Emergency Drug Dosages - print and keep in
advertisement

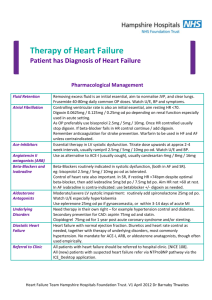
Use of Emergency Meds in the Doctor’s Bag Diagnosis Medication a) Adrenaline 1mg/ml ( 1:1000) Anaphylaxis b) Hydrocortisone Injection 100mg/ml “ c) Chlorpheniramine 10mg/ml Meningococcal Meningitis Benzyl Penicillin 600 mg Status Epilepticus Rectal Diazepam 10 mg rectube) Hypoglycaemia Glucagon 1 mg ( Age Dose Route >12 years 6-12 years Under 6 years > 12 years 6-12 years 6 months - 6 years Under 6 months >12 years 6-12 years 6 months - 6 years Under 6 months > 10 years 1-9 years < 1 year > 12 years and adults 2-12 years 1-2 years Adults & Children > 20 kg weight Children < 20 kg weight 500 micrograms ( 0.5mls) 300 micrograms (0.3mls) 150 micrograms ( 0.15mls) 200 mg 100 mg 50 mg 25 mg 10 mg 5 mg 2.5 mg 250 microgram / kg 1.2 grams 600 mg 300 mg 10mg - 20 mg 5mg - 10 mg 5mg IM IM IM IM or slow IV IM or slow IV IM or slow IV IM or slow IV IM or slow IV IM or slow IV IM or slow IV IM or slow IV IM IM IM Rectal Rectal Rectal 1mg IM 0.5mg IM ADDITIONAL NOTES FOR MENINGITIS Withhold Benzylpenicillin in children and young people who have a clear history of anaphylaxis after a previous dose; a history of a rash following penicillin is not a contraindication” Management of suspected bacterial meningitis WITH non-blanching rash: GIVE a single dose of parenteral benzylpenicillin at the earliest opportunity Management of suspected bacterial meningitis WITHOUT non-blanching rash:: DO NOT GIVE any parenteral antibiotic treatment unless urgent transfer to hospital is not possible. DR Sudhir Krishnan, November 2015