08. Mathematics Key Skills Reception - Year 6
advertisement

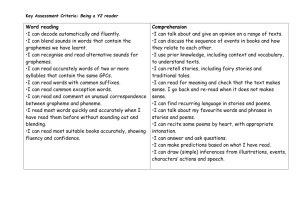
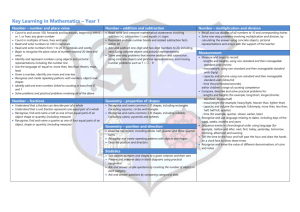
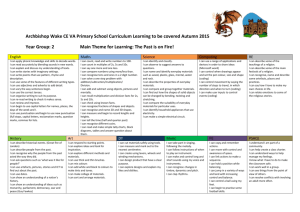
Key skills Reception By the end of Reception all children should be able to confidently: Counts to 20 Count backwards from at least 20. Counts objects to 10 and beginning to count beyond Finds one more than a given number up to 20 Begins to find one less than a given number up to 20 Estimates how many objects they can see and checks by counting them Recognises numbers 1-10 and begins to recognise numbers to 20 Selects the correct numeral to represent 1-10 objects Begins to write the correct numeral to represent 1-10 objects Begins to use correct vocabulary for addition and subtraction in practical activities Begin to compare numbers, e.g. knowing that 6 is bigger than 4. Know the story of 6 (3 + 3, 2 + 4, 1 + 5, 6 + 0), and the stories of 5 and of 4 and of 3... Recognise some 2-digit numbers related to their own experiences. E.g. Daddy is 34, I live at number 56, etc. Recognise the difference between ‘flat’ and ‘solid’ shapes and describe shapes by mentioning a property, e.g. this one rolls, this one has corners... Spot and continue patterns Compare the size of things using mathematical language, e.g. Tom is taller than me. Key skills Year 1 By the end of Year1 all children should be able to confidently: Count to and across 100 from any number Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals Read and write mathematical symbols: +, - and = Identify "one more" and "one less" Use number bonds and subtraction facts within 20 Count on and back in 2s, 5s and 10s Double to at least 20 Add and subtract 1-digit and 2-digit numbers to 20, including zero Recognise, find and name a half and a quarter Measure and begin to record length, mass, volume and time Recognise and know the value of all coins and notes Use language to sequence events in chronological order Recognise and use language relating to dates Tell the time to the half-hour, including drawing clocks Recognise and name common 2-D shapes common 3-D shapes Key skills Year 2 By the end of Year 2 children should be able to confidently: Count in steps of 2s, and 5s, and steps of 10 Recognise place value in two-digit numbers Compare and order numbers up to 100 using <, > and = Recall and use number addition/subtraction facts to 20, and derive related facts Add and subtract mentally and with objects one- and two-digit numbers Understand and use the inverse relationship between addition and subtraction Know 2×, 5× and 10× tables, including recognising odd & even numbers Calculate mathematical statements using x and ÷ symbols Recognise, find, name and write 1/3, 1/4, 1/2 and 3/4 of size, shape or quantity Write simple fraction facts, e.g. 1/2 of 6 = 3 Combine amounts of money to make a value, including using £ and p symbols Tell the time to the nearest 5 minutes, including drawing clocks Describe properties of 2-D shapes, including number of sides and symmetry Describe properties of 3-D shapes, including number of edges, vertices and faces Interpret and construct simple tables, tally charts and pictograms Key skills Year 3 By the end of Year 3 children should be able to confidently: Read and write numbers up to 1,000 in numerals and words Recognise the place value of each digit in a 3-digit number Compare and orders numbers up to 1,000 Find 10 or 100 more or less than a given number Confidently uses number bonds to 100 Double numbers to 100 Begin to multiply 2 digits by 1 digit using formal written methods Understand that the term product means multiply Count in multiples of 4, 8, 50 and 100 Compare and order numbers up to 1000 Add and subtract numbers mentally, including round numbers to HTU Add and subtract using standard column method Estimate answers to calculations and use the inverse to check answers Know 3×, 4× and 8× tables Count up and down in tenths Understand that tenths are objectives or quantities divided into ten equal parts Recognise and show equivalent fractions Find and write fractions of a set of objects Add and subtract fractions with common denominators (less than one) Measure, compare and calculate measures using standard units Measure the perimeter of simple 2-D shapes Add and subtract money, including giving change Tell and write the time from an analogue clock, including using Roman numerals Estimate and read time to the nearest minute Identify horizontal, vertical, parallel and perpendicular lines Identify whether angles are greater or less than a right angle Interpret and present data using bar charts, pictograms and tables Key skills Year 4 By the end of Year 4 children should be able to confidently: Count backwards through zero, including negative numbers Recognise place value in four-digit numbers Round any number to the nearest 10, 100 or 1000 Know tables up to 12 × 12 Use place value and number facts to carry out mental calculations Develop secure methods for mental addition and subtraction of pairs of 2-digit numbers Add numbers with up to 4 digits using the formal written methods Subtract numbers with up to 4 digits using the formal written methods Multiply 2 and 3-digit numbers by a 1-digit number using formal written methods Divide a 3-digit number by a 1-digit number using formal written methods Use and apply the terms multiple and factor Recognise and use hundredths Recognise and write decimal equivalents to ¼, ½ and ¾ 1 Divide one- or two-digit numbers by 10 and 100, using tenths and hundredths Round decimals with one decimal place to the nearest whole number Compare numbers up to two decimal places Find the area of rectilinear shapes by counting squares Convert between units of measurement, e.g. cm to m, g to Kg and ml to L; convert between units of time and between analogue and digital time Compare and classify shapes, including quadrilaterals and triangles Complete a simple symmetric figure with respect to a specific line of symmetry. Describe positions on a 2-D grid using co-ordinates Describe translations using a given unit to the left/right and up/down Interpret and present discrete and continuous data on appropriate graphs Key skills Year 5 By the end of Year 5 children should be able to confidently: Round to ten, a hundred, a thousand or ten thousand. Begin to read scales of different types Understand a one-place decimal number as a number of tenths and a twoplace decimal number as a number of hundredths. Understand the effect of multiplying and dividing by 10 and 100 to give 1place and 2-place decimal answers. E.g. 4.5 x 10 = 45, and 678 ÷ 100 = 6.78 etc. Add or subtract 0.1 or 0.01 to/from any decimal number with confidence, e.g. 5.83 + 0.01 or 4.83 – 0.1 Add and subtract mentally with confidence – where the numbers are less than 100 or the calculation relies upon simple addition/subtraction and place value. Examples include: 6,723 – 400, 78 + 46, 72 – 46, 8020 + 910, 100 – 64, 5000 + 12,000, etc. Confidently add 3- and friendly 4-digit numbers together using a secure written method Count forwards and backwards with positive and negative whole numbers, including through zero Add whole numbers with more than 4 digits using formal written methods Subtract whole numbers with more than 4 digits using formal written methods Multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a 1-digit number using a formal written method Multiply a 2-digit number by a 2-digit number using long multiplication Divide numbers up to 4 digits by a 1-digit number using short division and interpret remainders Know and recite all times tables including division facts. Reduce fractions to their simplest form, including tenths to fifths and hundredths to tenths, e.g. 40/100 = 4/10 = 2/5 which is also 0.4 Identify simple fraction and decimal equivalents: ½ ≡ 0.5, 0.25 ≡ ¼ and 0.75 ≡ ¾. Measure and compare capacities, weights and lengths, including perimeters using SI units; understand the concept of area and count squares to find areas. Understand the properties of triangles; find unknown angles in triangles and rectangles. Key skills Year 6 By the end of Year 6 children should be able to confidently: Read and write numbers up to 10,000,000 and determines the value of each digit Order and compare numbers up to 10,000,000 Consistently round numbers to a given multiple of 10 or decimal place Understand addition and subtraction with negative numbers down to -20 Double numbers with up to 2 decimal places Halve numbers with up to 2 decimal places Add number using formal written methods including numbers with decimals Subtract number using formal written methods including numbers with decimals Multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a 2-digit whole number using long multiplication Divide numbers up to 4 digits by a 2-digit whole number using long division Solve problems up to 2-step involving all 4 operations Scale up or down by a factor of 2, 5 or 10 Perform divisions mentally within the range of tables facts using remainders or rounding the answer up or down as appropriate, e.g. 68 ÷ 8 = 8 r4 or 8½ or how many toy spiders can be made if I have 68 legs? (Ans = 8) or how many minibuses each holding 8 children will be needed to transport 68 children? (Ans = 9). Uses common factors to simplify fractions Compare and order fractions including those >1 Recall and use equivalences between fractions, decimals and percentages in various contexts Finds basic percentages of numbers (50%, 25%, 75%, 5% and multiples of 10%) Understand the basic rules of solving simple equations where there is an unknown on one side Solve missing number problems. Generate and describe linear sequences. Measure areas and perimeters; understand that area is a measurement of covering and is measured in square units, and perimeter is a length, measured in cm, m or mm. Use 12 and 24 hour clocks; calculate time intervals; use timetables. Compare and classify geometric shapes; identify circles and parts of circles. Identify positions in the first and fourth quadrants on a co-ordinate grid; reflect and translate shapes. Find and interpret the mean (average) of several quantities.