SurveyExamples_ZTestProportion
advertisement

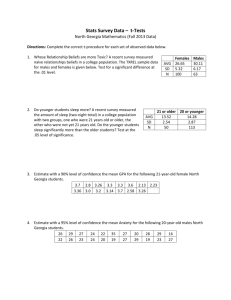
Stats Survey Data – Population Proportion Z-Procedures North Georgia Mathematics Directions: Complete the correct z-procedure for each set of observed data below. 1. Type A gender difference? A recent survey tested for Type A personalities among 202 undergraduates at North Georgia. Of the 128 females, 11 had Type A personalities. Of the 74 males, 9 had Type A personalities. Test for a gender difference at the .1 level. 2. Texting and Driving. A recent survey asked UNG students to report how often they texted while driving. Responses were “never,” “rarely,” “sometimes,” “often,” and “always.” Students were categorized as “frequently” texting if they selected “often” or “always.” Test whether more than 15% of North Georgia students text frequently while driving at the .05 level given that 47 of 201 respondents did so. 3. Making Friends. A recent study asked UNG students whether they made friends most easily with members of the opposite sex, same sex or either sex equally. Test at the .1 level whether there is a gender difference for same sex friendships given that, in the survey, 17 of 61 males and 22 of 114 females reported same sex friendships were the easiest for them to make. 4. Humor Styles. Research has shown a connection between naïve relationship beliefs and those who have a Self-Defeating primary humor style. Estimate the percentage of UNG students who have a Self-Defeating humor style using a 90% level of confidence given that 51 of 175 students tested in a recent study where found to be primarily Self-Defeating with their humor. 5. Coping Humor. A strong sense of Coping Humor indicates a person who uses humor to relieve stress and deal with the struggles of life. Test at the .05 level whether more than 10% of North Georgia students exhibit strong Coping Humor. A recent study used a criteria of scoring 30 or higher on the Coping Humor Scale to evaluate this criteria, and found that 21 of 175 North Georgia students did so. 6. Facebook Friends. A recent study found that apporximately 40% of North Georgia students had more than 800 friends on Facebook. For females invovled in Greek life, is this percentage higher? Test the hypothesis at the .01 level given that 23 of 34 Greek females had more than 800 friends. 7. Gender differences for texting while driving? A recent survey asked UNG students to report how often they texted while driving. Responses were “never,” “rarely,” “sometimes,” “often,” and “always.” Students were categorized as “frequently” texting if they selected “often” or “always.” For females, 22 of 109 “frequently” texted while driving. For males, 13 of 59 “frequently” texted while driving. Test for a gender difference at the .1 level. 8. Gender differences for texting while getting ready? A recent survey asked UNG students to report how often they texted while getting ready in the morning. Responses were “never,” “rarely,” “sometimes,” “often,” and “always.” Students were categorized as “frequently” texting if they selected “often” or “always.” For females, 50 of 109 “frequently” texted while getting ready. For males, 13 of 59 “frequently” texted while getting ready. Test for a gender difference at the .05 level. 9. Being Perfect. Estimate the percentage of North Georgia students with highly perfectionistic personalities given 31 of 186 students surveyed met the criteria in a recent survey. Use a 95% level of confidence. 10. Naïve about Relationships. A recent research project used a score of 36 or higher on the Toxic Relationships Beliefs Scale as a cutoff value to determine whether a student was particularly naïve about relationships. Test for a gender difference in relationship naivite at the .05 level given that 18 of 79 males and 16 of 135 females surveyed were found to be partically naïve. Solutions 1. 2 Proportion Z-Test. Fails sample size verification (only 9 successes in male population). Data not appropriate for z-procedures. 2. 1 Proportion Z-Test. Reject null: z = 3.57 and p = .0002 3. 2 Proportion Z-Test. Fail to reject null: z = 1.33 and p = .1837 4. 1 Proportion Z-Interval. Between 24.0% and 35.2%, margin of error = 5.6% 5. 1 Proportion Z-Test. Fail to reject null: z = 1.27 and p = .1019 6. 1 Proportion Z-Test. Reject null: z = 3.25 and p = .0006 7. 2 Proportion Z-Test. Fail to reject null: z = -.34 and p = .7335 8. 2 Proportion Z-Test. Reject null: z = 2.98 and p = .0029 9. 1 Proportion Z-Interval. Between 12.0% and 22.8%, margin of error = 5.4% 10. 2 Proportion Z-Test. Reject null: z = 2.12 and p = .0338