Chapter 10
advertisement
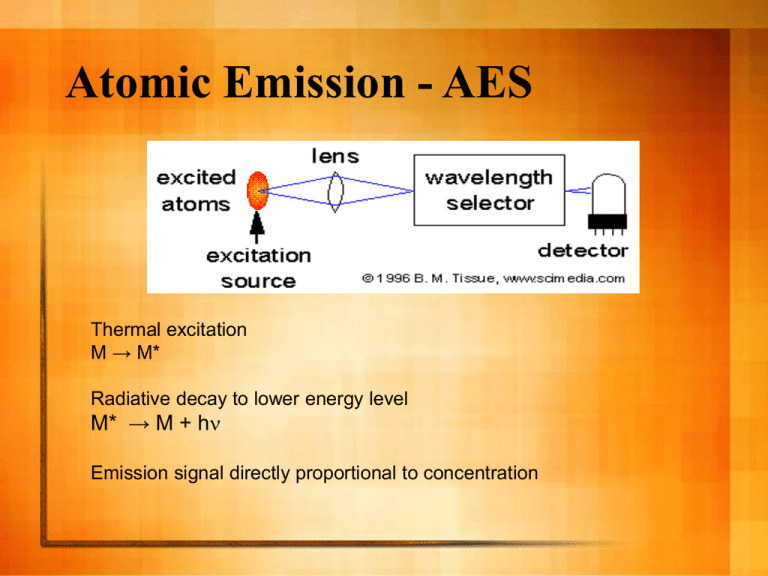
Atomic Emission - AES Thermal excitation M → M* Radiative decay to lower energy level M* → M + hn Emission signal directly proportional to concentration Holy Grail of Atomic Spectroscopy For one sample: The ability to measure all elements at all ranges of concentration at one time. Excitation Source The atoms are excited by energy provided by the source. The energy created by a flame can excite only a few atoms, e.g. alkali metals Other atoms (especially non-metals) need much higher energy - plasma If you only have a flame instrument, you can use AES for alkali metals (and a few others), otherwise you should use AAS to achieve good detection limits. Types of high energy analytical plasmas DC Arc 4000-5000 K HV Spark 40,000 Direct Current Plasma 6000-10,000 Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) 6000-8000 Microwave Induced Plasma (MIP) electrodeless 5000-7000 Capacitively Coupled Microwave Plasma (CMP) electrode 5000-7000 Plasmas Ionized gas that is electrically neutral Very high temperature and energy Contains ions, electrons, neutral atoms & molecules Inductively Coupled Plasmas Ionized Ar flow, sustained in a torch by the RF field generated by induction coils. Up to 20 mL/min Ar flow Annual cost of several thousand dollars Characteristics of Plasma AES Sufficient energy to excite all elements Capable of doing solids, liquids, or gases -sample introduction via nebulizer, ETV, laser ablation, others Tolerant to variety of solvents and solutions Simultaneous multielement analysis Large Linear Dynamic Range (LDR) Low LOD ICP-AES spectrum ICP AES Calibration Curve If you can interpret your spectrum, you can get great quantitative results. Calibration curve is plotted as log/log, because the LDR spans several orders of magnitude. Internal Standard An internal standard is used to compensate for various random (and even systematic) errors. A big random error in plasma emission spectroscopy is power/intensity fluctuations of the plasma. Reasoning: fluctuations effect on analyte will be the same as the effect on the internal standard. Quantitative Analysis - Calibration with Internal Standard Internal standard must be something not present in your standards or sample (in this example, Y) The signal plotted is the ratio: Intensity ratio = Analyte signal Yttrium signal Homework problem 3 500 y = 4.2781x + 7.1758 450 y = 0.7619x + 1.0441 2.5 log intensity ratio intensity ratio 400 350 300 250 200 150 2 1.5 1 100 0.5 50 0 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 Cu co ncentration (p pm) linear-linear plot 120 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 log co ncentration (ppm) log-log plot When your LDR spans more than 2 orders of magnitude, it can be helpful to do a log-log plot so you can see your data points better. ICP Advantages Analysis of solutions or dissolved solids Disadvantages ionization leads to complex spectra need high resolution monochromator LDR spans several orders of magnitude Expensive Detection limits in the parts per billion range Multielement analysis: Determine up to 70 elements in two minutes per sample Plasma source leads to messy background fluctuations