Read the following text! TEXT A Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline

Read the following text!
TEXT A
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. In general any organic compound is anything compound that contains a carbon.
In organic chemistry, compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds, which contain benzene or similar rings of atoms, and aliphatic compounds, which do not contain those rings.
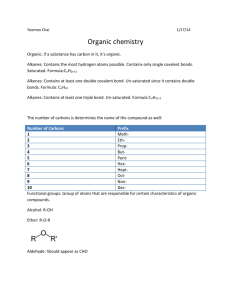
The aliphatic hydrocarbons are subdivided into three groups of homologous series according to their state of saturation:
paraffins, which are alkanes without any double or triple bonds,
olefins or alkenes which contain one or more double bonds, i.e. di-olefins (dienes) or poly-olefins
alkynes, which have one or more triple bonds.
Formaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula CH
2
O. It is a simple derivative of a hydrocarbon, hence its systematic name is methanal. The common name of the substance comes from its similarity and relation to formic acid. An aqueous solution of formaldehyde (formalin) can be useful as a disinfectant as it kills most bacteria and fungi
(including their spores).
Formaldehyde is used to inactivate bacterial products for toxoid vaccines (vaccines that use an inactive bacterial toxin to produce immunity). It is also used to kill unwanted viruses and bacteria that might contaminate the vaccine during production. Urinary tract infections are also often treated using a derivative of formaldehyde (methenamine), a method often chosen because it prevents overuse of antibiotics and the resultant development of bacterial resistance to them. In an acid environment methenamine is converted in the kidneys to formaldehyde, which then has an antibacterial effect in the urinary tract. This is not safe for long term use due to the carcinogenic effect of formaldehyde.
Salicylic acid is colorless crystalline organic acid , widely used in organic synthesis and functions as a plant hormone. In addition to being an important active metabolite of aspirin
(acetylsalicylic acid), which acts in part as a prodrug to salicylic acid, it is probably best known for its use in anti-acne treatments. The salts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates.
Carbohydrates are the most abundant class of organic compounds found in living organisms. They originate as products of photosynthesis, an endothermic reductive condensation of carbon dioxide requiring light energy and the pigment chlorophyll.
The formulas of many carbohydrates can be written as carbon hydrates, Cn(H
2
O)n, hence their name. The carbohydrates are a major source of metabolic energy, both for plants and for animals that depend on plants for food. Aside from the sugars and starches that meet this vital nutritional role, carbohydrates also serve as a structural material
(cellulose), a component of the energy transport compound ATP, recognition sites on cell surfaces, and one of three essential components of DNA and RNA.
1
Circle the correct answer.
1. Which branch of chemistry is the study of substances which are compounds of carbon? a) organic chemistry b) analytical chemistry c) inorganic chemistry d) physical chemistry e) no answer is correct
2. An organic molecule having only hydrogen and carbon atoms is also called a (n) a) protein b) hydrocarbon c) carbohydrate d) none of the above e) no answer is correct
3. Formaldehyde is: a) Carbohydrate b) Hydrocarbon c) Derivative of hydrocarbon d) An acid e) no answer is correct
4. Urinary tract infections could be treated with a) Salicylic acid b) Formaldehyde c) Methenamine d) Cellulose e) no answer is correct
5. An aqueous solution of formaldehyde is called formalin. a) True b) False
6. The salts of salicylic acid are probably best known for their use in anti-acne treatments: a) True b) False
7. Aspirin is: a) Formic acid b) ATP c) Salicylic acid d) Acetylsalicylic acid e) no answer is correct
2
8. Which of the following kills most bacteria and fungi? a) aspirin b) methanal c) dienes d) no answer is correct
9. Carbohydrates are used to kill unwanted viruses and bacteria that might contaminate the vaccine during production. a) True b) False
10. Which statement it false for carbohydrates a) Their common formula can be written Hn(CO
2
)n b) They are the most abundant class of organic compounds found in living organisms c) The carbohydrates are a major source of metabolic energy, both for animals that depend on plants for food and for plants.
11. What is true for salicylic acid? Make a cross.
It’s a gas
It’s a solid
Metabolite of aspirin
Metabolite of DNA
It’s salts are called salicylates
It’s esters are called salicylates
12.Choose one of the alternatives in the following text
There are three groups of isomeric/homologous series according to state of saturation/ aggregate state of carbohydrates/ hydrocarbons. Alkanes/alkenes don’t contain any double or triple bonds. Aliphatic compounds with one or more double bonds are called alkenes/alkynes, and with one or more triple bonds are named paraffins/alkynes.
13.Fill in the gaps with terms from TEXT A above.
Living organisms are mostly made of a class of organic compounds, called …(1). These compounds result of an endothermic process, … (2), in presence of light and in the green pigment chlorophyll. The main role of the carbohydrates is as … (3), but they are also important for the structure of the plant cell and as a component of three essential compounds, which are … (4), … (5) and …(6).
14.Select the formula of copper(I) nitrite: a) Cu(NO
2
)
2 b) Cu
2
NO
2
3
c) CuNO
2 d) CuNO
3 e) no answer is correct
15. Select the formula of calcium hypochlorite: a) CaClO
2 b) CaCl
2 c) CaHClO d) Ca(ClO)
2 e) no answer is correct
16.Select the formula of calcium hydrogen phosphate: a) Ca
3
(HPO
4
)
2 b) CaHPO
4 c) Ca(HPO
4
)
2 d) Ca(H
2
PO
4
)
2 e) no answer is correct
17. Locate the least electronegative elements in the periodic table: a) right bottom part of the table b) left bottom part of the table c) the region of transition elements d) left top part, near hydrogen e) no answer is correct
18. Select the compound with covalent bonds: a) Na
2
O b) CaCl
2 c) K
2
S d) SiO
2 e) no answer is correct
19. Select the substance with intermolecular hydrogen bonds: a) CH
4 b) H
2 c) KH
4
d) H
2
O e) no answer is correct
20.Select the ionic compound: a) CO
2 b) P
2
O
5 c) N
2
O
3 d) MgO e) no answer is correct
21. Electrolytic dissociation is: a) decomposition of electrolyte by electric current b) decomposition of substance to positive and negative ions c) the movement of ions to inversely charged electrodes d) redox reaction on electrodes e) no answer is correct
22. Select the weak electrolyte: a) NH
4
Cl b) KMnO
4 c) Na
3
N d) HNO
3 e) no answer is correct
23. Consider dissolving ammonia in water. Which species makes the conjugate pair with ammonia? a) OH - b) H
2
O c) H
3
O + d) NH
4
+ e) no answer is correct
24.Select the conjugate pair: a) NH
4
+ ; OH b) NH
3
; H
2
O
5
c) H
2
O; H
3
O + d) H
2
O; NH
3 e) no answer is correct
25. The concentration of OH in an aqueous solution at T=25 o C is 1.10
-3 . What is the concetration of H + ions? a) 1.10
-9 mol/L b) 1.10
-5 mol/L c) 1.10
-14 mol/L d) 1.10
-11 mol/L e) no answer is correct
26. Select the weak acid: a) HBr b) H
2
SO
4 c) HNO
3 d) HClO
4 e) no answer is correct
27. Select the element from the group IV (14) of periodic system: a) tin b) chromium c) selenium d) antimony e) no answer is correct
28. Select the redox reaction: a) KCl + AgNO
3
→AgCl + KNO
3 b) CaCl
2
→Ca 2+ + 2 Cl c) Ba + Cl
2
→BaCl
2 d) NaOH + HNO
3
→H
2
O + NaNO
3 e) no answer is correct
29. Select the molecular formula of toluene: a) C
6
H
8 b) C
10
H
10 c) C
5
H
7
6
d) C
7
H
8 e) no answer is correct
30. The systematic name for acetone is: a) propanon b) propanal c) propanoic acid d) ethandiol e) no answer is correct
31. The compound H
2
N-CH
2
-CH
3
belongs to: a) primary amines b) secondary amines c) tertiary amines d) dimethylamines e) no answer is correct
32. Select the dicarboxylic acid from the following acids: a) phthalic acid b) uric acid c) ascorbic acid d) picric acid e) no answer is correct
33.The simplest dicarboxylic acid is: a) malic b) lactic c) citric d) oxalic e) no answer is correct
34.Select the hydroxy carboxylic acid: a) fumaric acid b) oleic acid c) phthalic acid d) acrylic acid e) no answer is correct
7
35. Select the true statement: Esters can be made from hydroxy carboxylic acids ... a) only exceptionally b) with acids or alcohols c) only with alcohols d) only with acids e) no answer is correct
36. Select the type of bond in polysaccharides: a) peptide b) ether c) ester d) glycosidic e) no answer is correct
37. Which compound is not polysaccharide? a) starch b) amylose c) amylopectin d) cellulose e) no answer is correct, all are polysaccharides
38. Systematic name of palmitic acid is: a) hexadecanoic acid b) eicosanoic acid c) octadecanoic acid d) hexadecenoic acid e) no answer is correct, all are polysaccharides
39. Soaps are: a) esters of fatty acids and glycerol b) mixtures of fatty acids and glycerol c) the salts of higher fatty acids d) salts of alkanesulfonic acids e) no answer is correct
8
40.Select the correct statement about proteins: a) they are formed from amino acids linked by ester bond b) they are formed from nucleotides linked by glycosidic bond c) they are formed from monosaccharides linked by ester bond d) they are formed from amino acids linked by peptide bond
9