CIS_182_Exam_1_Review_(chs_1,2,3,4,FO,IO)
advertisement
Chapter 1
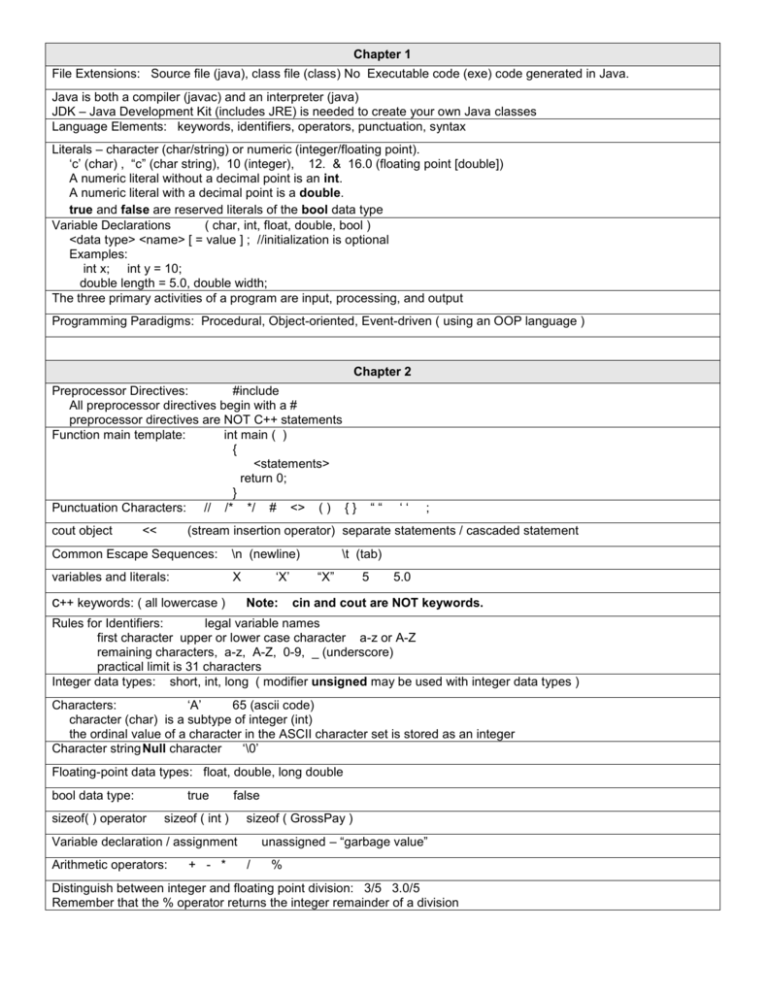
File Extensions: Source file (java), class file (class) No Executable code (exe) code generated in Java.
Java is both a compiler (javac) and an interpreter (java)
JDK – Java Development Kit (includes JRE) is needed to create your own Java classes
Language Elements: keywords, identifiers, operators, punctuation, syntax
Literals – character (char/string) or numeric (integer/floating point).
‘c’ (char) , “c” (char string), 10 (integer), 12. & 16.0 (floating point [double])
A numeric literal without a decimal point is an int.
A numeric literal with a decimal point is a double.
true and false are reserved literals of the bool data type
Variable Declarations
( char, int, float, double, bool )
<data type> <name> [ = value ] ; //initialization is optional
Examples:
int x; int y = 10;
double length = 5.0, double width;
The three primary activities of a program are input, processing, and output
Programming Paradigms: Procedural, Object-oriented, Event-driven ( using an OOP language )
Chapter 2
Preprocessor Directives:
#include
All preprocessor directives begin with a #
preprocessor directives are NOT C++ statements
Function main template:
int main ( )
{
<statements>
return 0;
}
Punctuation Characters: // /* */ # <> ( ) { }
cout object
<<
““
‘‘
;
(stream insertion operator) separate statements / cascaded statement
Common Escape Sequences:
\n (newline)
variables and literals:
X
c++ keywords: ( all lowercase )
‘X’
Note:
\t (tab)
“X”
5
5.0
cin and cout are NOT keywords.
Rules for Identifiers:
legal variable names
first character upper or lower case character a-z or A-Z
remaining characters, a-z, A-Z, 0-9, _ (underscore)
practical limit is 31 characters
Integer data types: short, int, long ( modifier unsigned may be used with integer data types )
Characters:
‘A’
65 (ascii code)
character (char) is a subtype of integer (int)
the ordinal value of a character in the ASCII character set is stored as an integer
Character string Null character
‘\0’
Floating-point data types: float, double, long double
bool data type:
sizeof( ) operator
true
false
sizeof ( int )
sizeof ( GrossPay )
unassigned – “garbage value”
Variable declaration / assignment
Arithmetic operators:
+ - *
/
%
Distinguish between integer and floating point division: 3/5 3.0/5
Remember that the % operator returns the integer remainder of a division
Chapter 3
cin object
>> (stream extraction operator)
Using a single statement / cascaded operators
Whitespace: spaces, tabs, newlines
Reading strings:
cin versus cin.get( ) versus cin.getline( )
Char Arrays: char Array[21] size / room for Null character ‘\0’
Array size declarator must be an integer named constant or integer literal
Array bounds - cin can accept more characters than the array can hold! Array bounds are not checked…
Mathematical expressions – operator precedence
( )
* / %
in order from left to right
+ –
in order from left to right
Type conversion: mixed data types in an expression
promote to highest type found
Type Casting:
C style casting: ( int ) x
C++ typecast:
int ( x )
ANSI standard C++: static_cast<int>(x)
Constants: const keyword:
const double PI = 3.14159;
preprocessor directive:
#define PI 3.14159
Combined Assignment Operators: +=, -=, *=, /=, %=
Output formatting: #include<iomanip>
stream manipulators
fixed, showpoint, setprecision( ), setw( ), left, right
cin member functions
cin.get( ), cin.getline( ), cin.ignore( )
Output mode:
automatic / fixed / scientific
default output mode is automatic
default precision is 6
automatic mode (significant digits ---> integer and decimal positions)
fixed mode (number of decimal positions)
setw( ) stream manipulator
width of output field, right-justifies
setprecision( ) set number of significant digits or decimal digits ( if used with fixed )
fixed
change mode to fixed ( change meaning of setprecision to decimal digits )
showpoint
left / right
Formatted input:
cin >> setw( 8 ) >> X;
cin.getline( array, size )
Math library functions:
#include <cmath>
Math library constants – M_PI and M_E
pseudorandom numbers:
rand( ), srand( ) seed value --> srand( time( NULL ) )
rand( ) % x
--> returns numbers in the range 0 .. x-1
1 + rand( ) % x --> returns numbers in the range 1 .. x
Chapter 4
Relational operators: <
<=
>
>=
==
!=
Evaluate to true ( 1 ) or false ( 0 )
what is true?
Any expression that evaluates to non-zero is considered "true".
if ( -5 ) expression –5 is considered true (its non-zero)
if statement:
if ( expression )
statement;
if/else statement:
if ( expression )
{ statements }
if ( expression-1 )
statement-1;
// don’t forget the ; here!
else
statement-2;
if/else if statement ( case structure ):
if ( expression-1 )
if ( expression-1 )
statement-1;
statement-1;
else
or
else if (expression-2)
if (expression-2)
statement-2;
statement-2;
else if … // two words! else if
else
if ….
Trailing else --- default case. Statement executed when all of the conditions are false.
Nested if statement:
if ( expression-1 )
{
if (expression-2)
statement-2;
}
Logical operators: ! (not)
if ( weight > 0 && weight <= 20 )
correct-weight-statement;
if ( weight <= 0 || weight > 20 )
weight-error-statement;
&& (and)
|| (or)
Connect two or more relational expressions
// test to see if a value is within a specific range
// test to see if a value is outside a specific range
Precedence is 1: ! (not) 2: && (and) 3: || (or)
Variable declarations and scope
{ } block
The scope of a variable is the block in which it is declared.
Variables with the same name ( nested blocks )
conditional operator:
test-expression ? t-expression : f-expression;
x < 0 ? y = 10 : z = 20;
if ( x < 0 )
y = 10;
else
z = 20;
Note: << has higher precedence than ?: (conditional) operator – put conditional expression in ( )
cout << ( (num % 2 == 0) ? “Even\n” : “Odd\n” );
char data type
a single character enclosed in single quotes: ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘\n’, ‘\t’ [escape sequences are a single character]
string class
#include<string>
string description;
string name = “Hector”
supported operators: [ ], relational, comparison, = (assignment)
switch statement:
switch ( integer-expression )
{
case constant-integer-expression : //integer or character literal
statement(s) ;
break (optional) ;
default (optional) :
statements;
}
Checking for file open errors
if ( ! inFile )
if ( inFail.fail( ) )
stream extraction operator returns a value of true or false
if ( inputFile >> number )
can be used to control a loop
while ( inputFile >> number ) // returns true as long as you are not at the end of the file
Note: can be used with cin object [ while ( cin >> number ) ] // returns true while not EOF ( Ctrl-D or Ctrl-Z )
Chapter 5
increment and decrement operators:
++ , – –
prefix and postfix modes
/ using in expressions
++val (1. increment 2. use in expression),
– –val (1. decrement 2. use in expression)
val++ (1. use in expression, 2. increment)
val– – (1. use in expression, 2. decrement
A loop is a block of code that is repeated while some condition is true or until some condition is true.
For any loop, there are three types of expressions which may be necessary
initialization-expression(s)
used to initialize a loop control variable and any other variables
that need to be initialized before executing a loop
text-expression
used to determine whether or not the body of the loop should be
executed
update-expression(s)
used to update a loop control variable ( if present )
while and do...while loops only require a test-expression. A For loop does not require any of these expressions.
while loop [ pre-test loop ]
while (expression)
statement;
executes while expression is non-zero
body of loop executed 0 or more times
while (expression)
{
statement-1;
statement-n;
}
counters ( 228),
accumulators, running totals (231)
sentinel – a special value that marks the end of a list of values. Used to satisfy the condition necessary to terminate a
loop. A sentinel value is outside the range of normal expected values.
while ( Emp_no != -1 )
{
loop body
}
do-while loop [ post-test loop ]
do
do-while loops are often used with menus
body of loop executed at least once
statement;
while (expression);
do {
statement-1;
statement-n;
} while (expression);
for loop [ pre-test loop ]
for ( initialization ; test ; update )
statement;
for ( initialization ; test ; update)
{
statement-1; statement-2;
}
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
statement-n;
only thing required in the parentheses is the semicolons ( ; ; )
initialization is performed once
test is performed every iteration of the loop
update is performed every interation of the loop after the body of the loop has been executed
pre-test loop - executed 0 or more times
may declare local variable(s) in the for loop header
may have multiple expressions separated by commas in the for loop header
for ( int x=2, y=3 ; x*y < =100 ; x++, y++ )
cout << setw(5) << x << setw(5) << y << endl;
Nested loops
for ( int j=0 ; j < 10 ; j++ )
for ( int k=0 ; k<10 ; k++)
cout << j << ‘\t’ << k << ‘\t’ << j+k << endl;
break keyword – used to terminate a loop early
while (1)
{
if ( x = = 10 )
break;
}
continue keyword - causes a loop to stop its current iteration and begin the next one
while (1)
{
if ( x = = 10 )
continue;
}
using a loop for input validation
cout << “Enter a number in the range of 1 – 100: “;
cin >> Number;
while ( Number < 1 | | Number > 100 )
{
cout << “Please enter a number in the range of 1 – 100: “;
cin >> Number;
}
File Input and Output:
3-step process:
1. open the file
2. process the file (read/write)
3. close the file
use of file stream objects requires the fstream header file #include<fstream>
File Stream Classes:
ifstream file used for input (read only)
ofstream file used for output (write only)
fstream file used for input, output or both
Declaration of a File Stream Object:
ifstream Infile;
ofstream outfile;
Use of the Open( ) Member Function:
infile.open(“customer.dat”);
outfile.open(“info.dat”);
use of a backslash in a path for a file specification
OutputFile.open(“a:\\files\\invtry.dat”); // requires two backslashes
closing a file
OutputFile.close( );
writing to a file using the stream insertion operator <<
outfile << “I love C++ programming…”;
using the stream extraction operator to read information from a file
>>
InputFile >> Emp_No;
InputFile >> FirstName;
remember the stream extraction operator stops reading when it encounters any whitespace character ( space, tab,
newline )






