cpr answers to 1-70
advertisement

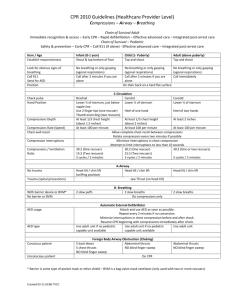
CPR Questions 1. What does high quality CPR do? a. Improves a victim’s chances of survival. 2. Name the critical characteristics of high quality CPR. (Just what is in bold) a. Start compressions within 10 seconds b. Push hard and fast c. Allow complete chest recoil d. Minimize interruptions (to less than 10 s) e. Give effective breaths f. Avoid excess ventilation 3. You should deliver compressions at a rate of ______________________. a. AT LEAST 100 compressions per min. 4. At what depth should your compressions be for and adult and child? a. 2” for and adult and 2” for a child (1 ½” for infant) 5. You should try to limit interruptions in compressions to less than __________. a. 10 s 6. How do you know you are giving effective breaths? a. Chest rise. 7. ECC stands for _________________. a. Emergency Cardiovascular Care. 8. The 5 links in the Adult Chain of Survival are: a. Recognition, Early CPR, Defibrillation, Advanced Life Support, Post Cardiac Care 9. Describe cardiac arrest in adults. a. Often sudden and results from a cardiac cause. 10. Cardiac arrest in children is usually the result of … a. Respiratory failure or shock. 11. List the 5 steps of the Pediatric Chain of Survival. a. Prevention b. Early Bystander CPR c. Activation of Emergency Response System d. Advanced Life Support e. Post-cardiac arrest care 12. Why is does the Pediatric Chain of Survival have the “Prevention” step in it? a. In children cardiac arrest is often secondary to respiratory failure and shock. Identifying children with these problems is essential to reduce the likelihood of pediatric cardiac arrest and maximize survival and recovery. Therefore, a prevention link is added. 13. What is the sequence of CPR? a. The BLS sequence of steps is C A B (Chest Compressions, Airway, Breathing). 14. A responder should check the victim for two things simultaneously. What are they? a. Check for a response and breathing at the same time. 15. CPR begins with ________________. a. Chest compressions 16. When should you activate the emergency response system and begin CPR? a. For an adult, you should activate the Emergency Response System immediately if the victim is unresponsive and is not breathing or not breathing normally. 17. After delivering 30 compressions, what should you do next? a. Open the airway and give two breaths 18. What type of defibrillator is preferred for an infant? a. A manual defibrillator is preferred for an infant. 19. What should you use if the preferred choice is not available? a. If a manual defibrillator is not available, use an AED equipped with a pediatric dose attenuator. 20. What should you use as a last resort? a. If neither a manual defibrillator nor an AED with a pediatric dose attenuator is available, use and AED without the pediatric dose attenuator. 21. The very first thing you should ALWAYS MAKE SURE OF BEFORE entering any scene to provide help? a. Make sure the scene is safe for you and the victim. (BSI, SCENE SAFE) 22. How should you assess the victim for response? a. Tap the victim’s shoulder and shout “Are you all right?” or “Hey, Hey are you ok?” 23. While you are assessing for response what else are you doing simultaneously? a. Looking for breathing. 24. If there is no response and no breathing or only gasping what should you do? a. Shout for help. If someone responds have them activate Emergency Response System. If no one responds, YOU should activate the Emergency Response System. 25. Define Agonal gasps and describe what a person who has agonal gasps looks like? a. Fish breathing. A person who gasps usually looks like he is drawing air in very quickly. The mouth may be open and jaw, head, or neck may move with gasps. Gasps may appear forceful or weak and may occur at a very slow rate. It can sound like a snort, snore, or groan. IT IS NOT NORMAL BREATHING AND IS A SIGN OF CARDIAC ARREST IN SOMEONE WHO IS UNRESPONSIVE. CPR Part II 26. How long should you check for a pulse? a. Feel for a pulse for at least 5s but not longer than 10s. 27. What should you do if you do NOT definitely feel a pulse? a. If you do not definitely feel a pulse, begin CPR starting with Chest Compressions (CAB). 28. What pulse point should you check for an adult and where is it located? a. For an adult, check the carotid pulse in the neck. 29. What are the two methods for opening an airway? a. Head tilt-chin lift and Jaw thrust. 30. Which method should you use if you suspect a spine injury? a. If spine injury is suspected, use JAW THRUST METHOD. 31. Over how long should you deliver a breath and what should you be sure the breath does? a. You should deliver a breath over 1s and you should make sure the chest rises. 32. What technique should you use to hold the bag valve mask in place? a. Use the C-E grip to hold a bag valve mask (BVM) in place. 33. The correct compression to ventilation RATIO for 1-RESCUER ADULT CPR is _____30____ compressions to _____2___breaths. 34. The correct RATE for giving compressions is ______100_______ compressions a minute. 35. When performing 2 RESCUER ADULT CPR, rescuer 1 performs _compressions___ and rescuer 2 performs __breaths__. 36. Why is it important to COUNT OUT LOUD when giving compressions? a. Effective teams communicate continuously. Counting out loud allows the rescuer providing breaths to anticipate when breaths will be given and prepare to give them efficiently to minimize interruptions in compressions. The count also helps both rescuers know when it is time to switch duties. 37. How long should it take to switch duties? a. It should take no more than 5s to switch duties. 38. The most important determinant of survival from sudden cardiac arrest with ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia is _the interval from collapse to defibrillation_____. (i.e. the faster you can defibrillate a victim of sudden cardiac arrest, the greater their chance of survival.) 39. AED stands for ___Automated External Defibrillator____. 40. What is ventricular fibrillation and how does the AED help VF? a. VF is when the heart muscle fibers quiver and do not contract together to pump blood. A defibrillator delivers an electric shock to stop the quivering of the heart fibers. This allows the muscle fibers of the heart to “reset” so that they can begin to contract at the same time. 41. What are the first two steps in using the AED (Bold print) and how long should it take to complete these two steps? a. Step 1- POWER ON THE AED b. Step 2- ATTACH AED PADS (DON’T FORGET TO PLUG IN PADS TO AED IF NECESSARY) 42. If “no shock” is advised, what do you do next? a. Resume CPR beginning with chest compressions 43. If rescuers can keep the time between the last compression and shock delivery to _LESS THAN 10s__, the shock is much more likely to be effective. Effectiveness of shock delivery _DECREASES_ significantly for every additional __10s__ that elapses between the last compression and shock delivery. 44. True or False. You can use the AED in water. a. FALSE, remove the victim from water and dry off chest. 45. In one cycle of CPR and AED use, how many times should you clear the victim? a. TWICE. Clear the victim before AED analyzes victim and clear them again before shocking them. 46. The correct compression to ventilation ratio for 1-RESCUER CHILD CPR is __30_____compressions and ____2____breaths. 47. The correct rate for delivering compressions for 1 RESCUER CHILD CPR is _AT LEAST 100_ compressions per min. 48. The correct compression to ventilation ratio for 2-RESCUER CHILD CPR is __15___ compressions and __2___ breaths. 49. When should you activate the emergency response system for a child victim when you DID NOT witness the arrest? a. Activate Emergency Response System AFTER 2 min. (5 cycles) of CPR 50. When should you activate the emergency response system for a child victim when you DID witness the arrest? a. If arrest is sudden and witnessed, activate Emergency Response System and get an AED immediately. 51. How do you determine if a victim is a child or an adult (seriously, there is a correct answer). a. Adults include adolescents (i.e. after the onset of puberty). Signs of puberty include chest or underarm hair in males and any breast development in females. CPR Part III 52. The correct compression to ventilation ratio for 1-RESCUER INFANT CPR IS __30___ compressions to ____2____ breaths. 53. The correct compression to ventilation ratio for 2-RESCUER INFANT CPR IS ___15___compressions to ____2____ breaths. 54. THE CORRECT RATE OF DELIVERING ALL COMPRESSION FOR ALL VICTIMS IS AT LEAST _100 COMPRESSIONS PER MIN. (Yes, I know you have answered this many times. It is important.) 55. What pulse point(s) can be used on a child (1-puberty) and where are they located? a. Carotid located in neck and femoral located in the inner thigh, midway between the hipbone and the pubic bone and just below the crease where the leg meets the abdomen. 56. What pulse point should be used on an infant and where is it located? a. Brachial located on the inside of the upper arm, between the infant’s elbow and shoulder. 57. ***Important question: In INFANTS AND CHILDREN, if there is no breathing and no pulse or if despite adequate oxygenation and ventilation, the heart rate is _less than 60 beats/ min_ with signs of poor perfusion, perform cycles of compressions and breaths (30:2 ratio), starting with compressions. 58. What should you do if an INFANT OR CHILD is not breathing but does have a pulse above 60/min? (Pg. 34 3A) a. Start rescue breathing, Give 1 breath every 3 to 5s. 59. The correct depth of compression for an INFANT is a. ___1 ½ “ (4 cm or 1/3 anterior-posterior diameter of chest____. 60. What are the two techniques for delivering compressions for an INFANT? a. 2 finger technique b. 2 thumbs encircling hands technique 61. Where should you place your two fingers to deliver compressions on an infant? (Pg. 36) a. Place 2 fingers in the center of the infant’s chest just below the nipple line. 62. Where should you place the palm of your hand to deliver compressions on an adult or child? (Pg. 10) a. Place palm in center of victim’s chest on the lower half of the breast bone. (Stay off of the xyphoid process) 63. If there is an advanced airway (endotracheal intubation, laryngeal mask airway etc.) in place during 2-RESCUER CPR, a. Do not stop compressions to give breaths. Give 1 breath every 6-8 s (8-10 breaths per min.), without attempting to deliver breaths between compressions. There should be no pause in chest compressions for delivery of breaths. (BOTTOM OF PAGE 43) 64. The correct rate for RESCUE BREATHING IN ADULTS is a. _1 breath every 5 - 6 s_(about 10-12 breaths per min)_. 65. The correct rate for RESCUE BREATHING IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN IS a. _1 breath every 3 – 5 s (about 12-20 breaths per min.). 66. Three signs of a Mild Airway Obstruction are : a. Victim has Good air exchange b. Victim can cough forcefully c. Victim may wheeze between coughs 67. What is the first thing you should do to care for a mild airway obstruction? a. Encourage them to continue coughing. (As long as good air exchange continues, encourage the victim to continue spontaneous coughing and breathing efforts. Do not interfere with victim’s own attempts to expel the foreign body, but stay with the victim and monitor his or her condition.) 68. Give at least 3 signs of a Severe Airway Obstruction. a. Poor or no air exchange b. Weak, ineffective cough OR NO COUGH AT ALL c. Possible cyanosis (turning blue) d. High pitched noise while inhaling or no noise at all e. Increased respiratory difficulty f. Unable to speak g. Clutching neck with the thumb and fingers, making the universal chocking sign. 69. How should you care for a person with a Sever Airway Obstruction? a. Ask the victim if he or she is choking. If the victim nods yes and cannot talk, severe airway obstruction is present and you must try to relieve the obstruction. Begin performing abdominal thrusts (Heimlich maneuver) until the object comes out or victim goes unresponsive. 70. When performing the Heimlich maneuver, you should place the thumb side of your fist a. Place the thumb side of your fist against the victim’s abdomen, in the midline, slightly above the navel and well below the breastbone. 71. How long should you perform the Heimlich maneuver? a. Until the object comes out or the victim becomes unresponsive. 72. What should you do if a choking victim becomes unresponsive? (Pg. 53 2nd paragraph). a. Activate the emergency response system, lower victim to ground and begin CPR, starting with compressions (do not check for a pulse). For an adult or child victim, every time you open the airway to give breaths, open the victim’s mouth wide and look for the object. If you see an object that can easily be removed, remove it with your fingers. If object not seen, keep doing CPR. NEVER PERFORM A BLIND FINGER SWEEP.