BI12_LG_U11 - BC Learning Network
advertisement
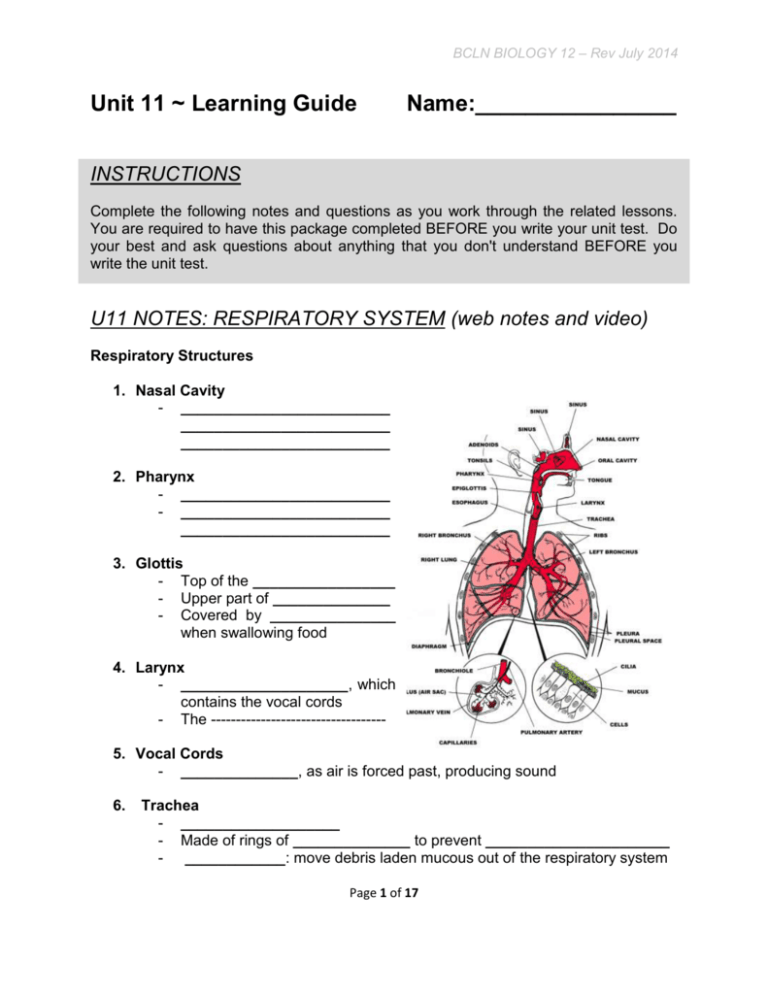
BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 Unit 11 ~ Learning Guide Name:________________ INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit test. Do your best and ask questions about anything that you don't understand BEFORE you write the unit test. U11 NOTES: RESPIRATORY SYSTEM (web notes and video) Respiratory Structures 1. Nasal Cavity - _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ 2. Pharynx - _________________________ - _________________________ _________________________ 3. Glottis - Top of the _________________ - Upper part of ______________ - Covered by _______________ when swallowing food 4. Larynx - ____________________, which contains the vocal cords - The ----------------------------------5. Vocal Cords - ______________, as air is forced past, producing sound 6. Trachea - ___________________ - Made of rings of ______________ to prevent ______________________ - ____________: move debris laden mucous out of the respiratory system Page 1 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 7. Bronchi - Branches of the _______________ - One to each _______________ - Bronchus; singular 8. Bronchioles ______________ _____________ of the bronchi ______________ for support 9. Alveoli - _______________ _______________ of very small bronchioles - Area where _____ _______________ _______________ 10. Pleural Membranes - ____________________________________________ of the lungs - ____________________________ - Allows the surface of the lungs to ____________ over the body wall easily - Seals off ________________________________________ 11. Thoracic Cavity - Chest cavity - From diaphragm to throat 12. Diaphragm - Horizontal muscle - Separates the _______________________________________________ 13. Ribs - Protects _____________________________ - When ribs contact with the intercostal muscles, they rise and increase ___________________________________________________________ Page 2 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 Air passageways: Filters, Warms, Moistens Several things happen to the air on its journey into the alveoli including: 1. Cleansed of debris: This is a two-part process: a. The initial cleaning is by the _________________________ ______________in the nasal passageways. b. The second is the process that occurs further along were the accumulation of debris can no longer get out of through the nose. This is the role of the mucous lining and the ____________________________________. Pretty well any material other than the gasses of the inhaled air will get caught in the mucous. The cilia are in ___________________________ beating the debris-laden mucous upward towards the ________________. When this material is detected at the back of the mouth, it is _________________ (or coughed up and spit out) 2. Adjusted to body temperature: The more contact the air has with moist tissues that are 37°C, the closer the air itself gets to 37°C. By the time air gets to the alveoli, there will be no __________________________________________ than that of the surrounded tissues. 3. Adjusted to 100% humidity: The air in the lungs is ____________________________ _____________. One of the things that happens to inhaled air is that it, too, becomes saturated with water. This is an obvious outcome of having passed over the mucous lined passageways. Specializations of Alveoli 1. They are ___________________________________. Up to 300 million alveoli in the human lung. This provides _______________________________________ ____________________________________. Page 3 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 2. They are _________________________________. Alveolar walls are only ____________________________. This aids in ______________________. 3. The alveoli have a coating of lipoprotein on their inner surface. This helps to maintain surface tension thus preventing them from ___________________________________ together during exhalation. 4. They are supplied with __________________________. These are nerve endings that are ______________________________. During inhalation, these signal when the alveoli are full enough (stretched). This marks the onset of ______________________. 5. The alveoli surfaces have a very rich blood supply from the pulmonary capillaries to ensure maximum diffusion. They are highly _________________________. 6. Made up of Squamous (flat) Epithelial cells. YOU SHOULD WATCH THE SPECIALIZATION OF THE ALVEOLI VIDEO BEFORE PROCEEDING ANY FURTHER! 3 Things That Make the Lungs Very Efficient at Gas Exchange 1. Huge surface area 2. Only 2 cell layers separate air in lungs from the blood 3. Moist Processes of the Respiratory System The Respiratory System supplied the body with oxygen for tis energy production. Without Oxygen, the body shuts down in minutes. The Respiratory System works closely with the Circulatory System. Page 4 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 Four Processes make up the Respiratory System 1. Breathing - Inspiration - ________________________________________________ - Expiration - _________________________________________________ 2. External Respiration - ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 3. Internal Respiration - ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 4. Cellular Respiration - Production of ___________________________________________ within the cells. Pleural Membranes 2 sets of membranes: 1. one joined to the lung 2. one joined to the ribs and diaphragm The two sets are close together separated by a slight amount of fluid (vacuum is created). If the membranes are punctured, air enters the intrapleural space, destroying the vacuum. _______________________________ _________. They maintain an interpleural pressure that is less than atmospheric pressure; keeping the lungs open. Page 5 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 Mechanics of Breathing: Inhalation and Exhalation The chest cavity is dome-shaped. The top and sides are surrounded by the ribs. The bottom is made up by the diaphragm. It is a ___________________ _______________________. Inhalation: 1. ___________________________________________________ are the PRIMARY STIMULI that cause us to breathe. When Carbon Dioxide and/or Hydrogen ion concentration gets too high, the Breathing center in the __________________________ is stimulated. 2. A nerve impulse is sent from the Medulla Oblongata _____________________________________________________. to the 3. The diaphragm contracts and ____________; the rib muscles contract (intercostal muscles) and raise the ribs. These actions increase the size of the chest cavity. Increased volume, ________________________________. 4. A partial vacuum is created in the lungs (air pressure in the lungs is reduced). 5. Air Rushes into the lungs from outside in order to rebalance the pressure. This is the process of inspiration. **NOTE: Air comes in because the lungs have already opened. The air does not force the lungs open. This is why it is said that we breathe by ________________________. (Low pressure sucks the air into out lungs) **NOTE: The lungs themselves have no muscles** Exhalation: 1. When the lungs are full, stretch receptors in the alveoli are stimulated 2. The Medulla Oblongata is notified and stops sending messages. 3. The diaphragm and rib muscles relax. 4. The chest cavity gets smaller. Decreasing volume, which increases the pressure in the lungs. _____________________________________________________. Page 6 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 Summary of Inhalation and Exhalation Page 7 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 In addition to the Respiratory Center in the Medulla Oblongata, there are other receptors that can respond to stimuli: a. Carotid bodies - in the ________________________________ b. Aortic bodies - in the _________________ These respond to high concentration of Hydrogen Ions but can also respond to levels of carbon dioxide in the blood. Gas Exchange When _____________________ diffuses from the cells into the blood, only a small amount of it (9%) reaching the blood is held in simple solution (as dissolved carbon dioxide). Another ______ attaches directly to the Hemoglobin to form _________________ ________________________. This remaining 64% combines with water to form ______________________________ and hydrogen ions. Each time blood passes through the tissues it picks up large quantities of _________________________________. This then reacts with water to form Bicarbonate (_______) and Hydrogen Ions (____). There are many substances in the blood capable of binding the excess free __________________. ________________________ is one of the most important of these substances. When Hydrogen (H+) combines with the hemoglobin (Hb), the Hb releases some of the oxygen attached to it. YOU SHOULD WATCH THE INHALATION AND EXHALATION VIDEO BEFORE PROCEEDING ANY FURTHER! Gas Exchange in Tissues Internal Respiration 1. 9% of CO2 diffuses into the blood from the cell and travels through the blood as dissolved CO2. 2. 27% of CO2 binds to hemoglobin to form carbaminohemoglobin. 3. 64% of CO2 joins with water to temporarily make carbonic acid which breaks down right away to the ______________________________________________ Page 8 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 ____________________. Carbonic Anhydrase = enzyme that runs this reaction. 4. Most of the released H+ is picked up by the combined form O2 and hemoglobin __________________________________. The binding of H+ by HbO2 produces ____________________________________________ aids in the release of oxygen. The H+ concentration and the slight increase in temperature alter the hemoglobin (protein denatures slightly) and releases oxygen easily. 5. Oxygen then enters the tissue moving from an area of high concentration to areas of low concentration. The blood leaving the tissues now contains large quantities of hemoglobin which is free of oxygen, and is called ____________________________ (HHb). The blood also contains large amounts of __________________________ (HCO3-). No further changes occur until the blood reaches the lungs. What to know….. **Be sure you understand all of the equations shown in the diagram to the right. Be able to name all the molecules and identify the equations as internal respiration.** Gas Exchange in the Lungs External Respiration 1. High concentration of Oxygen in lungs. Oxygen diffuses ___________________. Page 9 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 2. Oxygen joins with _______________________________ to form Oxyhemoglobin and Hydrogen ions. 3. H+ picked up by _________________________ to temporarily form carbonic acid which breaks down right away to produce CO2 + H2O. 4. The dissolved CO2 simply _____________________ into lung alveoli where it is expelled by normal breathing. 5. The _____________________________________ breaks down to CO2 and a hemoglobin molecule. The CO2 diffuses into the lungs and is expelled and the hemoglobin pick up oxygen. **NOTE: H+ does not accumulate because as soon as it released from HHb, it combines with HCO3- to release Carbon Dioxide. Hemoglobin is essential in the blood because it serves as a carrier for ____________________________________________________ ____________________ (acts like a buffer).*** ___________________________ which allows hemoglobin to grab oxygen easier. What to know….. ***Be sure you understand all of the equations shown in the diagram above. Be able to name all the molecules and identify the equations as external respiration. It's easy if you just reverse the equations from internal respiration.*** YOU SHOULD WATCH THE INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION VIDEO BEFORE PROCEEDING ANY FURTHER! Page 10 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 U11 PRACTICE: RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1. Label the respiratory system diagram below and provide a brief description of each structure's functions. (18 marks) o o o alveoli diaphragm larynx o o o pleura pharynx trachea o o o bronchial tube bronchioles nasal cavity 2. Use a flow chart with arrows to describe the path of air flow from the nose to the alveoli during inspiration. (7 marks) Page 11 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 3. Describe how debris and particulate in air is removed from the lungs. (3 marks) 4. Where is the respiratory center located? (2 marks) 5. What stimuli signal the respiratory center to initiate breathing? (2 marks) 6. What prevents the alveoli from over filling during forced inhalation such as when exercising? (1 mark) 7. How does oxygen gas move from the alveoli to the blood across the walls of the alveoli and the capillary? (1 mark) 8. Oxygen is actually transported throughout the blood primarily as a complex within red blood cells, what is this complex called? (1 mark) Page 12 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 9. In what form is carbon dioxide found in plasma? Carbon dioxide reacts with water in red blood cells to produce what compounds? What enzyme assists in this process? How does hemoglobin help with carbon dioxide transported by red blood cells? (5 marks) 10. Hemoglobin helps to buffer the blood by binding to excess hydrogen ions. What is the name of the complex that forms between hydrogen ions and hemoglobin? (1 mark) 11. Give the full name for the following abbreviated compounds related to respiration and gas exchange. (5 marks) O2 CO2 Hb HbO2 HHb HbCO2 H+ H2CO3 HCO3- H2O Page 13 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 12. List the set of equations that describe external respiration in the alveoli of the lungs. Remember the alveoli supply oxygen to the blood and receive carbon dioxide and water from the blood for removal. (4 marks) 13. List the set of equations that describe internal respiration in the capillary bed between the capillary and the tissue fluid. Remember the tissues receive oxygen from the blood and dump carbon dioxide and water into the blood (4 marks) ~ END OF BIOLOGY 12 UNIT 11 LEARNING GUIDE ~ Page 14 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 UNIT 11 ANSWER KEY U11 PRACTICE: RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1. Label the respiratory system diagram below and provide a brief description of each structure's functions. (18 marks) o o o alveoli diaphragm larynx o o o o o o pleura pharynx trachea bronchial tube bronchioles nasal cavity nasal cavity = warms, moistens and filters air pharynx = where food and air cross to enter esophagus and trachea, respectively larynx = voice box trachea = carries air from pharynx to bronchi of lungs Bronchial tubes = branch from trachea into each lung Pleura – membranes surrounding and protecting lungs Bronchioles = smaller branches off of bronchial tubes alveoli = blind air sacs where gas exchange occurs with capillaries diaphragm = contracts for inhalation, relaxes for exhalation 2. Use a flow chart with arrows to describe the path of air flow from the nose to the alveoli during inspiration. (7 marks) nose/mouth pharynx glottis trachea bronchi bronchioles alveoli Page 15 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 3. Describe how debris and particulate in air is removed from the lungs. (3 marks) = captured by mucus lining trachea and lungs, then mucus is propelled up to mouth by cilia, where it is then swallowed or spat out of the body = sometime coughing is necessary to help move mucus upwards 4. Where is the respiratory center located? (2 marks) = medulla oblongata of brain 5. What stimuli signal the respiratory center to initiate breathing? (2 marks) = increased CO2 and H+ concentration stimulate increased breathing rate via the respiratory center of the medulla oblongata 6. What prevents the alveoli from over filling during forced inhalation such as when exercising? (1 mark) = alveolar stretch receptors detect inflation of alveoli and send a signal via the Vagus nerve to the respiratory center of the medulla oblongata that stops the phrenic nerve and intercostal nerves from stimulating the diaphragm and intercostal muscles from contracting, resulting in relaxation of these muscles and exhalation 7. How does oxygen gas move from the alveoli to the blood across the walls of the alveoli and the capillary? (1 mark) = diffusion 8. Oxygen is actually transported throughout the blood primarily as a complex within red blood cells, what is this complex called? (1 mark) = oxyhemoglobin 9. In what form is carbon dioxide found in plasma? Carbon dioxide reacts with water in red blood cells to produce what compounds? What enzyme assists in this process? How does hemoglobin help with carbon dioxide transported by red blood cells? (5 marks) = dissolved CO2 in plasma = when CO2 reacts with H2O in red blood cells it is converted to bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) and hydrogen ions (H+) = carbonic anhydrase = reacts with CO2 to form carbaminohemoglobin Page 16 of 17 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 10. Hemoglobin helps to buffer the blood by binding to excess hydrogen ions. What is the name of the complex that forms between hydrogen ions and hemoglobin? (1 mark) = reduced hemoglobin 11. Give the full name for the following abbreviated compounds related to respiration and gas exchange. (5 marks) O2 = oxygen CO2 = carbondioxide Hb = hemoglobin HbO2 = oxyhemoglobin HHb HbCO2 = carbaminohemoglobin = reduced hemoglobin H+ = hydrogen ion H2CO3 = carbonic acid HCO3- = bicarbonate ion H2O = water 12. List the set of equations that describe external respiration in the alveoli of the lungs. Remember the alveoli supply oxygen to the blood and receive carbon dioxide and water from the blood for removal. (4 marks) Hb + O2 HbO2 HbCOs Hb + CO2 HHb Hb + H+ H+ + HCO3- H2CO3 H2O + CO2 13. List the set of equations that describe internal respiration in the capillary bed between the capillary and the tissue fluid. Remember the tissues receive oxygen from the blood and dump carbon dioxide and water into the blood (4 marks) HbO2 Hb + O2 H2O + CO2 H2CO3 H+ + HCO3Hb + CO2 HbCOs Hb + H+ HHb Page 17 of 17