. Based on the diagram which structure is the most primitive? A. Vertebral Column B. Hinged Jaws C. Four walking legs D. Amniotic Egg E. Hair 40. Which of the following is the best description of evolution? A. The genetic change in an individual over time B. The genetic change within a population over one generation C. The growth of an individual from birth to adulthood D. The increased reproduction of a population E. The genetic change within a population over time 41. Based on the diagram above which organism is the most complex A. Anthophyta B. Coniferophyta C. Pteridophyta D. Lycopodiophyta E. Bryophyta 42. Based on the diagram above which organism has seeds but no flowers A. Anthophyta B. Coniferophyta C. Pteridophyta D. Lycopodiophyta E. Bryophyta 43. Which of the following is the best description of evolution? F. The genetic change in an individual over time G. The genetic change within a population over one generation H. The growth of an individual from birth to adulthood I. The increased reproduction of a population J. The genetic change within a population over time 44. If a bird normally has green feathers produces offspring with blue feathers, this is most likely a result of: A. A genetic mutation B. Evolution C. Natural selection D. Natural variation E. Genotypic variation 48. What occurs when a small group from a population colonizes a new area? A. Artificial selection B. Founder effect C. Bottleneck effect D. Sympatric speciation E. Genetic drift 45. When a population suddenly reduces in size either from habitat loss, natural disaster or other changes in the environment, its genetic variation is affected. When this occurs, it is known as: A. Founder effect B. Geographic isolation C. Genetic drift D. Bottleneck effect E. Mutation 49. Which of the following animals is not listed as endangered? A. Rhinos B. Bluefin Tuna C. Giraffe D. Lions E. Leather back turtle 46. Which of the following is the best example of artificial selection? A. Bees pollinating different species of flowers. B. Adaptation of finches to different sources of food on different islands C. An isolated population of frogs develops a phenotype distinct from the original population D. Breeding of horses for speed E. A small population has an unusually high percentage of a rare phenotype 50. What is the correct order based on the IUCN classification of endangered animals 47. Which of the following decreases genetic variation? I. Bottle Neck II. Mutation III. Genetic Drift A. I B. II C. III D. I and II E. I and III A. B. C. D. E. VulnerableEndangered Critically endangered VulnerableThreatenedEndangered ThreatenedEndangered Critically endangered Threatened VulnerableCritically endangered ThreatenedEndangeredExtinct








