Name: Date: Evolution Notes Bell Work: 1. How would you define
advertisement

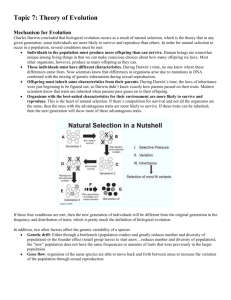
Name: __________________________________________ Date: _________________________ Evolution Notes Bell Work: 1. How would you define evolution? ____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What evidence have you heard of that supports the theory of evolution? ______________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What makes evolution possible? _____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is natural selection? Can you give an example? _____________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. How would selective breeding play a role in evolution? ___________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ NOTES: Evolution: ________________________________________________________________________________ Lamark’s Theory: Lamark thought that animals could adapt to their environments and then pass these acquired characteristics along to their offspring. For example: He thought that giraffes couldn’t reach the leaves on tall tree, so they stretched their necks until they got longer. Then these giraffes passed this trait on to their offspring. We know that can’t be true because you only pass on your DNA to your offspring. If you have surgery to make you taller this is not in your genes and cannot be passed on to your offspring. Darwin: In 1831 Charles Darwin went for a boat ride on the H.M.S. Beagle. On this trip he notices many he began to wonder why organisms seemed so well suited for their environments. He collected fossils as well as living specimen. Finally in 1859, Darwin publishes his theory of evolution in his paper “On the Origin of Species” Theory of Evolution: There is natural variation among different organisms within a species. This variation is cause by meiosis (crossing over and Mendel’s Laws) and fertilization (combining new traits from two different organisms) and mutations (changes in the sequence of DNA) Adaptations are variations that occur and make an organism better suited to survive and pass on its genes Organisms compete with each other for survival, causing natural selection. Natural selection – the organisms with the traits that are most beneficial will survive to reproduce and pass on those traits, while the others will die off. This is also know as survival of the fittest Over time, natural selection changes the inherited characteristics of a population, so modern organisms look different from their ancestors Taking this a step further, Darwin proposed common descent That all organisms evolved from one common ancestor Evidence used to support this theory of common descent: Fossil Record – by looking at structures left behind by previous organisms we can show the changes within species and try to make links and find common ancestors Geographic Distribution of Living Species – many organisms across the world are very similar, yet have distinct differences that make them more suited for their particular environment Homologous Structures – structures that serve different functions, but are structurally similar Early Development – most embryos with a backbone go through very similar stages during development and look very similar Artificial Selection: Sometimes humans interfere with natural selection (we’ve already talked about this because of selective breeding) We breed organisms based on traits that would normally not be selected in nature. Ex: We choose cows that produce more milk, dogs that have a gentle demeanor, crops that taste better or produce more, etc . . . What other examples of artificial selection can you think of? Rates of Evolution: Evolution is a slow process. Gradualism – Some scientists speculate that the genetic changes occurring in species occurs at a constant rate very slowly. They speculate that evolution is a process like erosion. It causes huge changes because tiny changes are occurring constantly. Punctuated Equilibrium – Other scientists speculate that there are long periods where nothing happens, but occasionally big changes in species occur. These could be because of dramatic changes in the climate such as an ice age or due to natural disasters. Patterns of Evolution: Convergent Evolution – when two species develop similar traits because they play similar roles in the environment. These adaptations are not similar because they share a common ancestor! EX: sugar gliders in Australia and flying squirrels in North America Divergent Evolution – when two species do share a common ancestor, but change drastically because of their different niches, or roles in the environment. EX: finches on the Galapagos Islands Phylogeny – evolutionary history of an organisms or group of organisms Video Questions: 1. What things do you think would help a zebra survive? 2. What things do you think help the lions survive? 3. Is this natural or artificial selection? How do you know? 4. What zebras did the lions attack? 5. If I told you that lions were colorblind, what other trait do you think has developed in the zebra population to help them survive? Discussion: 1. Is there natural selection within the human population? 2. If so, what traits are selected for in humans? 3. Moth example: a. Before the industrial revolution which moths thrived? b. After the industrial revolution which moths thrived? c. Is this natural or artificial selection? Explain. 4. Why is biodiversity important? Name: __________________________________________ Date: _________________________ Evolution Notes Evolution: ________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Lamark’s Theory: Lamark thought that animals could ________________ to their environments and then pass these _______________________ characteristics along to their _______________________ For example: He thought that ____________________ couldn’t reach the leaves on tall tree, so they ____________________ their necks until they got ___________________. Then these giraffes passed this __________________ on to their offspring. We know that _______________ be true because you only pass on your ___________ to your offspring. If you have ______________________ to make you ___________________ this is not in your _____________ and cannot be passed on to your offspring. Darwin: In 1831 Charles ____________________ went for a boat ride on the H.M.S. __________________. On this trip he notices many ____________________ organisms, he began to wonder why organisms seemed so __________ suited for their ____________________________ He collected ___________________ as well as ______________________ specimen. Finally in 1859, Darwin _______________________ his theory of _________________________ in his paper “______________________________________________” Theory of Evolution: There is natural __________________________ among different organisms within a _______________ This variation is cause by ___________________ (_________________ _____________ and Mendel’s Laws) and fertilization (combining __________ traits from two __________________ organisms) and _______________________ (changes in the sequence of DNA) Adaptations are _______________________ that occur and make an organism _______________ suited to ___________________ and pass on its _________________ Organisms ______________________ with each other for survival, causing ____________________ _____________________ Natural selection – the organisms with the ________________ that are most ___________________ will survive to _______________________ and pass on those traits, while the others will ________ off. This is also know as ______________________ of the _____________________ Over _______________, natural selection changes the ______________________ characteristics of a _______________________, so modern organisms look ______________________ from their ______________________ Taking this a step further, Darwin proposed __________________ ______________________ That all organisms ________________________ from one common _____________________ Evidence used to support this theory of common descent: _______________ Record – by looking at ___________________ left behind by ________________ organisms we can show the ________________ within species and try to make _______________ and find common ancestors Geographic Distribution of ___________________ Species – many organisms across the _____________ are very similar, yet have ____________________ differences that make them more suited for their particular ______________________ __________________________ Structures – structures that serve different _________________, but are __________________________ similar Early _________________________ – most ________________ with a backbone go through very similar stages during development and look very similar Artificial Selection: Sometimes __________________ interfere with __________________ selection (we’ve already talked about this because of ______________________ _______________________) We _____________ organisms based on traits that would normally not be selected in _______________ Ex: We choose cows that produce more _______________, dogs that have a ________________ demeanor, crops that taste better or produce more, etc . . . What other examples of artificial selection can you think of? Rates of Evolution: Evolution is a ______________ process. Gradualism – Some scientists speculate that the ____________________ changes occurring in species occurs at a ____________________ rate very slowly. They speculate that evolution is a process like _________________. It causes _____________ changes because tiny _________________ are occurring constantly. ________________________ Equilibrium – Other scientists speculate that there are ______________ periods where ____________________ happens, but occasionally __________ changes in species occur. These could be because of dramatic changes in the _____________________ such as an ice age or due to natural _____________________. Patterns of Evolution: _______________________ Evolution – when two species develop _________________ traits because they play similar ______________ in the environment. These ______________________ are not similar because they share a ______________________ ancestor! EX: sugar gliders in Australia and flying squirrels in North America Divergent ______________________ – when two species do _______________ a common ___________________, but change _________________________ because of their different ______________, or roles in the environment. EX: finches on the Galapagos Islands Phylogeny – evolutionary ____________________ of an organisms or group of organisms Critical Thinking Questions: 1. How would you define evolution? ____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What evidence have you heard of that supports the theory of evolution? ______________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What makes evolution possible? _____________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is natural selection? Can you give an example? _____________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. How would selective breeding play a role in evolution? ___________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Discussion: 1. Is there natural selection within the human population? 2. If so, what traits are selected for in humans? 3. Moth example: a. Before the industrial revolution which moths thrived? b. After the industrial revolution which moths thrived? c. Is this natural or artificial selection? Explain. 4. Why is biodiversity important? 5: In the space below, draw a family tree (Grandparents, parents, great grandparents, aunts, uncles, nieces, nephews, children, etc). Below it, save space to EXPLAIN who is DECENDENT from whom. (Look that word up if you don’t know it.)