Biology 20 - Mr. Lechner`s Biology 20 Wiki
advertisement

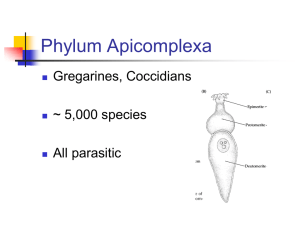
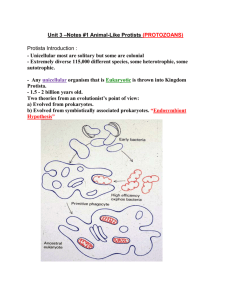
Biology 20 Unit 1 “Introduction to Biology” http://greenallbiology20.wikispaces.com/ Key Concepts: - Biology - Branches of Biology o zoology o botany o microbiology o cytology o ecology - Microscopes o light, electron o measuring with the microscope o magnification, resolution (resolving power) o proper care and use (microscopes) o preparing a wet mount slide o field of view o parts of the microscope - Chapter 1 – “Biology in the 21st Century (sections 1.1-1.5, pages 2-27) o biosphere o biodiversity o species o organism o cell o metabolism o DNA o system o ecosystem o homeostasis o evolution o adaptation o observation o data o hypothesis o experiments o independent, dependant variable o microscope o gene o molecular genetics o biotechnology o transgenic - 2 important theories in Biology o Alvarez Theory extinction of the dinosaurs Chicxulub Crater o Theory of Natural Selection (Evolution) Charles Darwin “Survival of the Fittest” Biology 20 Unit 2 Review “Diversity of Life” – part 1 Key concepts: Taxonomy - taxon (Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species) - dichotomous key - 3 domains – Archaea, Bacteria and Eukarya - 6 Kingdoms – Bacteria, Archaea, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia - binomial nomenclature (3 rules) - use of Latin in taxonomy - Linnaeus (Carl von Linne) - prokaryotes / eukaryotes Viruses – classification, composition, characteristics, viral infections Prokaryotes – Archaea & Bacteria: - obligate anaerobes obligate aerobes facultative aerobes Archaea: 4 groups: - methanogens psychrophiles halophiles thermophiles Kingdom Protista – 3 groups (plant-like, fungal-like, animal-like) - Plant-like protists – 6 phyla – Euglenoids (Euglenophyta), Diatoms (Bacillariophyta), Dinoflagellates (Dinoflagellata), Green Algae (Chlorophyta), Brown Algae (Phaeophyta), Red Algae (Rhodophyta) - Fungal-like protists – 2 phyla – slime molds (Myxomycota), water molds (Oomycota) - Animal-like protists – 4 phyla - Zooflagellates (Mastigophora), Sarcodines (Rhizopoda), Ciliates (Ciliophora), Sporozoans (Apicomplexa) Biology 20 Unit 2 Review “Diversity of Life” – part 2 Key concepts: Kingdom Fungi – chapter 19, section 19.5 - 4 main groups: o Primitive fungi (phylum Chytridiomycota) o Sac fungi (phylum Ascomycota) o Molds (phylum Zygomycota) o Club Fungi (phylum Basidoimycota) Kingdom Plantae – chapter 20, sections 20.2 & 20.3 - 2 main categories: non-vascular & vascular o Non-vascular plants – liverworts (phylum Hepatophyta) , hornworts (phylum Anthocerophyta) and mosses (phylum Bryophyta) o Vascular plants – can be subdivided into: Seedless and seed plants Seedless plants (spore producers) - club mosses (phylum Lycophyta), whisk ferns, horsetails and ferns (phylum Pterophyta) Seed plants – two types: Gymnosperms – (“naked seeds”) - cycads, ginkgos and conifers Angiosperms – (“flowering plants) – two types: o Monocots o Dicots Kingdom Animalia – chapters 23, 24, 25 - Two types: invertebrates & vertebrates - Invertebrates: o Sponges (Phylum Porifera) o Cnidarians (Phylum Coelenterata) o Flatworms (Phylum Platyheminthes) o Roundworms (Phylum Nematoda) o Segmented Worms (Phylum Annelida) o Mollusks (Phylum Mollusca) o Arthropods (Phylum Arthropoda) o Echinoderms (Phylum Echindoermata) One main vertebrate group: - Chordates (Phylum Chordata) o Sub-phylum Vertebrata – 7 classes: Jawless Fish Cartilaginous Fish Bony Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals Biology 20 Unit 3 “Ecological Organizations” Chapter 13 – “Principles of Ecology” - ecology community, ecosystem, biome observation, experimentation, modeling biotic, abiotic biodiversity keystone species producers, autotrophs consumers, heterotrophs chemosynthesis food chain, food web herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, detritivores, decomposers specialist, generalist trophic level hydrological cycle, biogeochemical cycle, carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle (nitrogen fixation), phosphorus cycle biomass, energy pyramid