HW Packet 1 - EPIC Chemistry
advertisement

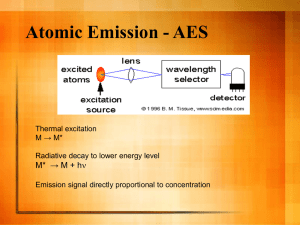
Name _________________________________________________ Date ___________________________________ HONORS Homework #1 Purple Due: April 16 & Green Due: April 17 Directions: Read the following passage and answer the questions below. Did you know that there are four states of matter? Read this article to find out about the fourth, plasma. The four states of matter are as follows: solid, liquid, gas and plasma. This last term is relatively unknown outside of the scientific world. What is plasma? How does it get the distinction of a state of matter? This article will address the nature and expanding science of plasma. Plasmas were identified by the English scientist William Crookes in 1879. He noted that plasmas are mixtures of particles and fields. They are found in everything from the sun to quarks, the smallest particles in the universe. Plasmas can generate explosions, freeze, carry electrical currents and support magnetic fields within themselves. Almost the entire universe is made of plasma, and it existed before any other forms of matter came into being. Space plasmas can contain enough heat to melt the earth thousands of times over. Crystal plasmas can freeze the earth at least a hundred times, one after the other. (The northern lights are one example of cooler plasma, or the interaction of the earth's atmosphere with solar winds.) And plasma can actually exist in a state about the size of a cell nucleus-an incredibly dense pinpoint of matter. A plasma, as defined by physicists, is a gas-like state of matter in which all (or many) of the electrons have been stripped from the nuclei they orbit. Atoms are not otherwise bound to each other as in a crystal or a metal. The negatively charged electrons and the positively charged nuclei (ions) co-exist and intermingle but do not, on the average, recombine to form stable, neutral atoms or particles. The term "plasma" was initially applied to ionized gas. Plasma is actually what fills the so-called "empty" space between the sun and the earth, and also most nebulae and stars. The space it fills between the earth and the sun is actually most characterized by the "solar wind," or the plasma emissions of the sun. Imagine heated waves moving from the sun, and the Big Bang, through the universe. This is plasma's common form in space. The key to this concept is the idea of movement. Plasmas consist of electrons and ions moving around in a contained space. Often, the ions are trying to return the neutral state of a Noble gas by filling their electron levels. Plasmas can come together into a neutral gas, but can never stay in this state due to the ions within them. We are just now learning to control plasma by using the electric and magnetic fields within them to steer them. Looking at the idea of plasma, one can see that it is possible that the universe is shaped and controlled by plasma's magnetic and electric fields. Actually, recombination of electrons and nuclei occurs continuously; this process is accompanied by the emission of light. This is why a plasma, such as occurs within a neon tube, lightening, or a flame, gives off a characteristic light. But, due to thermal energy (flame) or continued electrical excitation (neon tube), recombined electrons/ions are quickly knocked apart again, maintaining the average state of a mixture of free electrons and ions. So in a nutshell, plasma is made of atoms. Atoms contain a balance of positive and negative charges, brought on by negatively-charged electrons moving around a positively-charged nucleus. Plasma occurs when this balance is set to heat, or another form of disruption. Ions and negatively charged electrons make it different from a solid, liquid or gas. 1. Based off of the passage, how is plasma formed? 2. Based off of the passage, what is plasma made of? 3. Based off of the passage, what are 5 examples of plasma? 4. Based off of the passage above, what state of matter is plasma most alike? 5. Which state of matter are stars? 6. List the 4 states of matter in increasing order of Kinetic Energy. 7. Based on the passage, what do you think is the most common state of matter in the UNIVERSE and why? Determining Purpose Directions: Write a 1-2 sentence purpose for each question posed below. Remember to use the question stem in order “to determine” the purpose. 8. How are the volume and temperature of a gas related? 9. Which antacid is better at reducing acid reflux, also known as heartburn, Tums or Prilosec? 10. How are speed and acceleration related? 11. What is the relationship between the temperature of a substance and its kinetic energy? Conclusion Debrief Directions: Using the data below, answer the following questions. Figure 1. Relationships between the 4 states of matter 12. Based on Figure 1, which conclusion is best supported by the model? a. All bound states of matter consist of free moving particles b. All bound states of matter consist of organized systems of particles c. All liberated states of matter consist of organized systems of particles d. Gas, plasma, and liquid are considered to be liberated states of matter e. The state of matter, whether bound or liberated, does not depend on how the particles are organized 13. Based on Figure 1, which conclusion is best supported by the model? a. As the states of matter move from being organized, or bound, to unorganized, or liberated, the enthalpy of the system remains constant b. As the states of matter move from being organized, or bound, to unorganized, or liberated, the enthalpy of the system decreases c. As the states of matter move from being organized, or bound, to unorganized, or liberated, the enthalpy of the system increases d. As the states of matter move from being unorganized, or liberated, to unorganized, or bound, the enthalpy of the system increases e. Liquids have the highest enthalpy of all four states of matter 14. Based on Figure 1, which prediction would NOT be supported by the model? a. Vaporization only occurs between liquids and gases b. As the enthalpy of liberated states of matter decreases, they transition into the bound state c. As the enthalpy of bound states of matter increases, they transition into the liberated state d. There is an indirect route of transition between liquids and plasma e. There is a direct route of transition between liquids and plasma