File - Jessica G. Anderson
advertisement

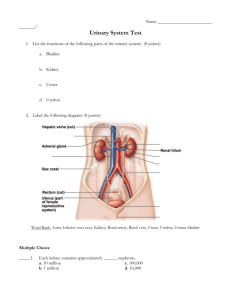
Jessica Anderson KNH 413 Quiz 1 Renal Disease RENAL-ROOT WORDS & COMBINING FORMS 1. Calyx a. Cuplike division of the kidney 2. Cortex a. Outer layer of the kidney 3. Glomerul/o a. Glomerula 4. Medulla a. Inner or central portion of the kidney 5. Nephr/o a. Kidney 6. Pyel/o a. Kidney 7. Py/o a. Pus 8. Ur/o a. Urine 9. Ren/o a. Kidney RENAL-ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Afferent arteriole a. Carries blood to the glomerulus 2. Bowman’s capsule (aka. Glomerular Capsule) a. A thin membranous double-walled capsule surrounding the glomerulus of a vertebrate nephron through which glomerular filtrate passes to the proximal convoluted tubule 3. Collecting tubule a. A nonsecretory tubule that receives urine from several nephrons and discharges it into the pelvis of the kidney 4. Distal convoluted tubule a. The convoluted portion of the nephron lying between the loop of Henle and the nonsecretory part of the nephron (collecting tubule) and concerned especially with the concentration of urine 5. Efferent arteriole a. Carries blood away from the glomerulus 6. Glomerular capsule a. BOWMAN’S CAPSULE 7. Glomerlus a. A network of thin-walled capillaries closely surrounded by a pearshaped epithelial membrane called the Bowman’s capsule (within the kidney). 8. Kidneys a. One of a pair of vertebrate organs situated in the body cavity near the spinal column that excrete waste products of metabolism, in humans are bean-shaped organs about 4.5in long lying behind the peritoneum in a mass of fatty tissue, and consist chiefly of nephrons by which urine is secreted, collected and discharged into the pelvis of the kidney whence it is conveyed by the ureter to the bladder 9. Loop of Henle (aka. Henle’s loop) a. The U-shaped part of a vertebrate nephron that lies b/n and is continuous with the proximal and distal convoluted tubules, that leaves the cortex of the kidney descending into the meduallary tissue and then bending back and reentering the cortex, and that functions in water resorption 10. Nephron (renal tube) a. Basic functioning unit of the kidney; each nephron has two main parts: the glomerulus and the tubule 11. Proximal convoluted tubule a. Portion of the nephron immediately succeeding the glomerulus; susceptible to disease because of its early exposure to toxins in the glomerular filtrate 12. Renal cortex a. Highly vascularlized granular layer of the kidney, containing approximately 1.25 million glomeruli and convoluted tubules, which filter body wastes from the blood, reclaim useful materials, and dispose of the remainder as urine. b. Part of kidney containing the glomeruli and the proximal and distal convoluted tubules 13. Renal medulla a. Inner part of the substance of the kidney, composed chiefly of collecting tubules, and in some species organized into a group of structures called the renal pyramids b. Inner, darker portion of the kidney parenchyma consisting of the renal pyramids 14. Renal Papillae a. The apex of a renal pyramid which projects into the lumen of a calyx of the kidney and through which collecting tubules discharge urine 15. Renal Pelvis a. Funnel-shaped expression of the upper end of the ureter into which the renal calices open; it is usually within the renal sinus, but under certain conditions a large part of it may be outside the kidney b. Into which urine is discharged before entering the ureter RENAL-PHYSIOLOGICAL TERMS 1. Aldosterone a. A hormone secreted by the adrenal glands that is important for maintaining salt and water balance in the body 2. Angiotensin a. A family of peptides of known and similar sequences, with vasconstrictive activity, produced by enzymatic action of renin on angiotensinogen. 3. Antidiuretic hormone (aka. Vasopressin) a. Polypeptide hormone that is secreted by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland or obtained synthetically that increases blood pressure and decreases urine flow 4. Bicarbonate a. Any salt containing the HCO3- anion. b. Radical group HCO3 or a compound, such as sodium bicarbonate, containing it 5. Carbonic acid a. An aqueous solution of carbon dioxide, H2CO3 b. Unstable acid formed by dissolving carbon dioxide in water 6. Diuretic a. A drug that promotes the formation and excretion of urine. b. Increases amount of urine produced and relieves excess fluid buildup in body tissues. i. Used to treat high blood pressure, lung disease, premenstrual syndrome, and other conditions. 7. Erythropoietin a. The hormone produced in the kidney that regulates marrow production of red blood cells 8. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) a. The filtration ability of the glomerulus; used as an index of kidney function; normal value is approximately 125 mL/min 9. Renin a. An enzyme produced in the kidneys that control the activation of the hormone Angiotensin, which stimulates the adrenal glands to produce Aldosterone. RENAL-SYMPTOMATIC TERMS 1. Acetonuria a. Excretion in the urine of large amounts of acetone, an indication of incomplete oxidation of large amounts of fat, and common in diabetic acidosis 2. Acidemia a. Condition of excess acid in the blood consistent with a pH < 7.35 3. Albuminuria a. The presence of albumin in the urine, a common sign of renal or chronic disease 4. Anuria a. Complete suppression of urine formation by the kidney 5. Azotemia a. A buildup of nitrogenous waste products such as urea in the blood and body fluids 6. Dysuria a. Difficult or painful urination 7. Hematuria a. The presence of blood in the urine 8. Hyperkalemia a. High serum postassium 9. Micturition a. Urination, the act of voiding urine i. Desire to urinate; the frequency of urination 10. Nocturia a. Excessive need to urinate/urination at night. 11. Oliguria a. Urine output less than 400mL, which is the minimum amount of normal urine that can carry away the daily load of metabolic waste products 12. Proteinuria a. The presence of too much protein in the urine 13. Pyuria a. The presence of pus in the urine; usually a sign of a UTI 14. Renal insufficiency (renal shut-down, lower nephron nephrosis) a. Reduced capacity to excrete metabolic waste products which accumulate systematically and are detectable clinicopathologically by renal function tests. The early state of uremia. 15. Renal Osteodystrophy a. A general term that refers to bone disease related to CKD, caused by over- or underproduction of PTH or by exposure to aluminum RENAL-DIAGNOSTIC TERMS 1. Acidosis a. Conditions that produce excess acid in the blood 2. Arteriolar nephrosclerosis a. Renal scarring due to arteriolar sclerosis resulting from long-standing hypertension; chronic renal failure develops infrequently b. Degeneration of the tubules (renal) and fibrotic thickening of the glomeruli – edema, hypertrophy of heart, degeneration of renal tubules, and glomerulonephritis 3. Glomerulonephritides (plural) a. Nephritis marked by inflammation of the capillaries of the renal glomeruli and membrane tissue that serves as a filter 4. Hypertrophy of the kidney a. Enlargement or growth the kidney due to increased size of its constituent cells 5. Nephritic syndrome a. A condition of inflammation of the glomerulus, resulting in hematuria proteinuria, and oliguria 6. Nephrolithiasis (renal calculi) a. Kidney stones, a common disorder in the United States 7. Nephromegaly a. Enlargement of the kidney 8. Nephrosclerosis a. Hardening of the kidney, usually associated with hypertension and disease of the renal arterioles. 9. Nephrotic syndrome a. Collection of symptoms which occur because the tiny blood vessels (the glomeruli) in the kidney become leaky. This allows protein (normally never passed out in the urine) to leave the body in large amounts. 10. Pyelonephritis a. Inflammation of both the parenchyma of a kidney and the lining of its renal pelvis, especially due to bacterial infection 11. Uremia (aka. Uremic syndrome) a. A general term used to encompass a cluster of symptoms resulting from disordered biochemical processes as chronic kidney disease progresses; early symptoms include fatigue, delayed thinking, and pruritis RENAL-OPERATIVE TERMS 1. Nephrectomy a. Surgical procedure removing a kidney or section of a kidney 2. Nephrolithotomy a. Incision of kidney or removal of calculi (kidney stones) 3. Nephrostomy a. The surgical formation of an opening b/n a renal pelvis and the outside of the body 4. Nephrotomy a. A incision into the kidney 5. Pyelolithotomy a. Surgical incision of the renal pelvis of a kidney for removal of a kidney stone 6. Pyeloplasty a. Plastic surgery of the renal pelvis of a kidney 7. Pyelotomy a. Incision into the pelvis of the kidney 8. Renal biopsy a. Surgical procedure in which a small piece of the kidney is removed from the body for examination, usually under a microscope. Examination of the tissue can provide info needed to diagnose, monitor or treat problems of the kidney 9. Renal transplantation a. The surgical transfer of a complete kidney from a donor to a recipient RENAL-SPECIAL PROCEDURES 1. Arterio-venous shunt a. A U-shaped plastic tube inserted b/n an artery and a vein; usually to allow repeated access to the arterial system for hemodialysis 2. Dialysis a. Renal replacement procedure that removes excessive and toxic byproducts of metabolism from the blood, thus replacing the filtering function of healthy kidneys 3. Hemodialysis a. A type of renal replacement therapy whereby wastes or uremic toxins are filtered from the blood by a semi-permeable membrane and removed by the dialysis fluid 4. Peritoneal dialysis a. A type of renal replacement therapy during which the peritoneal cavity serves as the reservoir for dialysate and the peritoneum acts as the semi-permeable membrane across which excess body fluid and solutes are removed RENAL-SPECIAL DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES 1. Intravenous pyelography (IVP) a. Radiographic technique for examining the structure and function of the urinary system b. Radiographic imaging of the kidneys, ureter, and bladder using X-ray and contrast dye that is injected intravenously 2. Nephrogram a. Radiographic examining of the kidney after the intravenous injection of water-soluble iodinated contrast material 3. Nephrosonography a. Process of recording the kidney using sound, such as an ultrasound test 4. Pyleogram a. Radiographic picture of the kidneys and ureters that is taken after the IV (intraureteral injection) of a radiopaque contrast medium. 5. Ultrasonic laminograms of kidney a. Painless/noninvasive procedure in which sound waves are bounced off the kidneys. Such sound-waves produce a pattern of echoes that are then used by the computer to create pictures of areas inside the kidney (sonograms) 6. Urogram a. Radiograph/x-ray of the urinary tract 7. Urography a. Radiograph/x-ray of the urinary tract (any part) RENAL-ABBREVIATIONS 1. ADH – anti-diuretic hormone 2. A/G – Albumin-Globulin Ratio 3. Alb - Albumin 4. BUN – Blood Urea Nitrogen 5. CAPD – Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis 6. Cath - catheter 7. Chr - chronic 8. CRF – Chronic Renal Failure 9. ERPF – Effective Renal Plasma Flow 10. ESRD – End Stage Renal Disease 11. Fld - fluid 12. GBM – glomerular basement membrane 13. GFR – glomerular filtration rate 14. HDU – High Density Unit 15. IVP – Intravenous Pyelogram 16. KUB – Kidney, Ureter, Bladder (can be plural) 17. LSK – Liver, Spleen, Kidneys 18. NPN – non-protein nitrogen 19. PDU- Power Doppler Ultrasound (ultrasonography) 20. PSP – Parathyroid Secretory Protein 21. PTH – Parathyroid Hormone 22. RER – Renal Excretion Rate 23. RPF – Renal Plasma Flow 24. RTA – Renal Tubular Acidosis 25. SUN – Serum Urea Nitrogen 26. UA – Urinalysis (Urine analysis) 27. UTI – Urinary Tract Infection