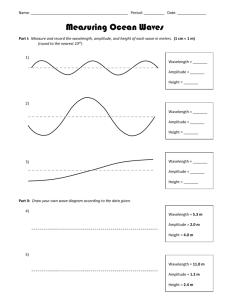
ELECTRON ARRANGEMENT WORKSHEET
advertisement
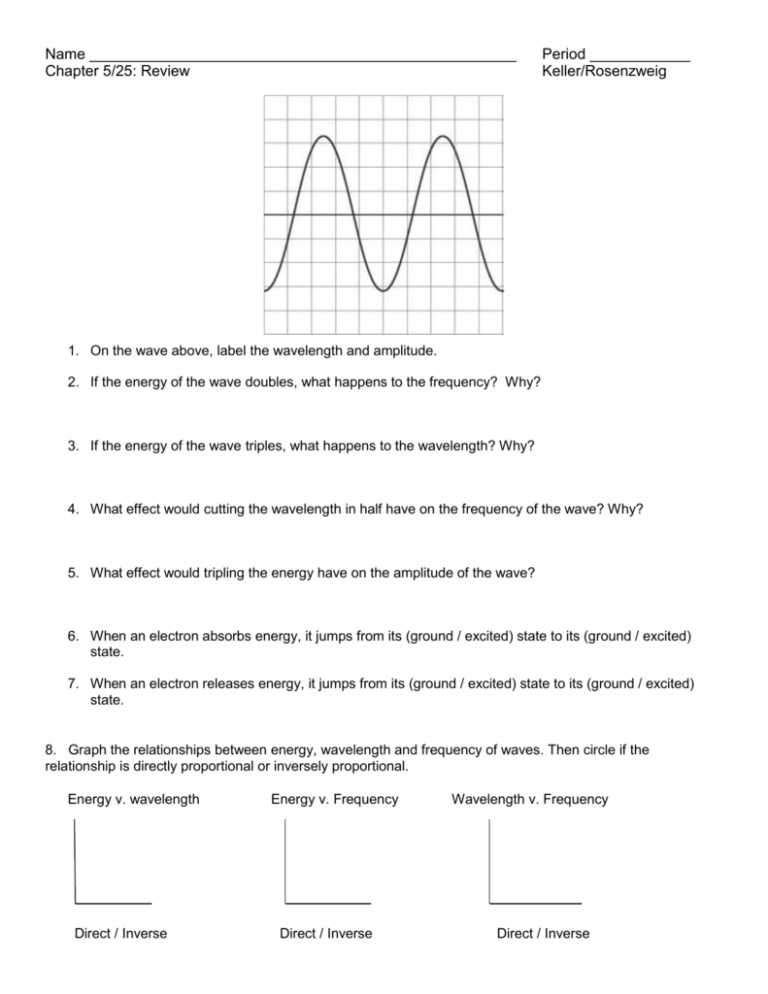
Name ___________________________________________________ Chapter 5/25: Review Period ____________ Keller/Rosenzweig 1. On the wave above, label the wavelength and amplitude. 2. If the energy of the wave doubles, what happens to the frequency? Why? 3. If the energy of the wave triples, what happens to the wavelength? Why? 4. What effect would cutting the wavelength in half have on the frequency of the wave? Why? 5. What effect would tripling the energy have on the amplitude of the wave? 6. When an electron absorbs energy, it jumps from its (ground / excited) state to its (ground / excited) state. 7. When an electron releases energy, it jumps from its (ground / excited) state to its (ground / excited) state. 8. Graph the relationships between energy, wavelength and frequency of waves. Then circle if the relationship is directly proportional or inversely proportional. Energy v. wavelength Direct / Inverse Energy v. Frequency Direct / Inverse Wavelength v. Frequency Direct / Inverse 9. Using the electromagnetic spectrum provided, arrange the types of electromagnetic radiation listed below in order of increasing (smallest to largest) energy, wavelength, frequency and speed: green light, orange light, radio waves, gamma rays Energy: _____________ < _____________ < _____________ < _____________ Wavelength: _____________ < _____________ < _____________ < _____________ Frequency: _____________ < _____________ < _____________ < _____________ Speed: _____________ < _____________ < _____________ < _____________ 10. Fill in the blanks to complete the following nuclear reactions: 236 1 0𝑛 94𝑃𝑢 3 1𝐻 145 54𝑋𝑒 + 1 0𝑛 + _________________ + _________________ 42𝐻𝑒 + 11𝐻 22 11𝑁𝑎 (beta decay with gamma radiation) 210 86𝑅𝑛 (beta capture) 248 98𝐶𝑓 (alpha decay ) 11. Complete the chart below. Name Symbol Charge Alpha Beta Gamma 12. What is the difference between fission and fusion? REVIEW: 13. How many atoms are in 45.7g of nickel? Mass Level of Radiation