Nerve Summary Chart
advertisement

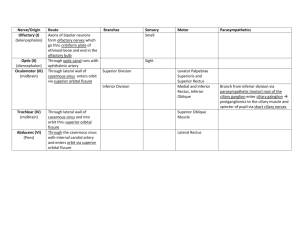
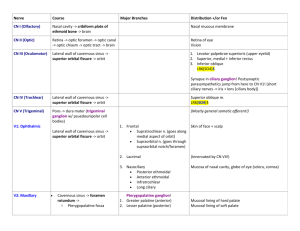
Nerve/Origin Olfactory (I) (telencephalon) Optic (II) (diencephalon) Oculomotor (III) (midbrain) Trochlear (IV) (midbrain) Abducens (VI) (Pons) Route Branches Axons of bipolar neurons form olfactory nerves which go thru cribiform plate of ethmoid bone and end in the olfactory bulb Through optic canal runs with ophthalmic artery Through lateral wall of Superior Division cavernous sinus enters orbit via superior orbital fissure Inferior Division Through lateral wall of cavernous sinus and into orbit thru superior orbital fissure Through the cavernous sinus with internal carotid artery and enters orbit via superior orbital fissure Sensory Smell Motor Parasympathetics Sight Levator Palpebrae Superioris and Superior Rectus Medial and Inferior Rectus, Inferior Oblique Superior Oblique Muscle Lateral Rectus Branch from inferior division via parasympathetic (motor) root of the ciliary ganglion enter ciliary galnglion postganglionics to the ciliary muscle and spincter of pupil via short ciliary nerves Facial (VII) (Pons) Second Branchial Arch Through internal acoustic meatus with vestibulocochlear nerve, into facial canal and goes laterally through petrous portion of temporal bone until middle ear (tympanic cavity). Then it turns backward “genu” at location of geniculate ganglion (sensory cell bodies). When reaches posterior wall of middle ear, it turns downward and exits via stylomastiod foramen Facial Proper: Branch to stapedius in facial canal, after exits stylomastoid foramen branches to posterior auricular and post belly digastrics/stylohyoid, then in parotid gland gives off temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, and cervical branches Through facial canal, exits stylohyoid foramen and enters substance of parotid gland Nervus Intermedius: Greater petrosal nerve Exits at level of geniculate ganglion, hiatus of greater petrosal nerve, foramen lacerum, ptergyoid canal (+ deep petrosal nerve) Pterygopalatie ganglion/fossa Nervus Intermedius: Chorda Tympani facial canal tympanic cavity just before stylomastoid foramen, inner surface of tympanic membrane (over malleolus) pterygotympanic fissure infratemporal fossa Taste to hard and soft palates via greater and lesser palatine nerves (V2) Preganglionics synapse in Pterygopalatine ganglion (hanging from V2) and send postanglionic parasympathetics through the following nerves: 1) Greater/lesser palatine 2) Posterior Nasal 3) Nasopalatine 4) Zygomatic – takes to lacrimal gland via lacrimal nerve (V1) With lingual nerve, Taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue Preganglionics travel with lingual nerve to the submandibular ganglion, where they synapse and follow the lingual nerve to 1) Submandibular gland 2) Sublingual gland 3) Linugal gland Vestibulocochlear (VIII) (Pons) Glossopharygneal (IX) (Medulla Oblongata) Third Branchial Arch Enters internal acoustic meatus with the facial nerve Vestibular Cochlear Balance Hearing Tympanic Sensory to the tympanic cavity (pain from the middle ear can be referred from or to the tonsils) Emerges from post-olivary sulcus, gains sensory fibers from petrous and superior ganglia, exit the jugular foramen Enters tympanic cavity, tympanic plexus, hiatus of the lesser petrosal nerve, foramen ovale, infratemporal fossa, auriculotemporal nerve (V3), and facial nerve Contains: 1) postganglionic sympathetic fibers (superior cervical ganglion) 2) Twig of facial nerve 3) Sensory 4)Preganglionic Parasympathetics Carotid Sensory from baroreceoptors/ chemoreceptors from the carotid sinus/body Motor Pharyngeal Lingual Parasympathetics travel through the tympanic plexus and reconverge as the lesser petrosal nerve. This descends through hiatus of lesser petrosal nerve and exits skull via foramen ovale infratemporal fossa. Here, the preganglionic parasympathetics synapse in otic ganglion. Postganglionic fibers then run with auriculotemporal and facial nerves to the parotid gland To the stylopharyngeus muscle Sensory to mucosa of pharynx and palatine tonsils To posterior 1/3 of the tongue Vagus (X) (Medulla Oblongata) 4-6th Branchial Arches Exits via post-olivary sulcus and descends to jugular foramen, where it receives sensory fibers from the superior and inferior ganglia. Exits via jugular foramen. Meningeal Branch Auricular Branch Carotid Branch Aortic Branch Pharyngeal Superior Laryngeal A) Internal Pierces thyrohyoid membrane, with superior laryngeal artery B) Exterior Runs with superior thyroid a. Recurrent Laryngeal Sensory to the dura mater External acoustic meatus to the tympanic membrane Sensory from baroreceoptors/ chemoreceptors from the carotid sinus/body Sensory from baroreceoptors/ chemoreceptors from the aortic arch/body Sensory to the Pharynx. Motor to the muscles of the pharynx (except stylopharyngeus IX) and palate (except tensor of the palate (V3) Larynx vocal cords, and Taste to epiglottis and valleculae of the tongue Sensory of larynx below vocal cords Cricothyroid muscle and cricopharyngeus portion (internal constrictor All muscles of larynx (except cricothyroid) Branches below the Laryngeal Nerves Accessory (XI) (Medulla Oblongata) Branchial arches beyond 6 Hypoglossal (XII) Medulla Oblongata Carry preganglionic parasympathetics to the thoracic viscera and abdominal organs (fore- and midgut Ascends from C3-C4 Sternocleidomastoid between dorsal and ventral and Trapezius rootlets, enters foramen magnum, exits skull via jugular foramen Emerges from pre-olivary All intrinsic and sulcus in line with ventral extrinsic muscles of roots of spinal nerves. tongue (except Leaves skull by hypoglossal palatoglossus canal tongue vagus) - Cell bodies of general sensory neurons (pseudounipolar) are in ganglia of: Trigeminal (V), Facial (VII), Glossopharyngeal (IX), and Vagus (X) - Taste neurons (pseudounipolar) are located in the ganglia of: Facial (VII), Glossopharyngeal (IX), and Vagus (X) - Nerves 9-11 (IX-XI) exit the jugular foramen!! - Branchiomeric Cranial Nerves (carry special visceral efferent/ branchial motor fibers): 1) Trigeminal – Branchial Arch 1 2) Facial – Branchial Arch 2 3) Glossopharyngeal – Branchial Arch 3 4) Vagus – Branchial Arch 4-6 5)Accessory – Theoretical arches beyond 6 Suprahyoid Muscles Digastric (anterior belly) V3 via inferior alveolar nerve (posterior belly) facial nerve Stylohyoid – facial nerve Mylohyoid – V3 via inferior alveolar nerve Geniohyoid – ventral root of C1 via hypoglossus Infrahyoid Muscles: Strap muscles (omohyoid, sternohyoid, sternothyroid) – ansa cervicalis Thyrohyoid - ventral root of C1 via hypoglossus Trigeminal Nerve – First Branchial Arch Division Opthalmic Division (V1) Through lateral wall of cavernous sinus and supraorbital fissure Branches Frontal Lacrimal Further Branches Supratrochlear Supraorbital (larger and more lateral) ---------------------- Nasociliary Long Ciliary Thru lateral wall of cavernous sinus and through foramen rotundum to the ptergyopalatine fossa Sensory To scalp and upper eyelid, to vertex of scalp Above lateral rectus To lacrimal gland and upper eyelid Sensory fibers to cornea Posterior Ethmoidal Thru posterior ethmoidal foramen Posterior ethmoidal air cells and sphenoidal air sinus Anterior Ethmoidal Anterior ethmoidal foramen, through cribiform plate to cranial cavity, through nasal slit, and to external nasal branch Under trochlea Anterior/Middle ethmoidal air cells, meninges, anterior nasal septum and ant. nasal wall, posterior ½ of nose skin Infratrochlear Maxillary Division (V2) Route Above trochlea/Thru supraorbital foramen Greater and Lesser Palatine (from pterygopalatine ganglion) Thru greater and lesser palatine foramina Posterior Nasal (pterygopalatine g Nasopalatine (pteyrgopalatine ganglion) From ganglion and thru Sphenopalatine foramen From ganglion and thru Sphenopalatine foramen and incisive foramen Middle corner of upper eyelid, side of nose Sensory to hard and soft palate Carry taste to hard and soft palates from pterygopalatine ganglion (VII – greater petrosal) Sensory to posterior nasal septum/walls To nasal septum, anterior hard palate Motor Parasympathetics CARRY: To lacrimal gland from zygomatic of V2 (from greater petrosal of VII) CARRY: SYMPATHETICS to the dilator of pupil and vasculature of eye CARRY: Parasympathetic branches to mucosa of hard and soft palate mucous CARRY: To nasal glands CARRY: To nasal/palatine glands Maxillary (V2) Zygomatic Zygomaticofacial Inferior orbital fissure To zygomatic and temporal regions of face Superior Alveolar Thru alveolar canals Infraorbital Inferior orbital fissure, Infraorbital groove, foramen, canal… TERMINAL BR. To teeth and gums, and maxillary sinus To lower eyelid, anterior cheek, upper lip, nasal vestibule, side of nose CARRY: To lacrimal gland via lacrimal nerve V1 Zygomaticotempo ral Mandibular Division (V3) Through foramen ovale to the infratemporal fossa Motor Branches Meningeal To muscles of mastication, ant. belly of digastric and mylohyoid, to tensor of palate and tensor tympani Runs with middle meningeal artery through the foramen spinosum Buccal To dura mater To corner of mouth and inside of mouth To the external ear and scalp over temporal region Temporalmandibular joint (TMJ!!!!!) Auriculotemporal Splits around the middle meningeal artery, reforms and runs to parotid gland Inferior Alveolar Mandibular foramen, mandibular canal, mental foramen mental nerve Lower teeth and gums, and lower chin Lingual Runs near 3rd molar and duct of submandibular gland Sensory to anterior 2/3 tonuge Taste from chorda tympanii CARRY: postganglionic parasympathetics from IX from lesser auricular and delivers to facial parotid gland Gives off motor branch to mylohyoid & ant. digastrics CARRY: (submandibular ganglion) from chorda tympani submandibular, sublingual and lingual glands)