Components of Blood - components, how blood separates, what
advertisement

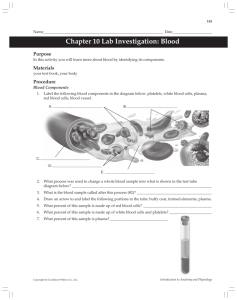
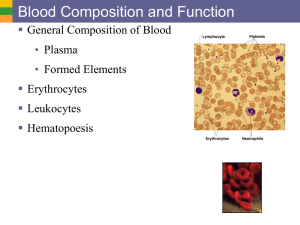
Components of Blood - components, how blood separates, what percentage is RBCs, buffy coat, plasma, etc. - physical characteristics of blood - what is contained in the blood plasma - how plasma proteins and salts function in maintaining osmotic pressure - what osmosis is - characteristics and the three examples of plasma proteins - types of formed elements - general characteristics of erythrocytes and leukocytes; differences between them - describe the function of hemoglobin - definition of anemia and leukemia - 5 types of leukocytes – be able to describe the function of each type - difference between lymphoid and myeloid stem cells - structure and function of platelets - what hematopoiesis is, where it occurs, what lymphoid stem cells produce and what myeloid stem cells produce Hematopoeisis and Hemostasis - what controls rate of RBC, WBC, and leukocyte production - blood doping – review questions and article - three phases of blood clotting and what occurs in those phases - describe a thrombus and an embolus Buffers: - Physiological acidsosis vs. normal acidosis - Where most H+ ions come from - Three systems in the body that control pH? Which plays the biggest role - Basic definition of an acid, base, strong acid, strong base, weak acid, and weak base - What a buffer is – how does it prevent changes in H+ ion concentrations? - two parts of the bicarbonate buffer system – sodium bicarbonate and carbonic acid - Why a weak acid or a weak base still might need buffering - what happens when an acid or base is added to a buffer system Blood Transfusions and Typing - what happens as a result of blood lose - what a transfusion is - What happens during a transfusion reaction (i.e. agglutination, blockage of kidney tubules, etc.) - Definition of an antigen - Definition of an antibody - Difference between a blood group and a blood type - Know how to go back and forth between blood type, antibodies present, and antigens present. - difference in production and presence of Rh vs. ABO antibodies - describe universal donor and universal recipient - what happens in various examples of blood transfusions