Curriculum Outline - Oldbury Wells School
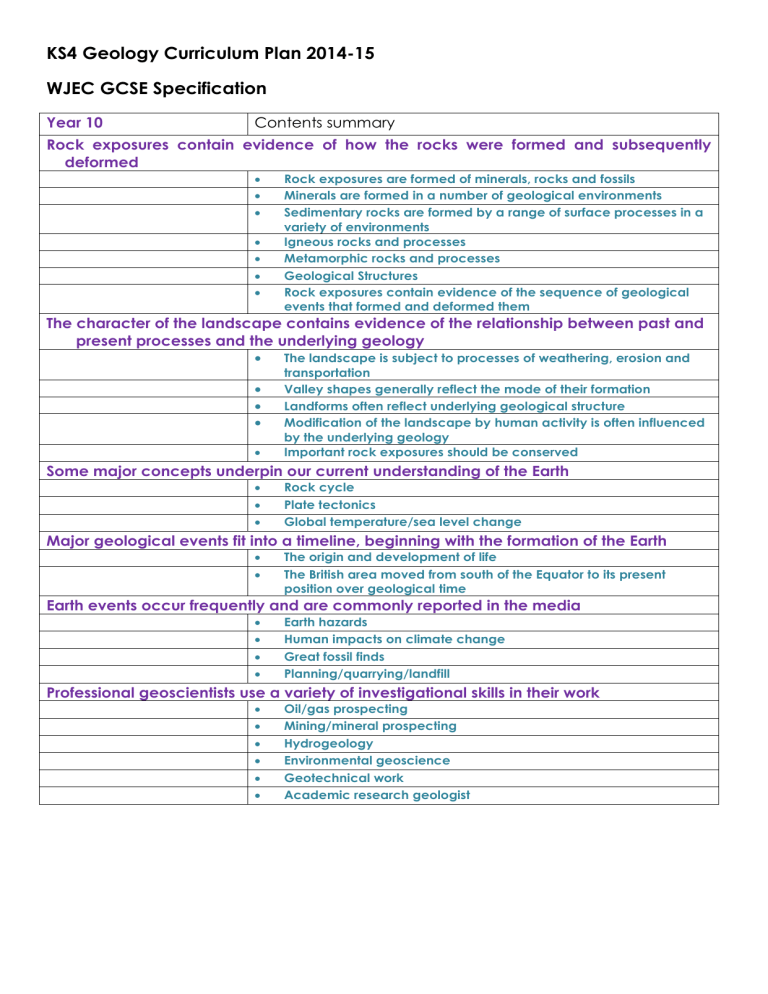
KS4 Geology Curriculum Plan 2014-15
WJEC GCSE Specification
Year 10 Contents summary
Rock exposures contain evidence of how the rocks were formed and subsequently
deformed
Rock exposures are formed of minerals, rocks and fossils
Minerals are formed in a number of geological environments
Sedimentary rocks are formed by a range of surface processes in a
variety of environments
Igneous rocks and processes
Metamorphic rocks and processes
Geological Structures
Rock exposures contain evidence of the sequence of geological
events that formed and deformed them
The character of the landscape contains evidence of the relationship between past and
present processes and the underlying geology
The landscape is subject to processes of weathering, erosion and transportation
Valley shapes generally reflect the mode of their formation
Landforms often reflect underlying geological structure
Modification of the landscape by human activity is often influenced by the underlying geology
Important rock exposures should be conserved
Some major concepts underpin our current understanding of the Earth
Rock cycle
Plate tectonics
Global temperature/sea level change
Major geological events fit into a timeline, beginning with the formation of the Earth
The origin and development of life
The British area moved from south of the Equator to its present position over geological time
Earth events occur frequently and are commonly reported in the media
Earth hazards
Human impacts on climate change
Great fossil finds
Planning/quarrying/landfill
Professional geoscientists use a variety of investigational skills in their work
Oil/gas prospecting
Mining/mineral prospecting
Hydrogeology
Environmental geoscience
Geotechnical work
Academic research geologist
26 hours per group in each area over the academic year.
Year 9 -
Food
Theory
Design skills
Practical skills
Textiles
Theory
Contents summary
The design and manufacture of a decorated fashion garment
Introduction of materials and components –source, fibres, yarns
Equipment names
Design skills
Practical skills
Resistant Materials
Theory
Design skills
Practical skills
Analysis of and industrial brief
Developing creativity
Designing for transfer printing process
Planning for an end user
Evaluation using consumer views
Introduction and use of basic textiles equipment
Manipulation of materials to create a useable end product.











