Guided Reader
advertisement

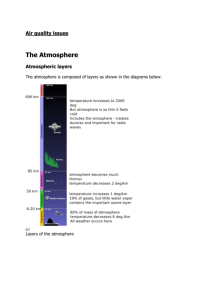
Name:_______________________________________ Date:_____________ Chapter 18 Guided Reader- Honors Chemistry Directions: Please answer the questions to the guided reading activity as you read chapter 18 of your textbook. A word of advice: write page numbers by your answers so you can reference them later. 1. Into how many regions is the Earth’s atmosphere divided? 2. What region is closest to the Earth’s surface? 3. What is the upper limit of #2 called? 4. What is the second closest region to the Earth’s surface? 5. What is the upper limit of #4 called? 6. What are the remaining regions? 7. What forms the boundaries of each region? 8. Describe how temperature changes throughout the atmosphere. 9. What percentage of the mass of the atmosphere is located in the troposphere? 10. The atmosphere is bombarded by _____________ and _________________ from the Sun. 11. What does ppm mean when dealing with gases? 12. Diatomic nitrogen contains a ___________ bond which is largely responsible for its _______ reactivity. 13. Diatomic oxygen contains a _________ bond, making it much more reactive than nitrogen. 14. High energy particles that bombard molecules and atoms in the outer regions of the atmosphere cause the molecules and atoms to go through ___________ changes. 15. What type of electromagnetic energy from the Sun can cause #14? 16. What two conditions must be met in order for #14 to occur? 17. What is photodissociation? 18. What absorbs most of the ultraviolet radiation (shorter than 240 nm in wavelength) in the outer regions of the atmosphere? 19. What forms when #18 occurs? 20. What other molecules absorbs ultraviolet radiation (shorter than 240 nm in wavelength) in the outer regions of the atmosphere? 21. What is photoionization? 22. What is the key absorber of photons ranging from 240 to 310 nm in wavelength? 23. Photodissociation of oxygen can occur between 30 to 90 km above the Earth’s surface. TRUE/FALSE 24. Describe how ozone is formed in the stratosphere. 25. What two factors affect the rate of ozone formation in the stratosphere? 26. Where is the highest rate of ozone formation? 27. What is the minimum amount of energy per mole of photons necessary to photodissociate ozone? 28. Write the four reactions that show ozone formation and decomposition. 29. What two reactions are photochemical? 30. What two reactions are exothermic chemical reactions? 31. The net result of all four is the conversion of solar radiant energy into __________________. 32. CFCs are synthetic/naturally occurring. CIRCLE 1 33. List four uses of CFCs. 34. CFCs exposed to high-energy radiation in the stratosphere _______________________. 35. Where does chlorine atom formation occur at the greatest rate? 36. What does free chlorine do in the stratosphere? 37. There are no natural sources that contribute chlorine and bromine to the atmosphere. TRUE/FALSE 38. List the minor atmospheric constituents that come from fossil-fuel combustion. 39. ________________________ are among the most unpleasant and harmful of the common pollutant gases. 40. What accounts for about 80% of the total sulfur dioxide released in the US? 41. Sulfur dioxide emission caused by #40 depends on the level of their ________________________. 42. Why is burning coal more problematic east of the Mississippi River? 43. Describe how sulfur dioxide becomes sulfuric acid. 44. What is the pH of uncontaminated rainwater? 45. What is the pH of acid rain? 46. What happens to living organisms in water below a pH of 4? 47. What compound in stone building materials is attacked by acid rain? 48. What can be injected into the furnace of a power plant to reduce the quantity of sulfur dioxide released into the environment? 49. _________ is the most abundant of all pollutant gases. 50. Although CO is not a threat to vegetation or materials, it does affect __________ because it binds to _________________. 51. CO binds very strongly to the __________ in hemoglobin at a much greater rate than __________. 52. __________________ are primary components of photochemical smog. 53. Nitric oxide oxidizes into ______________________ in air. 54. Describe how nitrogen dioxide becomes nitric oxide and atomic oxygen in the troposphere. 55. Why is ozone undesirable in the troposphere? 56. Aside from nitrogen oxides, list two other ingredients in photochemical smog. 57. Earth is in an overall ________________________ with its surroundings. 58. The troposphere is transparent to ____________ light but not transparent to _____________ radiation. 59. What is the influence of water vapor, carbon dioxide, and other atmospheric gases on Earth’s temperature called? 60. What gas plays a major role in maintaining Earth’s temperature at night? 61. What gas plays a secondary role? 62. Carbon dioxide concentrations fluctuated between ______________ over the past 150,000 years. 63. Today carbon dioxide concentrations are at about _______________. 64. Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere is expected to __________ from its present level in less than 100 years, resulting in a global temperature increase of ____________. 65. The world ocean covers _________% of Earth’s surface. 66. What percent of the water on Earth is the world ocean? 67. What percent of the water on Earth is fresh water? 68. What is the salinity of the world ocean? 69. What three properties of seawater vary with depth? 70. What is a thermocline? 71. What is a halocline? 72. What is a pycnocline? 73. How does carbon dioxide increases in the atmosphere affect the world ocean? 74. What is desalination? 75. Seawater can be desalinated using ________________. 76. An adult needs about _______ per day for personal consumption and hygiene. 77. The amount of _____________________ in water is an important indicator of water quality. 78. Cold water fish require at least __________ of dissolved oxygen for survival. 79. Why are excessive quantities of biodegradable organic materials in water detrimental? 80. What does biodegradable material end up as? 81. ___________________________________ takes over when the amount of dissolved oxygen to reduced beyond the point of aerobic bacteria survival. 82. What are the products of anaerobic bacheria? 83. What is eutrophication? 84. What are the five steps to municipal water treatment?