Review Vocab and Terms for Lab Safety, Measurment, Density
advertisement

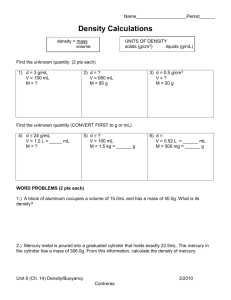
Unit 1 – Lab Safety, Measurement, Density, Buoyancy and Controlled Experiment NYS Standards: MST Standard #1 MST Standard #4 3.1h Density can be described as the amount of matter that is in a given amount of space. If two objects have equal volume, but one has more mass, the one with more mass is denser. 3.1i Buoyancy is determined by comparative densities. Lab Safety Chemical Safety – NEVER mix chemicals unless told to do so. Do not directly smell chemicals…..WAFT them. Eye Safety – Make sure to wear goggles. Make sure to use the eye wash station if you get something in your eyes. Thermal Safety – Make sure to wear gloves, use hot mitts and just use common sense. Electricity Safety – Respect electricity. Do not hang chords over tables or put in the way or areas where can walk. Do not mix with water. Hand Safety – Some object may be sharp. Make sure to wear gloves around these objects. Animal Safety – Sometimes in the lab you will work with animal or biological materials. When you are finished, make sure to wash your hands fully. Glassware Safety – Glass cools very slowly after being heated. Do now handle without protection. Never place hot glass on a wooden or metal desktop. Never eat or drink from the laboratory glassware. Measurement -A measurement is a record or an observation that cannot be made by the five senses alone. -Measurements are usually made with the use of an instrument. -When making a measurement make sure to record your answer to the tens place. Ex: 1.3cm -When making a measurement make sure to write the units. Ex: m, cm, mm, mL, L, g, kg, g/cm3, oC -There are five major types of measurement 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Length Temperature Volume Mass Density Matter – Anything that has mass and takes up space. Mass – The amount of matter in a given object. We use a Balance or Triple Beam Balance to measure mass. Mass is measured in Grams (g). Mass is always constant for an object no matter where the object is in the universe. Volume – The amount of space an object takes up. o There are three ways to measure volume. 1. If the object has straight edges and can be measured with a meter stick or ruler you can use the equation Volume = length x width x height Units = cm3 Example The sides of a cube are 3.0cm, 5.0cm, and 2.0 cm. V=LxWxH V = 3.0cm x 5.0 cm x 2.0 cm V = 30.0 cm3 2. Use a graduated cylinder 1. Place the graduated cylinder on a flat table. 2. Let the liquid settle 3. Read the bottom of the meniscus at eye level. The meniscus is the curved surface formed by liquids. 3. Water Displacement 1. Take an original volume of the water in the graduated cylinder. 2. Place the object in the water. 3. Observed the new volume and subtract the original volume from the new volume. Example The initial volume is 5.0 mL The final volume is 10.0mL 10.0mL -5.0mL 5.0mL is the volume of the object. o The unit for Liquid Volume is milliliters (mL) o The unit for Solid Volume is cubic centimeters (cm3) Temperature – A specific degree of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measured with the use of a thermometer. o The unit for temperature is degrees Celsius (oC) Length – The unit of measure to determine the distance of an object. We use a ruler or meter stick to measure length. Density – A measure of the amount of matter that occupies a given amount of space. o The equation for density is: D = Density M = Mass V = Volume A Density Visual Aid Example: An unknown object has a mass of 15.0 grams and a volume of 5.0 cm3. What is the density of this object? D=M÷V D = 15.0 g ÷ 5.0 cm3 D = 3.0 g/cm3 Buoyancy – An object’s ability to float in water. o Density greater than 1.0 g/cm3 = the object will sink o Density less than 1.0 g/cm3 = the object will float o However, when an object actually floats, some of the object can be found above the water and some of the object can be found below the water. Example: An object has a density of 0.53 g/cm3. What is the object’s buoyancy? 0.53 x 100 = 53% Sinks 100 – 53 = 47% Floats 47% 53% 47% of the object is above the water line and 53% of the object is below the water line. Controlled Experiment -There are three main parts to a controlled experiment: controls, variables, and trials. o Controls – Factors in an experiment that are held constant (the same) from one part of the experiment to another. There are usually many controls in an experiment. o Trials – The number of times an observation or measurement is made during an experiment. o Variables – Factors that change in an experiment. There are two types. Independent Variable – The variable that is purposefully changed or manipulated in an experiment. This is where you make the desired changes to test their results. Dependent Variable – Variable that changes in response to manipulations of the independent variable. The outcome of the dependent variable DEPENDS on the independent variable.