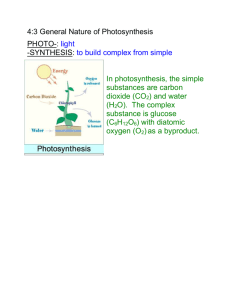
Definitions
advertisement
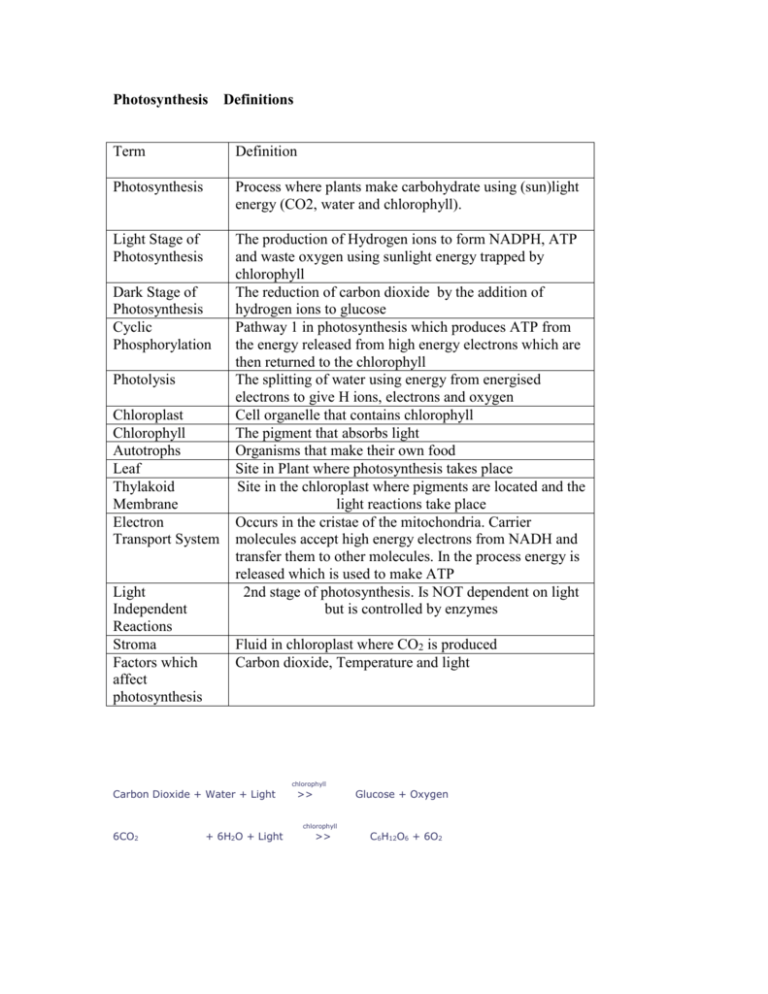
Photosynthesis Definitions Term Definition Photosynthesis Process where plants make carbohydrate using (sun)light energy (CO2, water and chlorophyll). Light Stage of Photosynthesis The production of Hydrogen ions to form NADPH, ATP and waste oxygen using sunlight energy trapped by chlorophyll The reduction of carbon dioxide by the addition of hydrogen ions to glucose Pathway 1 in photosynthesis which produces ATP from the energy released from high energy electrons which are then returned to the chlorophyll The splitting of water using energy from energised electrons to give H ions, electrons and oxygen Cell organelle that contains chlorophyll The pigment that absorbs light Organisms that make their own food Site in Plant where photosynthesis takes place Site in the chloroplast where pigments are located and the light reactions take place Occurs in the cristae of the mitochondria. Carrier molecules accept high energy electrons from NADH and transfer them to other molecules. In the process energy is released which is used to make ATP 2nd stage of photosynthesis. Is NOT dependent on light but is controlled by enzymes Dark Stage of Photosynthesis Cyclic Phosphorylation Photolysis Chloroplast Chlorophyll Autotrophs Leaf Thylakoid Membrane Electron Transport System Light Independent Reactions Stroma Factors which affect photosynthesis Fluid in chloroplast where CO2 is produced Carbon dioxide, Temperature and light chlorophyll Carbon Dioxide + Water + Light 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light >> Glucose + Oxygen chlorophyll >> C6H12O6 + 6O2 Term Photosynthesis Light Stage of Photosynthesis Dark Stage of Photosynthesis Cyclic Phosphorylation Photolysis Chloroplast Chlorophyll Autotrophs Leaf Thylakoid Membrane Electron Transport System Light Independent Reactions Stroma Factors which affect photosynthesis Definition Term Definition Process where plants make carbohydrate using (sun)light energy (CO2, water and chlorophyll). The production of Hydrogen ions to form NADPH, ATP and waste oxygen using sunlight energy trapped by chlorophyll The reduction of carbon dioxide by the addition of hydrogen ions to glucose Pathway 1 in photosynthesis which produces ATP from the energy released from high energy electrons which are then returned to the chlorophyll The splitting of water using energy from energised electrons to give H ions, electrons and oxygen Cell organelle that contains chlorophyll The pigment that absorbs light Organisms that make their own food Site in Plant where photosynthesis takes place Site in the chloroplast where pigments are located and the light reactions take place Occurs in the cristae of the mitochondria. Carrier molecules accept high energy electrons from NADH and transfer them to other molecules. In the process energy is released which is used to make ATP 2nd stage of photosynthesis. Is NOT dependent on light but is controlled by enzymes Fluid in chloroplast where CO2 is produced Carbon dioxide, Temperature and light