GroupQuestionNotetakingOrganizerAnswers
advertisement

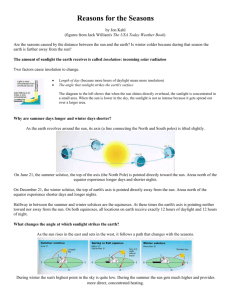
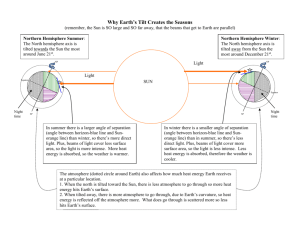
Question Big Ideas Learned What is responsible for the length of one day on Earth? What is responsible for the length one year on Earth? A day is one rotation of Earth on its axis. ~ 24 hours Compare a day and year on Earth, Mercury, and Jupiter. Explain your thinking. Planets rotate on their axis at different rates; days are different lengths. (some gas planets, some rock planets) A year is one revolution of Earth around the sun. ~365.25 days Planets closer to the sun take a shorter time to make a revolution, causing a shorter year. What is a leap year and how does it relate to a regular year? Why is the leap year a part of our calendar? Earth’s year, one revolution around the sun, is actually about 365.25 days. Every 4 years we add a day to make up for the .25 days extra each year. How old would a 7th grader (about 13 years) be on other planets in our solar system? Explain your thinking. Planets closer to the sun take a shorter time to make a revolution, causing a shorter year. Planets farther away from the sun take longer to make a revolution around the sun, causing a longer year. Considering the motion of the earth, how far do you travel in an earth day? Remember, you are not at the equator. How far do you travel in an earth year? We travel rotationally each day x 365 days in a year. We also travel a revolution around the sun. Add those totals for distance. Question Big Ideas Learned What happens to Earth’s axis of rotation as Earth orbits the Sun? How does this affect seasons. Earth’s axis remains tilted at 23.5 degrees. When the N hemisphere is tilted toward the sun, it receives more direct sunlight than the S hemisphere; we have summer. When the N hemisphere is tilted away from the sun, it receives less direct sunlight than the S hemisphere; we have winter. If you wanted to enjoy longer periods of daylight in the summertime, would you head closer to the equator or farther from it? Why? How about longer periods of sunlight in the winter? Explain. Summer (in the N hemisphere) – longer days – toward N pole – the pole is tipped toward the sun. At one day in summer it has constant daylight – summer solstice. If Earth’s axis were tilted so much that the North Pole sometimes pointed straight at the sun, how would the hours of daylight be affected at your location? How about at the poles? Would it be the same for each season? In N hemisphere: Summer – near constant daylight, would be warmer, N pole melting. Spring / Fall – similar to what it is now Winter – near constant night, would be colder, more freezing How do the average temperatures and the seasonal changes at the equator differ from those at the poles? In other words, how does their summer compare to their winter and other seasons? Why? Remember to consider all the seasons. Near poles – large difference between summer and winter temps because of tilt and increasing/decreasing amount of direct sunlight. If Earth stayed exactly the same distance from the sun throughout the year, would the seasons be different? Explain what you think would happen. What would the long-term affects be? Seasons would be basically the same because there would still be a tilt. Winter (in the N hemisphere) – longer days – toward equator. Near equator – summer and winter are basically the same since the equator receives direct sunlight constantly. Temps would change a tiny bit because of changes in distance from sun.