TN Growth Measures Planning Document - PK
advertisement

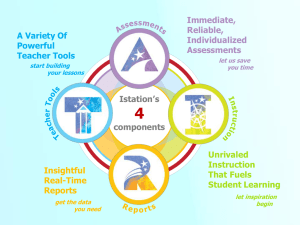
In #11, please provide the website where a reader could find the User Document. Please complete #18. No other specific changes are needed at this time. Please refer to the General Suggestions listed in the email sent by Heather Gage on March 3. TN Growth Measures Planning Document DEVELOPMENT TEAM: PK-Grade 3 DATE: February 18, 2011 INSTRUMENT SUGGESTION (include only one per document): istation Each Development Team should consider and answer the following questions for EACH instrument they recommend to the TN Department of Education. Completed planning documents and evidence documentation should be emailed to heather@educationfirstconsulting.com. **If the team is recommending a composite value-added score and/or a school-wide value-added measure, please go directly to number 19. QUESTIONS FOR ALL DEVELOPMENT TEAMS: 1. Does the instrument provide a valid and reliable academic score that would measure student growth? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. score achievement definition/level(s), scale score scale definition and example, technical manual, technical research studies, etc…) SEE ANSWER IN #2 BELOW. 2. Is the instrument valid and reliable? Provide documentation as evidence for each. (e.g. technical manual, technical research studies, face validity evidence, etc…) (Answering questions 1 and 2) ISIP is the assessment instrument that istation (formally Imagination Station) has developed. ISIP provides a valid and reliable academic score that measures student growth. See Appendix A which includes studies of the Catified Assessment that defines achievement scores and provides concurrent validity for the ISIP assessment. The istation model is an internet-based reading curriculum and assessment program that is designed to provide intervention to students in all of the areas and/or criteria for No Child Left Behind Law (NCLBL). Developed using scientifically based reading research, istation is a revolutionary, internet-based reading instruction and intervention program. The function of istation is to assess students, deliver differentiated instruction, and provide immediate (instant) data to schools so that more informed decisions may be made regarding placement in tiered instruction. Tiered instruction is a function of federal and state guidelines to more aptly categorize instructional levels of students. Thus a Tier I student is high functioning and near or on expected grade level and may need only intermittent interventions to sustain their academic growth. Tier II students function below their expected grade level and need continual reading intervention to accelerate achievement. Tier III students function two or more grade levels below their expected grade level and need intensive intervention for their reading skills to grow. External research of which some is academic and some is action research which offers evidence that istation is helping to increase student achievement in reading is noted as follows: The reports highlighted in blue are available in Appendix A, the other reports are available upon request: • At-Risk Including Reading Achievement of At-Risk Students From this study in, five school districts across the country, rural, suburban, urban areas all reported dramatic results after using the istation Reading Curriculum/Program with students who were at risk of reading failure. Students made striking improvements in the five key research- based reading components: phonemic awareness, phonics, vocabulary, fluency, and comprehension. With individualized Internet-based instruction and data driven teacher intervention, districts narrowed the achievement gap of “at-risk” learners. Other results of istation use are depicted in the following brief reviews of each study. These studies may be found in the attachment: • Research Based or Experimental or Quasi-Experimental Design, the following reports were also conducted by a third party: o Fort Worth Independent School District/TIMES and University of Houston TARGET Grant Proposal • Conducted under the direction of Dr. David Francis (2003-2004) revealed a positive impact in K-2. o Chambersburg Area School District/Shippinsburg University • Conducted by Dr. Jim Ryland, a professor at Shippinsburg, PA. There were gains in literacy indicated as measured by DIBELS that were statistically significant. o ISIP Validity and Reliability Analysis for the Chambersburg Area School District for 2007-2008 School Year • Dr. Jim Ryland and Dr. Reid Lyon of SMU conducted a Concurrent Validity study in 2007-2008. ISIP was found to have strong concurrent validity with DIBELS and surpassed DIBELS in the ability to predict end- of-year state test scores. o The Efficacy of Computer Assisted Tier 2 Assessment and Intervention as Part of A Response-to-Intervention Model o o o o o • Dr. Reid Lyon and Dr. Patricia Mathes, both of SMU professors are presently conducting a 3 year efficacy study in the Dallas Independent School District. ISIP Concurrent and Predictive Validity Study • Dr. David Francis reviewed the validated report written by Dr. Patricia Mathes after which he recommended that the ISIP test be placed on the Texas Commissioner’s List for Approved Assessments for grades K-3. Pacific Coast Research Conference in 2010 • The following paper was presented by Dr. Kevin Kalinowski and Dr. Patricia Mathes, Using Computer Adaptive Testing to Measure Reading Ability in Support of RTI. Presentation is in attachment. Florida Center for Reading Research • In 2007, both ISIP and the interactive curriculum were submitted to the state of Florida’s Call for Intervention program K3. istation was the only online intervention program to be approved by the Florida Textbook Department. istation’s Indicators of Progress Early Reading Validity and Reliability Evidence for Pre- Kindergarten • Dr. Patricia Mathes with SMU was the principal investigator of the study which showed very large evidence of validity with regards to letter knowledge, vocabulary and comprehension reading ability. Research and Development of ISIP AR Items • ISIP Advanced Reading assesses students in grades 4-10 in reading. This is a brief description showing how several state standards were used in the ISIP AR assessment for grades 4-10. The areas of reading primarily used for these assessments were Comprehension, Spelling and Vocabulary. From these standards, testlets were comprised of one reading passage and four questions about the passage. The istation model has sufficient instructional resources to deliver the training, products and services described in this proposal. It has existing implementations from the east coast to the west coast and has trained, implemented and serviced 450 districts and over 1,500 schools in 34 states. Over 35,000 teachers and staff have been trained in the past eight years. Some of the larger school districts being served include: Hillsborough County in Florida (600 persons), Prince Georges County in Maryland (700 persons), El Paso ISD, Texas (800), CypressFairbanks ISD in Texas (1,400 persons), Shelby County (Memphis) Tennessee (300), Katy ISD in Texas (1,200). Several districts have chosen a train-the-trainer model only, while others have requested that each teacher and administrator involved be trained by the istation trainers. Currently there are over 750,000 students being served by istation. They engagement of students and the acceleration of reading achievement will be apparent and provide the impetus to permit achievement where high mobility rates are at 45% or higher. istation has received follow-up surveys relative to training and also surveys after the implementation of the entire program. Teachers have made multiple comments from the surveys. Such comments include many statements regarding noted achievement for special education, ELL, dyslexia, and at-risk students in that there was evidence of closing the achievement gaps: • Since having our last data conference teachers are beginning to see istation’s value more and more. They have been very positive about their discovery of how well it documents student’s growth and how they can monitor intervention lessons as well as the ease in retrieving lessons. • It became a learning tool to see how the children progressed in all realms of learning. • The staff have found the information and lesson suggestions very useful especially as it applies to the Rti process. • The ease of use both for the students and teachers has been great. The teachers were able to see correlation between ISIP results and classroom results. • Teacher like having the assessment reports and the intervention lessons. It is an effective tool for the intervention process. • During parent conferences and report card reviews teachers express they use it with their students and appreciate having the program as an additional tool for their classroom. • When we were talking about moons the other day. I had the students new the answer, they said that it was on istation. • The students like to do and ask to go to work on the istation. • My students have made enormous gains in reading. Reading Research serves as the basis for all istation assessments and curriculum. The methodology behind istation Reading is based on best practices proven to be successful for reading growth and achievement. The National Reading Panel findings are the basis for the research. istation’s reading curriculum and assessments are based on solid research and independent studies. The data from these studies have proven the effectiveness and applicability of istation products and shown the positive impact of istation solutions on reading results. White Papers provide summaries that detail scientifically-based methods that build the foundation of the istation Reading products. Available upon request. • Correlation Paradox • Early Intervention Services and Response to Intervention • Research-based Preschool Early Literacy Curriculum • Supplemental Education Services • English Language Learners and istation Reading Curriculum State Adoptions and Awards • ISIP has been approved as an assessment for Early Reading in Texas K-3 • ISIP has been approved for School Readiness Certification System in Texas • • • • • istation Program has been an approved intervention in Florida for Supplemental/Intervention Textbook Adoption istation has been reviewed with no deficiencies by the Florida Center of Reading Research istation has been endorsed by the National Council of Administrators of Special Education (CASE) istation won the Bessie Award for Best Educational Software istation has been approved by the Virginia Department of Education as an assessment (ISIP) for the state. The curriculum program has also been approved as an RtI and intervention program • ISIP assessment has been approved by the National Response to Intervention Association as a Universal Screener and Progress Monitoring Instrument. There is a wide consensus about what comprises the elements of effective reading instruction (e.g. National Reading Panel, 2000; Rayner, Foorman, Perfette, Petsetsley, Seidenberg, 2001; Snow, Burns, Griffin, 1998). The development of istation has adhered to this research. Studies There has been evidence from several school district regarding the following issues: (1) decrease in referrals to special education. This is especially evident when “at risk” students have been provided the ISIP assessment and istation curriculum as an Early Intervening Service (EIS); (2) Identified special education students whose IEP reflect lesser time needed in special education and more time in general education classes; (3) Identified special education students whose IEP reflect total movement to the mainstream classroom; (4) Schools moving out of AYP deficit status; (5) Acceleration in reading achievement for the ELL populations; (6) Fewer referrals to the dyslexia program. From the list of references provided within attachment, at least one reference who has shown positive movement as related to each of the six issues stated above is listed below: • Issue 1: Decrease in Special Education Referrals o Katy ISD, TX o Shelby County Public Schools, TN o Cy Fair ISD, TX • Issue 2: Decrease time in Special Education o Shelby County Public Schools, TN • Issue 3: Movement from Special Education to Mainstream o Shelby County Public Schools, TN o Cy Fair ISD, TX • Issue 4: Moving from AYP deficit stats o Prince Georges County Public Schools, MD • Issue 5: Accelerated Reading Achievement in ELL populations o Semionle County Florida, FL o HEB ISD, TX • Issue 6: Fewer Referrals to the Dyslexia Program o Katy ISD, TX o Cy Fair ISD, TX Please refer to persons from these districts listed in the References attached as needed for more information. District/State Information: Shelby County School District (Tennessee) Shelby County School District uses the istation program as the basis for their RTI program. Prior to the referral of students to their special education program, students must be assessed weekly for a 9-12 week period using the istation assessment ISIP. Shelby County special education department required all of ISIP data reports be submitted for review prior to a student being accepted in Special Education. The istation program also has teacher directed lessons available related to each skill deficit noted by the assessment. Teachers must show they have provided such intervention. This can be done by a “click” by the teacher noting the date and name of teacher providing the intervention. o Results: In 24 months the referral rates to special education were reduced from 38% to 11%. o Shelby County officials credit the implementation of the RTI process based on the fidelity of implementation of the istation program which includes, online catified assessment, teacher directed lessons and the istation online curriculum program. o Now, 80% of Shelby County students are at a Tier I Level; 15% at a Tier II Level; and only 5% at a Tier III Level. Most of their Tier III students are in special education. Yet, they are able to show growth within Tier III. o Shelby County’s Tier I students are progress monitored every other month. But their Tier II and Tier III students are progress monitored monthly. • Virginia o Marion Intermediate School (Smyth County, VA) made consists of 430 third, fourth and fifth grade students. This school had not mad AYP for the last two years. After using the istation assessment and curriculum during the 2009-2010 school year, the percentage of all students passing the SOL reading test jumped from 79% to 90%. o The Virginia Department of Education required schools who had not met AYP to use the istation assessment program in the five months prior to their state high stakes test. The state tests in reading scores rose 5% across the state. Kathlean Smith, at the state department credits the rise to teacher and administrators actually having valid assessment data from which to work. Next year, the schools that did not make AYP in 2009-2010 will be required to not only use the ISIP assessment but also use the online reading curriculum for intervention. 3. Could the instrument be used for a statewide standardized administration? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. administration manual, administration criteria, effective standardized practices for administration, etc…) The ISIP assessment is presently being used for a statewide standardized administration for reading for grades K-12 for the state of Virginia because the student data can be exported and/or uploaded to a designated port. The Virginia Department of Education required schools who had not met AYP to use the istation assessment program in the five months prior to their state high stakes test. The state tests in reading scores rose 5% across the state. Kathlean Smith, at the state department credits the rise to teacher and administrators actually having valid assessment data from which to work. Next year, the schools that did not make AYP in 2009-2010 will be required to not only use the ISIP assessment but also use the online reading curriculum for intervention. 4. Could the instrument be implemented in all classrooms statewide? If yes, what resources would be required? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. technology required or not, costs per student for administration, scoring, and reporting, time considerations for administration, collection, and reporting) ISIP assessment can be implemented in all classrooms statewide. Computers are required, along with the following technical requirements: Specification Operating System Processor Memory System Requirements Windows Windows® 2000, XP, or Vista, 7 500 Mhz Pentium® III 256 MB RAM Mac OS X 10.3.9 or later 500 Mhz G4 256 MB RAM Hard Disk Graphic Display Sound Card Internet Connection 750 MB free space 800x600 with headphones 768 kbps or greater 750 MB free space 800x600 with headphones 768 kbps or greater ISIP can be administered to students within the classroom by rotating students to computers (3 or 4) or taking the entire class to a computer lab for 20-25 minutes. The actual assessment is online and requires 20-25 minutes to complete. At present, over 750,000 students are assessed by this assessment. These students are all assessed within one week by efficiently using the computers available. Upon completion of the assessment, reports are immediately available. When students are actually enrolled as subscribers to the assessment, demographic data is also available. Therefore, the timing for administration, collection of data and reporting is as follows: • Administration of ISIP o If computer labs are available, a classroom of students may be assessed within a 20-25 minute time period. o If students are assessed within the classroom, the rotation of students takes a little more time but a class of 27 students can be assessed via 3 computers in a class in about 4-5 hours. o Collection of data – as each administration is completed, reporting is instantaneous. Therefore, as each classroom is completed, as each campus is completed, and as each school district is completed, all data becomes available immediately with easy to read and use data reports to show growth. These reports also explicitly depict students’ instructional weaknesses in reading so that each Teacher, each Principal, each Administrative district staff and statewide staff is immediately aware of the state’s student strength and weaknesses in the area of reading. As the states decide to begin using ISIP, a window of assessments can be provided so that with a given time, all data will be available to the state offices. ISIP provides the initial screen/benchmark and can automatically progress monitor as often as desired. Assessment can be done automatically each month or can be done as a 3-4 benchmark, if desired. If only desire to measure students once a year, this can also be done. To show one year’s growth per year of instruction, the ability scores are used to measure from the beginning of the year to the beginning of the next year or to measure during a given year. The ability scores may be used from a beginning of the year score to the end of the year. Thus at least two administrations would be the necessary. These ability scores are noted on the Instructional Tier Goals in Appendix B. o Cost – The assessment is purchased on an annual basis (i.e. August to August) so that all summer programs are also assessed. The cost is $5 per student annually. This cost includes administration, scoring, reporting, and support services. All items related to ISIP are online. 5. Does the instrument measure content that represents essential instructional objectives? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. instrument to TN curriculum comparison and alignment, depth of knowledge reporting and alignment, etc…) ISIP measures the reading essential instructional objectives. It is aligned to the Tennessee Curriculum and the Common Core Curriculum. The istation company has aligned its curriculum and assessment to these standards. These alignments are lengthy but can be provided as the Development Team desire. 6. What scoring metrics are used for this instrument? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. scale score, scale, raw score, rubric score, etc…) The scoring metrics used for ISIP are as follows: • All scores are catified (shows ability scores) • All scores are also shown in percentiles • All students’ scores are also placed in Tier 1, Tier 2 and Tier 3 to easily show student growth and to also assist in providing a framework for RtI. • ISIP is an integrated, computerized adaptive testing that accurately reports the reading ability level of each student and measures growth over time. Adaptive assessments use interactive content to measure a student’s reading ability and skill development. Test questions range from easy to hard for each reading domain. To identify the students’ overall reading ability and individual skill ability, the difficulty of the test questions presented changes with every response. The ability score shows how a student is doing compared to their previous performance and to other students at the same grade level. The chart below depicts the subtest of the ISIP for PK-Grade 3: Grade Subtests Pre Kindergarten Letter Knowledge Vocabulary Phonemic Awareness Kindergarten 1st Grade Listening Comprehension Phonemic Awareness Letter Knowledge Vocabulary Phonemic Awareness Letter Knowledge Vocabulary Alphabetic Decoding Comprehension Spelling 2nd Grade Vocabulary Comprehensi on Spelling Text Fluency 3rd Grade Vocabulary Comprehensi on Spelling Text Fluency See Appendix B to view the Instructional Tier Goals for ISIP. These are the rages of ability scores by Tier Levels. See Appendix C to note normal scores by percentiles as related to the ability scores. 7. Does the scoring take into consideration all cognitive levels? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. Blooms Taxonomy, learning domains, knowledge dimensions, etc…) The cognitive levels of students are evidence by CAT and Tier Percentiles. Within the response to question 6 and the Appendix B & C, the cognitive levels of students are acknowledged. In using the Instructional Tier Goals, the ability level scores and the nationally normed percentiles, each student’s scores and academic growth can be determined in a reliable and valid manner. Also the Reading Level Correlation Chart (see Appendix D) is very helpful for teachers and principals to better understand student growth. 8. What performance (achievement) levels have been determined for the instrument? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. advanced, proficient, basic, below basic, below proficient, mastery, etc…) The responses offered in the responses to questions 6 & 8 provide the levels of achievement by the tiers, Tier I refers to a student who scores on or above their expected level (40th percentile or above); Tier II students score below their expected level (from the 30th percentile through the 39th percentile); Tier III students score far below their expected level (from 0 to 29th percentile). The national norms (percentiles) allow the viewer to note all academic growth from the smallest increment of growth to the largest. Movement of growth within tiers can be noted. 9. Could an individual student growth score be calculated from the instrument’s score? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. scale score, gain score, rubric score, etc…) SEE #10 BELOW 10. What measure of growth could be used based on the instrument? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. growth score, TVAAS, norm population, etc…) (Answering questions 9 and 10) Individual student growth scores are calculated after each assessment and immediately available visually by the Student Summary Report, see Appendix E for this report. Please note the CAT scores (ability level) is noted, like tier levels, the grade level equivalency and the percentile ranking. Therefore, no matter how small the growth, the ability score and that score’s relation to the percentile score can show any amount of growth. Please note the following reports available. All reports noted as district reports are also available as statewide reports. istation Reports Report Executive Summary Report Overview Brief overview of ISIP – ISIP Summary Presents by Tiers and Skill Growth Number & percentage of students in each tier for current month Targeted User Manager Account for campus, area or district Teacher, Campus, area, or district ISIP Cumulative Review Summarizes progress from the beginning of the intervention to the present month. Campus, area or district Shows number of students within each tier and depicts tier movement. Uses bar and pie graphs. Shows ISIP Skill Growth by Instructional Tier Goals Grand Level and Subtest Identifies student ability scores by tier level District, area, campus, teacher Glossary ISIP Summary by Area Describes each of the subtests Number of students by tier level in each grade and campus within the area. Depicts each school in the area by tier and scores All report users District and area ISIP Summary by School Depicts the number of students and percentage at each tier. Lists each teacher by grade level depicting tier levels Area, campus ISIP Summary Teacher Report Number and percentage of students at each tier level Teacher, campus, area, district with their ability level scores for each subtest Priority Report Alerts teachers of students needing additional support & provides lessons based on demonstrated weaknesses by tier and cycle level Student Summary Depicts overall status of each student: grade level, Teacher, campus, area, district current reading program cycle, last date used, total hours used, Lexile levels, ISIP Results for each subtest, ability level for each subtest and overall reading including tier levels for each. Each time a student is progress monitored, a data point is placed on the graph Teacher, campus 11. Could data be collected at more than one point in time? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. pre-post test design, prior year administration, multiple administrations, etc…) The data as suggested in responses 8 & 9 can be collected as often as the state desires. Historical data is available and can be obtained by the state by following the direction in the User’s Guide, which is also online [where]. 12. Is the instrument designed for secure administrations? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. secure design, secure delivery, etc…) The istation company ensures the security of the data. Please see Appendix F for istation’s Practices and Policy. 13. How are students with disabilities provided equal access through the instrument? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. accommodations, modifications, etc…) The following accommodations provide equal access through ISIP: Modifications/Accommodations for Students with Disabilities istation provides persons and employees with disabilities access comparable to access to persons without disabilities with the exception of a totally blind or totally deaf disabled person. Accommodations and modifications are specified below that will assist disabled persons (adults and students) with access to the total istation program. Several functions of istation serve as modifications and/or accommodations for special needs students which typify the universal design of istation: • Touch – screen overlay. This is a USB touch screen that can be applied to monitors and acts like a standard pointing device. Special needs specialist have been pleased that istation Reading worked so well with the touch-screen overlay. Even a student using a head stylus can use this device. • Zoom Tech zooming software. This is a type of software that allows the user to zoom in to a very low screen resolution (so things get bigger) with automatic scrolling of the screen when the mouse is moved. This is extremely helpful for the visually impaired. • Students’ fluency is measured on an individual basis. The program then allows each child to receive instruction at his fluency rate. It will not move faster than his identified fluency rate. Therefore, if a student is guessing and/or randomly clicking, the program will alert the teacher. • When asking a child to choose the correct answers, the program automatically decreases the number of possible answers from four to two depending on the students’ needs. • In reading, istation stories, the program models the expected fluency rate for each level. The words are sounded out phonologically and phonetically with illustrations to provide multiple ways for a student to learn. Stories are read to the student as needed. • Illustrated sentences are provided from single skill readers to multiple skill readers. 13 14. How are students exposed to the format of the instrument prior to the administration? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. practice assessments, item samples, similar instrument integrated into instructional measurement, etc…) Since ISIP is totally administered online, the student is given explicit information about the assessment they are getting ready to take. The narrator models the test, then has the student do practice sessions, then requests the student now takes the test. See Demo CD and DVD enclosed to actually experience these activities. 15. Are there any noted unintended consequences? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. bias, misinterpretation of results, restricting curriculum, fairness, etc…) As of this date, no user has indicated any unintended consequences. 16. How does the instrument impact instruction? Provide documentation as evidence. (e.g. differentiate instruction, improve student achievement, direct student interventions, etc…) ISIP impacts instruction by the following: Teacher Directed Lessons (TDLs) are provided. The TDLs are written as direct instruction and provide explicit instruction through the following lesson design: teach, guided practice, independent practice, and reteach if needed. These TDLs automatically are suggested as each student shows a need in any of the reading subtest. These lessons are designed for Tier I, Tier II and Tier III students. After the teacher uses the lesson in small group instruction, the teacher can then indicate online that the student has received this instruction. Thus there is an audit which is excellent for an RtI program model. See Appendix G for a sample of TDL. It should be noted that there are over1000 TDLs available for teachers to use in small group instruction. 17. What are the barriers to using the instrument (statutorily, regulatory, etc.)? As of this date, these do not appear to be any barriers in using the ISIP assessment statutorily. 14 18. How has the team reached out to other educators in its representative category (grade/subject) for ideas? Please explain the result of that outreach. IF THE DEVELOPMENT TEAM RECOMMENDS EITHER A COMPOSITE VALUE-ADDED MEASURE (claiming of specific tested students) OR A SCHOOL-WIDE VALUE-ADDED MEASURE FOR THE EDUCATOR CATEGORY, THE TEAM MUST PROVIDE THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION (instead of the questions above): 19. Please provide a brief description of the process the development team took that led to the decision to recommend using either a composite value-added measure and/or a school-wide value-added measure for evaluation purposes. Be sure to include: a. The rationale for this choice and why other instruments are not being recommended. b. How the team reached out to other educators in its representative category (grade/subject) for ideas? Please explain the result of that outreach. NOT APPLICABLE 15