Food Products and Processing Systems AG2
advertisement
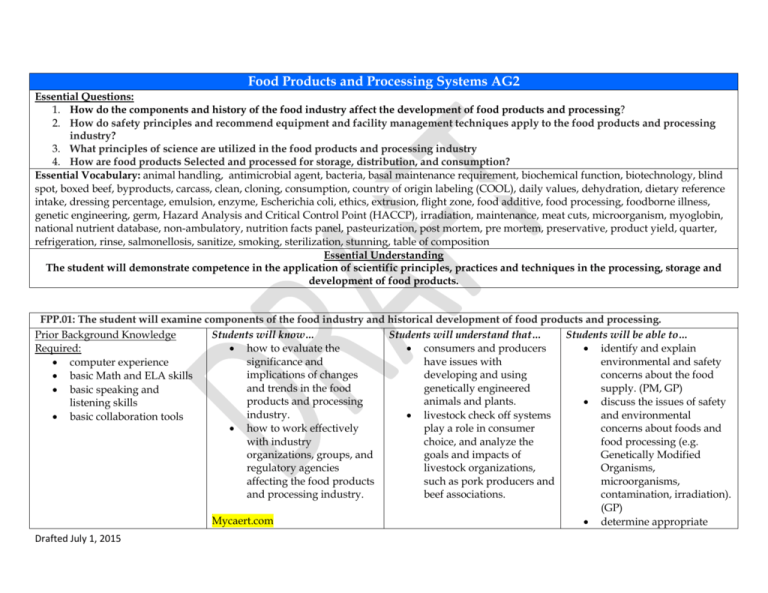
Food Products and Processing Systems AG2 Essential Questions: 1. How do the components and history of the food industry affect the development of food products and processing? 2. How do safety principles and recommend equipment and facility management techniques apply to the food products and processing industry? 3. What principles of science are utilized in the food products and processing industry 4. How are food products Selected and processed for storage, distribution, and consumption? Essential Vocabulary: animal handling, antimicrobial agent, bacteria, basal maintenance requirement, biochemical function, biotechnology, blind spot, boxed beef, byproducts, carcass, clean, cloning, consumption, country of origin labeling (COOL), daily values, dehydration, dietary reference intake, dressing percentage, emulsion, enzyme, Escherichia coli, ethics, extrusion, flight zone, food additive, food processing, foodborne illness, genetic engineering, germ, Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP), irradiation, maintenance, meat cuts, microorganism, myoglobin, national nutrient database, non-ambulatory, nutrition facts panel, pasteurization, post mortem, pre mortem, preservative, product yield, quarter, refrigeration, rinse, salmonellosis, sanitize, smoking, sterilization, stunning, table of composition Essential Understanding The student will demonstrate competence in the application of scientific principles, practices and techniques in the processing, storage and development of food products. FPP.01: The student will examine components of the food industry and historical development of food products and processing. Students will know… Students will understand that… Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to evaluate the consumers and producers identify and explain significance and have issues with environmental and safety computer experience implications of changes developing and using concerns about the food basic Math and ELA skills and trends in the food genetically engineered supply. (PM, GP) basic speaking and products and processing animals and plants. discuss the issues of safety listening skills industry. and environmental livestock check off systems basic collaboration tools play a role in consumer concerns about foods and how to work effectively with industry choice, and analyze the food processing (e.g. organizations, groups, and goals and impacts of Genetically Modified regulatory agencies livestock organizations, Organisms, affecting the food products such as pork producers and microorganisms, and processing industry. beef associations. contamination, irradiation). (GP) Mycaert.com determine appropriate Drafted July 1, 2015 APSR:C1-3 APSR:C7-19 Animalcaretraining.org Vocabulary: biotechnology cloning consumption ethics genetic engineering industry response to consumer concerns to assure a safe and wholesome food supply. (GP) FPP.02: The student will apply safety principles; recommend equipment and facility management techniques to the food products and processing industry. Students will know… Students will understand that … Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to manage operational food processing follows identify reasons for using a procedures and create procedures to ensure that planned maintenance computer experience equipment and facility foods are safe. program to maintain basic Math and ELA skills maintenance plans. equipment and facilities. following the Best basic speaking and (GP) Management Practices for how to implement Hazard listening skills Analysis and Critical Animal Treatments and describe contamination basic collaboration tools Control Point (HACCP) Health Maintenance is hazards (physical, procedures to establish economically and socially chemical, and operating parameters. responsible. biological)associated with food products and how to apply safety and following the Best processing. (PM, GP, AHH) sanitation procedures in Management Practices the handling, processing, Record Keeping and describe the effects foodand storing of food Inventory Control is borne pathogens have on products. required by law. food products and humans. (AHH) Agednet.com explain the importance of FS127 record keeping in a food Vocabulary: products and processing bacteria system. (LRE) clean Country of origin labeling Drafted July 1, 2015 (COOL) Escherichia coli foodborne illness germ Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) microorganism rinse salmonellosis sanitize FPP.03: The student will apply principles off science to the food products and processing industry. Students will know… Students will understand that … Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to apply principles of information in food labels explain the application of science to food processing can be interpreted for food chemistry and physics to computer experience to provide a safe, composition and nutrient food science. (GP) basic Math and ELA skills wholesome and nutritious content. explain the “My Plate” basic speaking and food supply. graphic in relation to the principles of science are listening skills applied to the food essential nutrients for the basic collaboration tools Mycaert.com products and processing human diet. (AHH) ALSF:A1-3 industry. compare and contrast the AGEDnet.com the meat industry processes nutritive value of food and FS115 meat for convenience, food groups. (AHH) preservation and safety. discuss common food Vocabulary: constituents (e.g. proteins, basal maintenance carbohydrates, fats, requirement vitamins, minerals). (AHH) biochemical function compare and contrast food daily values constituents and their dehydration relative value to product taste, appearance, etc.) dietary reference intake (AHH) emulsion extrusion Drafted July 1, 2015 food processing irradiation maintenance national nutrient database nutrition facts panel pasteurization refrigeration smoking sterilization table of composition FPP.04: The student will select and process food products for storage, distribution, and consumption. Students will know… Students will understand that … Prior Background Knowledge Required: how to utilize harvesting, sodium nitrite and salt can selection and inspection be used in cured meat computer experience techniques to obtain quality products. basic Math and ELA skills food products according to common major steps are basic speaking and industry standards. involved in the processing listening skills of animal carcasses. how to evaluate, grade, and basic collaboration tools classify processed food average dressing products. percentages for cattle, sheep, and hogs are how to process, preserve, package, and present food effected by many factors. and food products for sale there are common and distribution. wholesale and retail cuts of Mycaert.com beef, pork, and lamb. ALSF:A4-2 analyzing factors that affect APSR:C6-1 quality and yield grades APSR:C6-2 can improve products. livestock psychology and Agednet.com proper handling practices LA013 improve productivity and FS114 animal welfare. the meat industry produces Drafted July 1, 2015 Students will be able to… identify quality and yield grades of food products. (LRE) discuss factors that affect quality and yield grades of food products. (LRE) identify and describe accepted animal treatment and harvesting techniques. (PM, GP, AHH) compare and contrast accepted animal treatment an harvesting techniques. (GP, AHH) describe the importance of pre-mortem and postmortem inspections of animals. (AHH) explain desirable and undesirable characteristics of both pre-mortem and Vocabulary: animal handling antimicrobial agent blind spot boxed beef byproducts carcass dressing percentage enzyme flight zone food additive meat cuts myoglobin non-ambulatory post mortem pre mortem preservative product yield quarter stunning and maintains a quality product. care and handling of nonambulatory animals must be humane. Drafted July 1, 2015 post-mortem animals in relation to the production of food products. (AHH) identify and describe foods derived from meat, egg, poultry, fish, and dairy products. (GP) discuss and describe qualities of processed meat, egg, poultry, fish, and dairy products. (GP) identify and describe products derived from grains, legumes, and oilseeds. (GP) discuss desirable qualities of grain, legume, and oilseed products. (GP) identify and explain common weights and measures used in the food products and processing industry. (GP, AS) weigh and measure food products and perform conversions between units of measure. (PM, GP, AS) explain methods and materials for processing foods for sale as fresh-food products. (AS) identify and explain storage conditions to preserve product quality. (GP, AHH)