Unit 7 - Leona QSI Math Site
advertisement

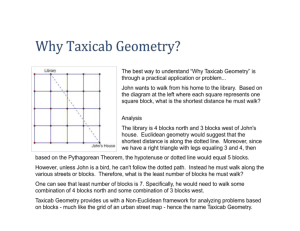
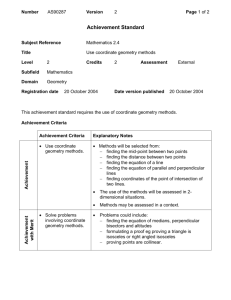
Course: Geometry C Department: Math Grade(s): 9-12 Unit 7: LEONA QSI Curriculum Map Teacher: Course Group: Geometry A,B,C Pre-Requisites: Geometry A,B Essential Questions: How are figures measured? Measurement (16 days) Area/Perimeter Measuring Circles and Parts of Circles How do the formulas used to measure a figure relate to what is being measured? Core Content AZCCRS Standards (High School Standards) = Major □ = Supporting ○= Additional ★= Modeling ○G.C.B.5 Derive using similarity the fact that the length of the arc intercepted by an angle is proportional to the radius, and define the radian measure of the angle as the constant of proportionality; derive the formula for the area of a sector. G.GPE.B.7 Use coordinates to compute perimeters of polygons and areas of triangles and rectangles, e.g., using the distance formula. (★) Surface Area ○G.GMD.A.1 Give an informal argument for the formulas Volume for the circumference of a circle, area of a circle, volume of a cylinder, pyramid, and cone. Use dissection arguments, Cavalieri's principle, and informal limit arguments. Density ○G.GMD.A.3 Use volume formulas for cylinders, pyramids, cones, and spheres to solve problems. (★) Measurements with Changing Parameters ○G.GMD.B.4 Identify the shapes of two-dimensional crosssections of three-dimensional objects, and identify three-dimensional objects generated by rotations of two-dimensional objects. G.MG.A.2 Apply concepts of density based on area and volume in modeling situations (e.g., persons per square mile, BTUs per cubic foot). (★) Mathematical Practices MP.1-8 Using properties of special right triangles and trig ratios to calculate perimeter and area of regular polygons. Use distance and midpoint to compute perimeters and areas of polygons. Understand and apply properties of similarity to the parts of a circle, which may include an introduction to radian measurements Calculate the arc length and area of a sector on a circle. Understand and apply Cavalieri’s principle which states that the volume will stay the same with a right figure and a non-right figure. Key Vocabulary: Perimeter, Circumference, Area, Two-Dimensional, ThreeDimensional, Prism, Pyramid, Cube, Cylinder, Cone, Sphere, Hemisphere, Volume, Surface Area, Lateral Area, Density, Intercepted Arc, Minor Arc, Major Arc, Length of Arc, Area of Sector, Radian, Cavalier’s Principle, Dissection, Limits Tier 3 Assessment Resources Support Identify the names of polygons, and three dimensional figures Formal Find the area of irregular shaped polygons. In Formal Use nets to determine surface area of 3dimensional figures. 1. Pre Test Quizzes 2. http://map.mathshell.org/materials/lessons.php?t askid=213#task213 3. http://emergentmath.com/2012/11/08/moremath-food-blogging-i-may-need-some-helpfrom-my-southern-friends/ 4. Dan Meyer Obscure Geometry 5. http://emergentmath.com/2012/01/07/can-wemake-an-even-edgier-brownie-pan-what-aboutthe-perfect-brownie-pan/ 6. http://fivetriangles.blogspot.com/2012/12/40dog-on-lead.html 7. http://emergentmath.com/2011/02/18/the-pizzacasbah-30-inch-pizza-challenge/ Unit Test Checking for Understanding Questioning Completion of Project/Activity/A ssignments Summarization of Learning Daily Exit Slip Area and Perimeter http://map.mathshell.org/materials/lessons.php?t askid=212#task212 8. Use principles such as dissection and Cavalier’s to derive the formulas for circumference of a circle, area of a circle, volume of a cylinder, pyramid, and cone. Derive area and volume, surface area and lateral area formulas for figures. http://fawnnguyen.com/don-stewards-completequadrilateral/ Similar in Figures and Ratios of Length, Perimeter, Area, Volume, Surface Area 9. http://www.tarleton.edu/team/documents/9to12/ geometry/geometry1_5.pdf 10. http://www.nctm.org/standards/content.aspx?id =33195 11. http://www.nctm.org/standards/content.aspx?id =25097 12. http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/polyhedr on-models.html Updated: 2/9/2016 Course: Geometry C Department: Math Grade(s): 9-12 LEONA QSI Curriculum Map Teacher: Course Group: Geometry A,B,C Pre-Requisites: Geometry A,B Use volume formulas for cylinders, pyramids, cones, and spheres to solve problems. Area of Sectors and Arc Length 13. http://map.mathshell.org/materials/lessons.php?t askid=441#task441 Understand and apply density formulas to solve problems. 14. http://musingmathematically.blogspot.ca/2012/0 7/bike-trail-task.html Apply properties of similarity to solve problems with 3Dimensional figures. 15. http://jdevarona.wordpress.com/2012/07/13/letthe-random-problem-ideas-begin/ Volume 16. http://map.mathshell.org/materials/lessons.php?t askid=216#task216 17. http://mrpiccmath.weebly.com/blog/3-actsmmm-juice 18. http://mrpiccmath.weebly.com/blog/3-acts-popbox-design 19. http://mrmeyer.com/threeacts/youpourichoose/ 20. http://threeacts.mrmeyer.com/popcornpicker/ 21. https://s3.amazonaws.com/threeacts/dollarwall.z ip 22. http://threeacts.mrmeyer.com/coincarpet/ 23. http://threeacts.mrmeyer.com/carcaravan/ 24. http://threeacts.mrmeyer.com/besttriangle/ 25. https://s3.amazonaws.com/threeacts/applemothe rship.zip Cavalier’s Principle for Volume 26. http://education.ti.com/en/us/activity/detail?id= 0CB018E255D84C3D88F156B16F39752B&ref =%2Fcalculators%2Fdownloads%2FUS%2FAc tivities%2FSearch%2FSubject%3Fs%3D5022% 26sa%3D5024%26t%3D5054%26d%3D1008 27. Density Updated: 2/9/2016 LEONA QSI Curriculum Map Teacher: Course Group: Geometry A,B,C Pre-Requisites: Geometry A,B Course: Geometry C Department: Math Grade(s): 9-12 http://www.yummymath.com/wpcontent/uploads/cows-global-warming.pdf 28. Unit 8: Essential Questions: How can figures and their measurements be used to model real objects? Modeling How can modeling be used to solve problems? (14 days) Modeling Relationship between Twoand ThreeDimensional Objects Applied Geometry and Design AZCCRS Standards = Major □ = Supporting ○= Additional ★= Modeling ○G.GMD.B.4 Identify the shapes of two-dimensional crosssections of three-dimensional objects, and identify three-dimensional objects generated by rotations of two-dimensional objects. G.MG.A.1 Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects (e.g., modeling a tree trunk or a human torso as a cylinder). (★) G.MG.A.2 Apply concepts of density based on area and volume in modeling situations (e.g., persons per square mile, BTUs per cubic foot). (★) G.MG.A.3 Apply geometric methods to solve design problems (e.g., designing an object or structure to satisfy physical constraints or minimize cost; working with typographic grid systems based on ratios). (★) Mathematical Practices MP.1-8 Core Content (High School Standards) Key Vocabulary: Perimeter, Circumference, Area, Two-Dimensional, ThreeDimensional, Prism, Pyramid, Cube, Cylinder, Cone, Sphere, Hemisphere, Volume, Surface Area, Lateral Area, Density, Intercepted Arc, Minor Arc, Major Arc, Length of Arc, Area of Sector, Radian, Similarity, Model, Approximation, Assumption, Net, Cross-Section, Revolution, BTU, Population Density, Topography Tier 3 Assessment Resources Support Use technology to identify the shapes of 2-dimensional cross-sections of 3dimensional objects. Lateral area versus surface area. Use technology to Identify 3dimentional objects created by revolving 2-dimensional objects. Identify nets for polyhedrons, cylinders, and cones. Apply surface area and volume in a context to solve a problem with given constraints. Calculate basic surface areas using nets Solve problems in a context to maximize or minimize the dimensions of a figure. Apply concepts of density based on area and volume in modeling situations (e.g., persons per square mile, BTUs per cubic foot). Formal Pre Test 1. 2. Quizzes Unit Test 3. In Formal 4. Checking for Understanding Questioning 5. Cross Sections https://tube.geogebra.org/student/b248823 http://nlvm.usu.edu/en/nav/frames_asid_126_g_ 3_t_3.html?open=instructions&from=topic_t_3. html http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/activities/C rossSectionFlyer/ http://www.learner.org/courses/learningmath/ge ometry/session9/part_c/index.html Modeling between 2 and 3 Dimensional Objects http://map.mathshell.org/materials/lessons.php?t askid=428#task428 Completion of Project/Activity/A ssignments 6. http://map.mathshell.org/materials/lessons.php?t askid=439#task439 Summarization of Learning 7. http://www.korthalsaltes.com/ 8. http://math.arizona.edu/~models/ 9. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/topics/SolidGeo metry.html Daily Exit Slip 10. http://www.andrewlipson.com/mathlego.htm Apply geometric methods to solve design problems (e.g., designing an object or Applied Geometry Models 11. http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072532947/st Updated: 2/9/2016 Course: Geometry C Department: Math Grade(s): 9-12 LEONA QSI Curriculum Map Teacher: Course Group: Geometry A,B,C Pre-Requisites: Geometry A,B structure to satisfy physical constraints or minimize cost; working with typographic grid systems based on ratios). udent_view0/chapter9/cross-sections_of_a_cube.html 12. http://illuminations.nctm.org/Lesson.aspx?id=2 788 13. Interactive 2D Figures Rotation to form 3D solids http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/activities/3 DTransmographer/ Updated: 2/9/2016